Abstract
Purpose
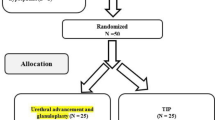
To report the feasibility of modified tubularized incised plate (TIP) urethroplasty technique for proximal hypospadias in 63 cases.
Methods
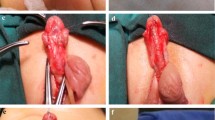
From January 2004 to March 2010, 63 patients underwent one-stage TIP urethroplasty (modified Snodgrass technique repair) using 2–3 of three covering layers (corpus spongiosum, dartos, and tunica vaginalis). The primary meatus was proximal penile, penoscrotal, scrotal, and perineal in 38, 13, 10, and 2 patients, respectively. All patients had chordee that was corrected with dorsal plication. Glanuloplasty was performed in all cases. Complications and cosmetic results were documented after 6–72 months of follow-up.
Results
A total of 63 boys with proximal hypospadias underwent Snodgrass hypospadias repair at a mean age of 8.5 months (range 6–54). Mean operative time was 210 ± 35 min. Patients were followed up with 6-month intervals for up to 6 years postoperatively. After 6 years of follow-up, nine urethrocutaneous fistulae, four bleeding, four meatal stenoses, and one urethral stricture were reported. Cosmetic result was satisfactory according to parent’s opinion and another surgeon. No residual chordee was observed in any cases (without artificial correction).
Conclusion
In conclusion, this preliminary report can be estimated as an alternative technique with acceptable complication and cosmetic results for proximal hypospadias correction.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TIP:
-
Modified tubularized incised plate
References
Aulagne M, Harper L, de Napoli-Cocci S, Bondonny J, Dobremez E (2010) Long-term outcome of severe hypospadias. J Pediatr Urol. 6(5):469–472
Snodgrass WT (2011) Hypospadias. Pediatr Urol 177–190
Snodgrass W, Elmore J (2004) Initial experience with staged buccal graft (Bracka) hypospadias reoperations. J Urol 172(4):1720–1724
Ghanem MA, Nijman RJM (2010) Outcome analysis of tubularized incised urethral plate using dorsal dartos flap for proximal penile hypospadias repair. J Pediatr Urol 6(5):477–480
Snodgrass WT (1999) Tubularized incised plate hypospadias repair: indications, technique, and complications. Urology 54(1):6–11
Zheng D-C, Yao H-J, Cai Z-K et al (2015) Two-stage urethroplasty is a better choice for proximal hypospadias with severe chordee after urethral plate transection: a single-center experience. Asian J Androl 17(1):94
Cheng EY, Vemulapalli SN, Kropp BP et al (2002) Snodgrass hypospadias repair with vascularized dartos flap: the perfect repair for virgin cases of hypospadias? J Urol 168(4):1723–1726
Springer A, Krois W, Horcher E (2011) Trends in hypospadias surgery: results of a worldwide survey. Eur Urol 60(6):1184–1189
Manzoni G, Bracka A, Palminteri E, Marrocco G (2004) Hypospadias surgery: when, what and by whom? BJU Int 94(8):1188–1195
Shanberg A, Sanderson K, Duel B (2001) Re-operative hypospadias repair using the Snodgrass incised plate urethroplasty. BJU Int 87(6):544–547
Braga LHP, Lorenzo AJ, Skeldon S et al (2007) Failed pyeloplasty in children: comparative analysis of retrograde endopyelotomy versus redo pyeloplasty. J Urol 178(6):2571–2575
Mureau MAM, Slijper FME, Slob AK, Verhulst FC, Nijman RJM (1996) Satisfaction with penile appearance after hypospadias surgery: the patient and surgeon view. J Urol 155(2):703–706
Marrocco G, Vallasciani S, Fiocca G, Calisti A (2004) Hypospadias surgery: a 10-year review. Pediatr Surg Int 20(3):200–203
