Abstract
Objectives
Gemcitabine resistance is a major obstacle for effective treatment of bladder cancer. This study was aimed to investigate the potential role of miR-129-5p in the development of gemcitabine resistance in bladder cancer cells and its underlying mechanism.
Methods
The IC50 for gemcitabine in 20 bladder cancer cells was first profiled from Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer. miR-129-5p level and gene mRNA expression were detected using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Cell viability, apoptosis, and gene protein level were assessed by MTT, flow cytometry, and Western blot, respectively. Regulatory relationship between Wnt5a and miR-129-5p was determined using luciferase reporter assay.
Results
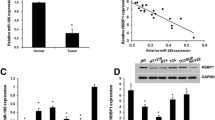
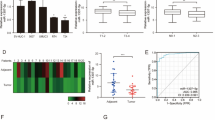
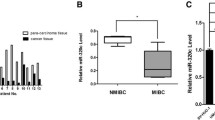
We found that down-regulated miR-129-5p level contributed to gemcitabine resistance in bladder cancer cells and tissues. We also observed restoration of miR-129-5p could significantly increase cell sensitivity to gemcitabine and promote cell apoptosis. Mechanism analysis revealed that Wnt5a is a direct target gene of miR-129-5p and knock-down of Wnt5a reversed gemcitabine resistance.
Conclusions
Taken together, our findings indicate that miR-129-5p and Wnt5a may be novel therapeutic targets for overcoming gemcitabine resistance in bladder cancer treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meyers PA, Schwartz CL, Krailo M, Kleinerman ES, Betcher D, Bernstein ML, Conrad E, Ferguson W, Gebhardt M, Goorin AM, Harris MB, Healey J, Huvos A, Link M, Montebello J, Nadel H, Nieder M, Sato J, Siegal G, Weiner M, Wells R, Wold L, Womer R, Grier H (2005) Global cancer statistics. J Clin Oncol 23:2004–2011
Kirkali Z, Chan T, Manoharan M, Algaba F, Busch C, Cheng L, Kiemeney L, Kriegmair M, Montironi R, Murphy WM, Sesterhenn IA, Tachibana M, Weider J (2005) Bladder cancer: epidemiology, staging and grading, and diagnosis. Urology 66:4–34
Crinò L, Cappuzzo F (2002) Gemcitabine in non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Opin Pharmacother 3:745–753
Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, Figer A, Hecht JR, Gallinger S, Au HJ, Murawa P, Walde D, Wolff RA, Campos D, Lim R, Ding K, Clark G, Voskoglou-Nomikos T, Ptasynski M, Parulekar W, National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group (2007) Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol 25:1960–1966
Chew HK, Doroshow JH, Frankel P, Margolin KA, Somlo G, Lenz HJ, Gordon M, Zhang W, Yang D, Russell C, Spicer D, Synold T, Bayer R, Hantel A, Stiff PJ, Tetef ML, Gandara DR, Albain KS (2009) Phase II studies of gemcitabine and cisplatin in heavily and minimally pretreated metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:2163–2169
Pachon V, Garciaalfonso P, Iglesias L, Siso I, Abad G, Khosravi P, Diaz V, Perez-Manga G (2005) Gemcitabine plus continuous infusion of 5-FU for heavily pretreated advanced colorectal cancer patients. Phase I/II study. J Magn Magn Mater 323:2174–2178
von der Maase H, Hansen SW, Roberts JT, Dogliotti L, Oliver T, Moore MJ, Bodrogi I, Albers P, Knuth A, Lippert CM, Kerbrat P, Sanchez Rovira P, Wersall P, Cleall SP, Roychowdhury DF, Tomlin I, Visseren-Grul CM, Conte PF (2000) Gemcitabine and cisplatin versus methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin in advanced or metastatic bladder cancer: results of a large, randomized, multinational, multicenter, phase III study. J Clin Oncol 18:3068–3077
Anghel RM, Gales LN, Trifanescu OG (2016) Outcome of urinary bladder cancer after combined therapies. J Med Life 9:153–159
von der Maase H, Sengelov L, Roberts JT, Ricci S, Dogliotti L, Oliver T, Moore MJ, Zimmermann A, Arning M (2005) Long-term survival results of a randomized trial comparing gemcitabine plus cisplatin, with methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin, plus cisplatin in patients with bladder cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:4602–4608
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N (2008) Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet 9:102–114
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Lu X, Ma J, Chu J, Shao Q, Zhang Y, Lu G, Li J, Huang X, Li W, Li Y, Ling Y, Zhao T (2017) MiR-129-5p sensitizes the response of Her-2 positive breast cancer to trastuzumab by reducing Rps6. Cell Physiol Biochem 44:2346–2356
Ma Z, Cai H, Zhang Y, Chang L, Cui Y (2017) MiR-129-5p inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell stemness and chemoresistance through targeting DLK1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 490:309–316
Wu Q, Yang Z, Xia L, Nie Y, Wu K, Shi Y, Fan D (2014) Methylation of miR-129-5p CpG island modulates multi-drug resistance in gastric cancer by targeting ABC transporters. Oncotarget 5:11552–11563
