Abstract
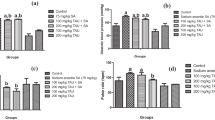
This study evaluated the diuretic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunological effects of a commercial diuretic (CD) (composed of ammonium chloride, potassium citrate, sodium chloride, ascorbic acid, biotin, halfa bar extract, and hexamine) on chickens with induced urolithiasis. A total of 100 one-day-old white Hy-Line chicks were fed a basal diet containing 20% crude protein (CP) and 1% Ca until they reached 48 days of age. Then, the birds were divided into five groups (G1-G5). G1 was fed a basal diet and kept as a negative control, G2 was fed a high protein (HP) diet containing 25% crude protein, G3 was fed high calcium (HC) diet containing 5% Ca, G4 was fed HP diet supplemented with CD, and G5 was fed HC diet supplemented with CD. The CD was supplemented with drinking water (at a dose of 0.5 ml/ liter) for 1 week. The experiment was held for 78 days. Clinical signs, postmortem lesions, and mortality rates were observed. Biochemical analytes, redox status biomarkers, and expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) were measured. Tissue samples were taken for histopathological examination. No signs of CD toxicity were observed during the toxicity test prior to the experiment. Compared to all groups, birds in G2 and G3 showed impaired renal function and alterations in biochemical, redox status, lipid peroxidation, post-mortem, and histopathological lesions along with upregulation of IL-6 and IFN-γ in the kidney and spleen. In conclusion, commercial diuretic supplementation for one week improves renal function, redox status, immune and anti-inflammatory responses in chickens with induced urolithiasis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- CD:
-
commercial diuretic
- HP:
-
high protein
- HC:
-
high calcium
- IL:
-
interleukin
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- Ca:
-
calcium
- P:
-
Phosphorus
- mRNA:
-
messenger ribonucleic acid
- CP:
-
crude protein
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- NO:
-
nitric oxide
- TAC:
-
total antioxidant capacity
- CAT:
-
catalase
- GST:
-
Glutathione-S transferase
- GSH:
-
reduced glutathione
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- GAPDH:
-
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- NH4Cl:
-
ammonium chloride
- NF-kB:
-
nuclear factor kabba
- TGF-β1:
-
transform growth factor β
- NRC:
-
National Research Council
- cDNA:
-
complementary deoxynucleic acid
- H&E:
-
haematoxylin and eosin
- PAS:
-
periodic acid-Schiff
- PCT:
-
proximal convoluted tubule
- DCT:
-
distal convoluted tubule
References
Ali A, Ibrahim M, Eladl AE, Saif YM, Lee CW (2013) Enhanced replication of swine influenza viruses in dexamethasone treated juvenile and layer turkeys. Vet Microbiol 162:353–359
Allie-Hamdulay S, Rodgers AL (2015) Prophylactic and therapeutic properties of a sodium citrate preparation in the management of calcium oxalate urolithiasis: Randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Urol Res 33:116–124
Awadin WF, Eladl AH, El-Shafei RA, El-Adl MA, Ali HS (2019) Immunological and pathological effects of vitamin E with Fetomune Plus® on chickens experimentally infected with avian influenza virus H9N2. Vet Microbiol 231:24–32
Azzeha FS, Al-Hebshia AH, Al-Essimiia HD, Alarjahb MA (2017) Vitamin C supplementation and serum uric acid: A reaction to hyperuricemia and gout disease. Pharma Nutr 5:47–51
Bancroft JD, Marilyn G (2008) Theory and practice of histological techniques, vol. 2, 6th ed., Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, Oxford, pp 123–125
Carleton HM, Drury RA, Wallington EA (1967) Carleton’s Histological technique, 4th edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Cavalcanti NG, Marques CD, Lins TU, Pereira MC, Rêgo MJ, Duarte A, Pitta MG (2016) Cytokine profile in gout: inflammation driven by IL-6 and IL-18. Immunol Investing 45:383–395
Cicerello E, Merlo F, Fandella A, Faggiano L, Maccatrozzo L (2007) Potassium citrate therapy ameliorates the natural course of Nephrolithiasis in Medullary Sponge kidney. Eur Urol Suppl 6:116
Daniel WW (1999) Biostatistics: A Foundation for Analysis in the Health Sciences, 7th edn. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Dhara AK, Guha C, Biswas U, Chakraborty GC, Sera AK, Jana PS (2010) Therapeutic efficacy of different drugs on gout in broilers. Indian Vet J 87:1151–1153
