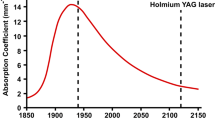
Abstract
Objective
PlasmaKinetic electrode, holmium laser, green laser and Nd: YAG laser have been used for treating benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH). To compare the pathological changes of thermal injury by these different devices.
Material and methods
Tissues donated by several male patients with prostate cancer who have written a consent. The tissues were diced them into small squares with 1 cm long on a side. Cutting experiments were performed in the normal temperature circulating water environment, the specimens of the prostate tissue were fixed in 4% formalin. The sections were then undergone HE and NADH-NBT staining.
Results
The penetration depths and coagulation zone of tissue after treatment were ranked as Nd:YAG laser > plasma Kinetic electrode > green light laser > holmium laser respectively.
Conclusion
Holmium laser might have less thermal damage to tissue, although it still needs more research including clinical study. Our results will provide clinicians with some alternative basis for the application.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mohamed HM, Aly MS, Hussein TD (2017) Genetic alterations in benign prostatic hyperplasia patients. Ger Med Sci 15:Doc16. https://doi.org/10.3205/000257
Anderson BB, Pariser JJ, Helfand BT (2015) Comparison of patients undergoing PVP versus TURP for LUTS/BPH. Curr Urol Rep 16(8):55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-015-0525-7
Benoist N, Bigot P, Colombel P, Amie F, Haringanji C, Chautard D, Azzouzi AR (2009) Tuna: clinical retrospective study addressing mid-term outcomes. Prog Urol 19(1):54–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.purol.2008.07.010
Liu Z, Li YW, Wu WR, Lu Q (2017) Long-term clinical efficacy and safety profile of transurethral resection of prostate versus plasmakinetic resection of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology 103:198–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2017.02.006
Fried NM, Murray KE (2016) High-power thulium fiber laser ablation of the canine prostate. Proc Spie 5686:176–182
Liao N, Yu J (2012) A study comparing plasmakinetic enucleation with bipolar plasmakinetic resection of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Endourol 26(7):884–888. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2011.0358
Inamura S, Ito H, Shinagawa T, Tsutsumiuchi M, Taga M, Kobayashi M, Yokoyama O (2018) Prostatic stromal inflammation is associated with bladder outlet obstruction in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate 78(10):743–752. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.23518
Peng B, Huang J, Wang G, Zhang H, Liu M (2016) Transurethral enucleation of prostate with button electrode plasmakinetic vaporization for the treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Sci Rep 6:39583. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39583
Kim KS, Lee SH, Cho HJ, Suh HJ, Lee DH, Choi YS (2019) Comparison of bipolar plasma vaporization versus standard holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: surgical procedures and clinical outcomes for small prostate volumes. J Clin Med. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071007
Cho MC, Yoo S, Park J, Cho SY, Son H, Oh SJ, Paick JS (2019) Effect of preoperative detrusor underactivity on long-term surgical outcomes of photovaporization and holmium laser enucleation in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia: a lesson from 5-year serial follow-up data. BJU Int 123(5A):E34–E42. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.14661
Teng J, Zhang D, Li Y, Yin L, Wang K, Cui X, Xu D (2013) Photoselective vaporization with the green light laser vs transurethral resection of the prostate for treating benign prostate hyperplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJU Int 111(2):312–323. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11395.x
Mustafa M, Sowedy A, Nashrati O, Dindar S (2019) The efficacy of green light laser prostatectomy in the management of urinary retention due to prostate hyperplasia. Lasers Med Sci 34(6):1201–1205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-018-02712-1
Palmero-Marti JL, Panach-Navarrete J, Valls-Gonzalez L, Ganau-Ituren A, Miralles-Aguado J, Benedicto-Redon A (2017) Comparative study between thulium laser (Tm: YAG) 150W and greenlight laser (LBO:ND-YAG) 120W for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperpplasia: short-term efficacy and security. Actas Urol Esp 41(3):188–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acuro.2016.09.009
Gravas S, Bachmann A, Reich O, Roehrborn CG, Gilling PJ, De La Rosette J (2011) Critical review of lasers in benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). BJU Int 107(7):1030–1043. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09954.x
Van III Way CW (2000) Electrosurgery 101. Curr Surg 57(2):172–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0149-7944(00)00196-3
Gilling P, Barber N, Bidair M, Anderson P, Sutton M, Aho T, Kramolowsky E, Thomas A, Cowan B, Kaufman RP Jr, Trainer A, Arther A, Badlani G, Plante M, Desai M, Doumanian L, Te AE, DeGuenther M, Roehrborn C (2019) Two-year outcomes after aquablation compared to TURP: efficacy and ejaculatory improvements sustained. Adv Ther 36(6):1326–1336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-019-00952-3
Acknowledgements
The work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant No. 81900687 and 81970656); Shanghai Science and Technology Commission Fund (Grant No. 18411960500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, M., Chen, Y., Zhan, M. et al. Comparison of thermal injury depth of the prostate between plasma kinetic electrode, holmium laser, green light laser and Nd:YAG laser. Int Urol Nephrol 53, 863–867 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02723-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02723-4