Zhang P, Li J, Song Y, Wang X (2017) MiR-129-5p inhibits proliferation and invasion of chondrosarcoma cells by regulating SOX4/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 42:242–253
Wang Q, Yu J (2018) MiR-129-5p suppresses gastric cancer cell invasion and proliferation by inhibiting COL1A1. Biochem Cell Biol 96:19–25
Geng Z, Xu F, Zhang Y (2016) MiR-129-5p-mediated Beclin-1 suppression inhibits endothelial cell autophagy in atherosclerosis. Am J Transl Res 8:1886–1894
Duan L, Hao X, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Zhang G (2014) MiR-129-5p is down-regulated and involved in the growth, apoptosis and migration of medullary thyroid carcinoma cells through targeting RET. FEBS Lett 588:1644–1651
Yang J, Li T, Gao C, Lv X, Liu K, Song H, Xing Y, Xi T (2014) FOXO1 3′UTR functions as a ceRNA in repressing the metastases of breast cancer cells via regulating miRNA activity. FEBS Lett 588:3218–3224
Fan P, Liu L, Yin Y, Zhao Z, Zhang Y, Amponsah PS, Xiao X, Bauer N, Abukiwan A, Nwaeburu CC, Gladkich J, Gao C, Schemmer P, Gross W, Herr I (2016) MicroRNA-101-3p reverses gemcitabine resistance by inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase M1 in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett 373:130–137
Wang H, Li Q, Niu X, Wang G, Zheng S, Fu G, Wang Z (2017) miR-143 inhibits bladder cancer cell proliferation and enhances their sensitivity to gemcitabine by repressing IGF-1R signaling. Oncol Lett 13:435–440
Wu ZH, Tao ZH, Zhang J, Li T, Ni C, Xie J, Zhang JF, Hu XC (2016) MiRNA-21 induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition and gemcitabine resistance via the PTEN/AKT pathway in breast cancer. Tumour Biol 37:7245–7254
Kikuchi A, Yamamoto H, Sato A, Matsumoto S (2012) Wnt5a: its signalling, functions and implication in diseases. Acta Physiol 204:17–33
McDonald SL, Silver A (2009) The opposing roles of Wnt-5a in cancer. Br J Cancer 101:209–214
Bo H, Zhang S, Gao L, Chen Y, Zhang J, Chang X, Zhu M (2013) Upregulation of Wnt5a promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells. BMC Cancer 13:496
Zhang A, He S, Sun X, Ding L, Bao X, Wang N (2014) Wnt5a promotes migration of human osteosarcoma cells by triggering a phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt signals. Cancer Cell Int 14:15
Takiguchi G, Nishita M, Kurita K, Kakeji Y, Minami Y (2016) Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling in mesenchymal stem cells promotes proliferation of gastric cancer cells by activating CXCL16-CXCR6 axis. Cancer Sci 107:290–297
Wang B, Tang Z, Gong H, Zhu L, Liu X (2017) Wnt5a promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20171092
Cao Y, Wang X, Xu C, Gao Z, Zhou H, Wang Y, Cao R, Liu T, Liu T (2016) 4-HPR impairs bladder cancer cell migration and invasion by interfering with the Wnt5a/JNK and Wnt5a/MMP-2 signaling pathways. Oncol Lett 12:1833–1839
Säfholm A, Tuomela J, Rosenkvist J, Dejmek J, Härkönen P, Andersson T (2008) The Wnt-5a-derived hexapeptide Foxy-5 inhibits breast cancer metastasis in vivo by targeting cell motility. Clin Cancer Res 14:6556–6563
Prasad CP, Chaurasiya SK, Guilmain W, Andersson T (2016) WNT5A signaling impairs breast cancer cell migration and invasion via mechanisms independent of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 35:144
Cheng R, Sun B, Liu Z, Zhao X, Qi L, Li Y, Gu Q (2014) Wnt5a suppresses colon cancer by inhibiting cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Physiol 229:1908–1917
Oishi I, Suzuki H, Onishi N, Takada R, Kani S, Ohkawara B, Koshida I, Suzuki K, Yamada G, Schwabe GC, Mundlos S, Shibuya H, Takada S, Minami Y (2003) The receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2 is involved in non-canonical Wnt5a/JNK signalling pathway. Genes Cells 8:645–654
Ishitani T, Kishida S, Hyodo-Miura J, Ueno N, Yasuda J, Waterman M, Shibuya H, Moon RT, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Matsumoto K (2003) The TAK1-NLK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade functions in the Wnt-5a/Ca(2+) pathway to antagonize Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Cell Biol 23:131–139
Topol L, Jiang X, Choi H, Garrett-Beal L, Carolan PJ, Yang Y (2003) Wnt-5a inhibits the canonical Wnt pathway by promoting GSK-3-independent beta-catenin degradation. J Cell Biol 162:899–908
Asem MS, Buechler S, Wates RB, Miller DL, Sharon SM (2016) Wnt5a signaling in cancer. Cancers 8:79
Hung TH, Hsu SC, Cheng CY, Choo KB, Tseng CP, Chen TC, Lan YW, Huang TT, Lai HC, Chen CM, Chong KY (2014) Wnt5A regulates ABCB1 expression in multidrug-resistant cancer cells through activation of the non-canonical PKA/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget 5:12273–12290
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, J., Wang, Q., Wu, G. et al. miR-129-5p inhibits gemcitabine resistance and promotes cell apoptosis of bladder cancer cells by targeting Wnt5a. Int Urol Nephrol 50, 1811–1819 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1959-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-018-1959-x