El-Ashker M, Abdelhamid F, Risha E, Salama M, El-Sebaei M (2015) Vitamin C ameliorates gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury in equines: an experimental study. J Equine Vet Sci 35:238–243
El-Askary HI, Meselhy MR, Galal AM (2003) Sesquiterpenes from Cymbopogon proximus. Molecules 8:670–677
Esfandiary A, Rajaian H, Asasi K, Lari MA, Jalae J (2010) Diuretic effects of several chemical and herbal compounds in adult laying hens. Int J Poult Sci 3:247–253
Eladl AH, Arafat N, El-Shafei RA, Farag VM, Saleh RM, Awadin WF (2019) Comparative immune response and pathogenicity of the H9N2 avian influenza virus after administration of Immulant®, based on Echinacea and Nigella sativa, in stressed chickens. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 65:165–175
Eladl AH, Mosad SM, El-Shafei RA, Saleh RM, Ali HS, Badawy BM, Elshal MF (2020) Immunostimulant effect of a mixed herbal extract on infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) vaccinated chickens in the context of a co-infection model of avian influenza virus H9N2 and IBDV. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 72:101505
El Sebaei MG, Arafat N, El-Shafei RA, El-Adl MA, Farag A, Aziza AE, Eladl AH (2021) Biochemical and molecular investigation of oxidative stress associated with urolithiasis induced by increased dietary calcium or protein in chickens. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 105:129–139
Feger M, Alesutan I, Castor T, Mia S, Musculus K, Voelkl J, Lang F (2015) Inhibitory effect of NH4Cl treatment on renal Tgfss1 signaling following unilateral ureteral obstruction. Cell Physiol Bioch 37:955–964
Gouda A, Amer SA, Gabr S, Tolba SA (2020) Effect of dietary supplemental ascorbic acid and folic acid on the growth performance, redox status, and immune status of broiler chickens under heat stress. Trop Anim Health Prod 52:2987–2996
Guo X, Huang K, Tang J (2005) Clinicopathology of gout in growing layers induced by high calcium and high protein diets. Brit Poult Sci 46:641–646
Hong YH, Lillehoj HS, Lee SH, Dalloul RA, Lillehoj EP (2006) Analysis of chicken cytokine and chemokine gene expression following Eimeria acervulina and Eimeria tenella infections. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 114:209–223
Huang HY, Appel LJ, Choi MJ, Gelber AC, Charleston J, Norkus EP, Miller ER (2005) The effects of vitamin C supplementation on serum concentrations of uric acid: results of a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 52:1843–1847
Ibrahim FY, El-Khateeb AY (2013) Effect of herbal beverages of Foeniculum vulgare and Cymbopogon proximus on inhibition of calcium oxalate renal crystals formation in rats. Ann Agricult Sci 58:221–229
Inokuchi T, Moriwaki Y, Tsutsui H, Yamamoto A, Takahashi S, Tsutsumi Z, Yamamoto T (2006) Plasma interleukin (IL)-18 (interferon-γ-inducing factor) and other inflammatory cytokines in patients with gouty arthritis and monosodium urate monohydrate crystal-induced secretion of IL-18. Cytokine 33:21–27
Khan SR (2014) Reactive oxygen species, in Eammation and calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis. Trans Androl Urol 3:256–276
Kidd MT (2004) Nutritional modulation of immune function in broilers. Poult Sci 83:650–657
Killian ML (2014) Avian influenza virus sample types, collection, and handling. In: Animal Influenza Virus (pp. 83-91). Humana Press, New York, NY
Kumar SM, Satyanarayana ML, Mallikarjuna AR, Shivakumar R (2008) Serum biochemistry and epidemiology of gout in broiler chicks. Indian Vet J 85:452–453
Kurutas EB (2016) The importance of antioxidants which play the role in cellular response against oxidative/nitrosative stress: current state. Nutr J 15:71
Lasisi TJ, Raji YR, Salako BL (2016) Salivary creatinine and urea analysis in patients with chronic kidney disease: a case control study. BMC Nephrol 17:10
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Medzhitov R (2008) Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 454:428
Mir MS, Darzi MM, Khan AA, Ganaie NA, Gupta S, Nashiruddullah N (2005) Investigation of an outbreak of Gout in Kashmir Favorella Poultry. Indian J Vet Pathol 29:35–37
Mubarak M, Sharkawy A (1999) Toxopathology of gout induced in laying pullets by sodium bicarbonate toxicity. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 7:227–236
Nyika A (2009) Animal research ethics in Africa: an overview. Acta Trop 112:S48–S52
Ngo TC, Assimos DG (2007) Uric Acid Nephrolithiasis: Recent Progress and Future Directions, Reviews in Urology. Manag Update 9:1
NRC (1994) Nutrient requirements of poultry, 9th, Revised. National Academy Press, Washington DC
