Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the clinical value of the holographic imaging technology in combination with robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy (RAPN) for renal hilar tumor treatment.
Patients and methods
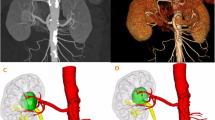
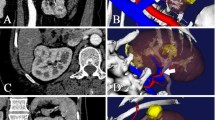
From Dec. 2018 to Dec. 2021, patients diagnosed with renal hilar tumor were included in this retrospective study. Before the surgery, the engineers established the holographic image models based on the enhanced CT data. The models were used in patient consultation, pre-surgery planning and surgery simulation. During the RAPN, the navigation was achieved by real-time overlapping of the holographic images on the robotic surgery endoscopic views. The navigation technique helped the surgeon to identify the important anatomic structures such as tumor, renal vein, renal artery, and pelvis.
Results
There were total of eight patients with renal hilar tumor who underwent RAPN combined with holographic imaging technique. The mean age was 57.3 years, the median ASA score was 2. The mean tumor size was 42.4 mm and the median RENAL Nephrometry score was 9.5. The clinical stages were cT1a (37.5%) and cT1b (62.5%). All the procedures were performed uneventfully by one surgeon. The mean operative time was 144.3 min, and the mean warm ischemia time was 27.9 min. The mean estimated blood loss was 86.3 ml. There was no conversion to open surgery or radical nephrectomy. There were no Clavien–Dindo ≥ 3 perioperative complications.
Conclusions
Using the holographic imaging technique, the pre-surgery planning, simulation of renal arterial clamp and excision of the tumor, and intraoperative navigation were feasible and helpful in facilitating RAPN.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gill IS, Aron M, Gervais DA et al (2010) Clinical practice. Small renal mass. N Engl J Med 362(7):624–634
Boylu U, Basatac C, Yildirim U et al (2015) Comparison of surgical, functional, and oncological outcomes of open and robot-assisted partial nephrectomy. J Minim Access Surg 11(1):72–77
Lebed B, Jani SD, Kutikov A et al (2010) Renal masses herniating into the hilum: technical considerations of the “ball-valve phenomenon” during nephron-sparing surgery. Urology 75(3):707–710
Kutikov A, Uzzo RG (2009) The R.E.N.A.L. nephrometry score: a comprehensive standardized system for quantitating renal tumor size, location and depth. J Urology 182(3):844–853
Porpiglia F, Bertolo R, Checcucci E et al (2018) Development and validation of 3D printed virtual models for robot-assisted radical prostatectomy and partial nephrectomy: urologists’ and patients’ perception. World J Urol 36(2):201–207
Porpiglia F, Checcucci E, Amparore D et al (2019) Three-dimensional elastic augmented-reality robot-assisted radical prostatectomy using hyperaccuracy three-dimensional reconstruction technology: a step further in the identification of capsular involvement. Eur Urol 76(4):505–514
Porpiglia F, Amparore D, Checcucci E et al (2019) Three-dimensional virtual imaging of renal tumours: a new tool to improve the accuracy of nephrometry scores. BJU Int 124(6):945–954
Zeng S, Zhou Y, Wang M et al (2021) Holographic reconstruction technology used for intraoperative real-time navigation in robot-assisted partial nephrectomy in patients with renal tumors: a single center study. Transl Androl Urol 10(8):3386–3394
Weprin S, Falagario U, Veccia A et al (2021) Simplified PADUA renal (SPARE) nephrometry scoring system: external validation, interobserver variability, and comparison with RENAL and PADUA in a single-center robotic partial nephrectomy series. Eur Urol Focus 7(3):591–597
Schiavina R, Novara G, Borghesi M et al (2017) PADUA and R.E.N.A.L. nephrometry scores correlate with perioperative outcomes of robot-assisted partial nephrectomy: analysis of the Vattikuti Global Quality Initiative in Robotic Urologic Surgery (GQI-RUS) database. BJU Int 119(3):456–463
Zhu G, X J, Weng GB et al (2020) Application of holographic image navigation in urological laparoscopic and robotic surgery. Chin J Urol 41(2):117–123
Zhang K, Zhu G, Li HB, Martinez Portillo FJ (2018) Application of 3D image reconstruction in robotic urological surgery. Chin J Urol 39(9):690–693
Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y et al (2019) European association of urology guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: the 2019 update. Eur Urol 75(5):799–810
Mir MC, Derweesh I, Porpiglia F et al (2017) Partial nephrectomy versus radical nephrectomy for clinical T1b and T2 renal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. Eur Urol 71(4):606–617
George AK, Herati AS, Rais-Bahrami S et al (2014) Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for hilar tumors: oncologic and renal functional outcomes. Urology 83(1):111–115
Gill IS, Colombo JR Jr, Frank I et al (2005) Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy for hilar tumors. J Urol 174(3):850–853 (discussion 853–854)
Gorin MA, Ball MW, Pierorazio PM et al (2013) Outcomes and predictors of clinical T1 to pathological T3a tumor up-staging after robotic partial nephrectomy: a multi-institutional analysis. J Urol 190(5):1907–1911
Dulabon LM, Kaouk JH, Haber GP et al (2011) Multi-institutional analysis of robotic partial nephrectomy for hilar versus nonhilar lesions in 446 consecutive cases. Eur Urol 59(3):325–330
Correa AF, Yankey H, Li T et al (2019) Renal hilar lesions: biological implications for complex partial nephrectomy. Urology 123:174–180
Porpiglia F, Fiori C, Checcucci E et al (2018) Hyperaccuracy three-dimensional reconstruction is able to maximize the efficacy of selective clamping during robot-assisted partial nephrectomy for complex renal masses. Eur Urol 74(5):651–660
Shirk JD, Thiel DD, Wallen EM et al (2019) Effect of 3-dimensional virtual reality models for surgical planning of robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy on surgical outcomes: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open 2(9):e1911598
Bernhard JC, Isotani S, Matsugasumi T et al (2016) Personalized 3D printed model of kidney and tumor anatomy: a useful tool for patient education. World J Urol 34(3):337–345
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Wang, L., Sun, Y. et al. Combination of holographic imaging with robotic partial nephrectomy for renal hilar tumor treatment. Int Urol Nephrol 54, 1837–1844 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03228-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-022-03228-y