OECD (2001) Acute Oral Toxicity - Acute Toxic Class Method, Test Guideline No. 423, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, OECD
Quarantelli A, Bonomi A, Righi F, Renzi M, Gabbi C, Cacchioli A, Alpigiani I (2003) The effects of different levels of dietary biotin on the performances and on bone growth in the broiler. Ital J Anim Sci 2:453–455
Rehman ZU, Che L, Ren S, Liao Y, Qiu X, Yu S, Sun Y, Tan L, Song C, Liu W, Ding Z, Munir M, Nair V, Meng C, Ding C (2018) Supplementation of vitamin E protects chickens from Newcastle Disease virus mediated exacerbation of intestinal oxidative stress and tissue damage. Cell Physiol Bioch 47:1655–1666
Rincon-Choles H, Jolly SE, Arrigain S, Konig V, Schold JD, Nakhoul G, Navaneethan SD, Nally JV, Rothberg MB (2017) Impact of uric acid levels on kidney disease progression. Am J Nephrol 46:315–322
Semins MJ, Matlaga BR (2010) Medical evaluation and management of urolithiasis; Review. Therap Advan Urol 2:3–9
Simms D, Cizdziel PE, Chomczynski P (1993) TRIzol: A new reagent for optimal single-step isolation of RNA. Focus 15:532–535
Sinkalu VO, Ayo JO (2008) Diurnal fluctuations in rectal temperature of black Harco pullets administered with vitamins A and C during the hot-dry season. Int J Poult Sci 7:1065–1070
SPSS, Statistical Packages for the Social Sciences (2007) Statistical software for windows version 16.0, Microsoft, Chicago, IL., USA
Strazzullo P, Puig JG (2007) Uric acid and oxidative stress: relative impact on cardiovascular risk. Nutr Metabol Cardiovas Dis 17:409–414
Suarez M, Youssef RF (2015) Potassium Citrate: Treatment and Prevention of Recurrent Calcium Nephrolithiasis. J Clin Nephrol Res 2:1015
Wideman RF (2016) Confirming the promise to prevent physiological disorders of organs: urolithiasis in laying hens. J Appl Poult Res 25:292–304
Widyaningsih TD, Putri WD, Murtini ES, Rochmawati N, Nangin D (2017) Anti-inflammatory and anti-hyperuricemia properties of chicken feet cartilage: treatment on gouty arthritis animal model. J Appl Pharm Sci 7:202–207
Wood LG, Fitzgerald DA, Gibson PG, Cooper DM, Garg ML (2000) Lipid peroxidation as determined by plasma isoprostanes is related to disease severity in mild asthma. Lipids 35:967–974
Zhang H, Elliott KE, Durojaye OA, Fatemi SA, Schilling MW, Peebles ED (2019) Effects of in ovo injection of L-ascorbic acid on growth performance, carcass composition, plasma antioxidant capacity, and meat quality in broiler chickens. Poult Sci 98:3617–3625
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the departments of Biochemistry, Pharmacology, Histology and Poultry diseases, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Mansoura University for their help and facilities of the present study. The Servicescape, United States and the authorship, translation & publication (ATP) center, Mansoura University are thanked for the proofreading and editing of manuscript.
Funding
This study received no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mahmoud El Sebaei: Methodology, investigation, data analysis, writing of original draft & editing. Reham El-Shafei: Methodology, Investigation. Mohamed El-Adl: Methodology, Investigation. Amany Farag: Methodology, Investigation. Abdelfattah Eladl: Methodology, investigation, data analysis, writing of original draft & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All the procedures of biosecurity and biosafety as well as handling, management, and euthanasia of birds during and after the experiment were approved by the Research Ethical Committee of Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Mansoura University with the code number of (R/80). Moreover, handling, restrain and euthanasia of chicks were following the "Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals".
Consent to participate
All authors contributed to the experimental study and design. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Consent for publication
All authors gave their consent for research publication.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest by the authors to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sebaei, M.G.E., El-Shafei, R.A., El-Adl, M.A. et al. Biochemical and molecular effects of a commercial diuretic with herbal extract on experimentally induced urolithiasis in chickens. Vet Res Commun 46, 419–430 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-021-09866-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-021-09866-4