Snodgrass W, Villanueva C, Bush NC (2014) Duration of follow-up to diagnose hypospadias urethroplasty complications. J Pediatr Urol. 10(2):208–211
Jayanthi VR (2003) The modified Snodgrass hypospadias repair: reducing the risk of fistula and meatal stenosis. J Urol 170(4):1603–1605
Sozubir S, Snodgrass W (2003) A new algorithm for primary hypospadias repair based on tip urethroplasty. J Pediatr Surg 38(8):1157–1161
Filinte GT, Akan M, Temiz G, Aycicek Cardak GN, Gonullu E (2014) Applications of triangular glanular flap in hypospadias repairs for different purposes. J Plast Surg Hand Surg 48(1):34–37
Lacy JM, Hendrix LN, Grant C, Ziada AM (2014) Distal hypospadias repair using only glans wing mobilization and approximation. Can J Urol 21(2):7241–7245
Amilal B, Arup M (2008) Acute postoperative complications of hypospadias repair. Indian J Urol 24:241
Gargollo PC, Cai AW, Borer JG, Retik AB (2011) Management of recurrent urethral strictures after hypospadias repair: Is there a role for repeat dilation or endoscopic incision? J Pediatr Urol 7(1):34–38
Snodgrass WT, Nguyen MT (2002) Current technique of tubularized incised plate hypospadias repair. Urology 60(1):157–162
Snodgrass W, Koyle M, Manzoni G, Hurwitz R, Caldamone A, Ehrlich R (1998) Tubularized incised plate hypospadias repair for proximal hypospadias. J Urol 159(6):2129–2131
Snodgrass W, Koyle M, Manzoni G, Hurwitz R, Caldamone A, Ehrlich R (1996) Tubularized incised plate hypospadias repair: results of a multicenter experience. J Urol 156(2):839–841
Snodgrass WT (2001) Re: effect of the depth and width of the urethral plate on tubularized incised plate urethroplasty. J Urol 166(2):633
Snodgrass W, Lorenzo A (2002) Tubularized incised-plate urethroplasty for proximal hypospadias. BJU Int 89(1):90–93
Chen S, Yang S, Hsieh C, Chen Y (2001) Tubularized incised plate urethroplasty for proximal hypospadias. BJU Int 86(9):1050–1053
Snodgrass W, Cost N, Nakonezny PA, Bush N (2011) Analysis of risk factors for glans dehiscence after tubularized incised plate hypospadias repair. J Urol 185(5):1845–1851
Kajbafzadeh A-M, Arshadi H, Payabvash S, Salmasi AH, Najjaran-Tousi V, Sahebpor ARA (2007) Proximal hypospadias with severe chordee: single stage repair using corporeal tunica vaginalis free graft. J Urol 178(3):1036–1042
Lorenzo A, Snodgrass W (2002) Regular dilatation is unnecessary after tubularized incised-plate hypospadias repair. BJU Int 89(1):94–97
Kajbafzadeh A-M, Sabetkish S, Mahboubi AH, Sabetkish N (2014) Single incisional approach for reconstruction of hypospadias and concomitant inguinal hernia. J Pediatr Urol 10(1):45–51
Yamataka A, Kobayashi H, Okada Y, Tsukamoto K, Lane GJ, Miyano T (2003) A novel technique for reinforcing the neourethra in hypospadias associated with bilateral undescended testis: use of the gubernaculum. J Pediatr Surg 38(12):1799–1801
Snodgrass W, Yucel S (2007) Tubularized incised plate for mid shaft and proximal hypospadias repair. J Urol 177(2):698–702
Cendron M, Ellsworth PI (1999) Treatment of complex hypospadias by the Snodgrass technique. Ann Urol 33(5):364–367
Xu N, Xue X-Y, Li X-D et al (2014) Comparative outcomes of the tubularized incised plate and transverse island flap onlay techniques for the repair of proximal hypospadias. Int Urol Nephrol 46(3):487–491
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 9383 kb)
Supplementary material 2 (MP4 7934 kb)
Supplementary material 3 (MP4 3606 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arshadi, H., Sabetkish, S. & Kajbafzadeh, AM. Modified tubularized incised plate urethroplasty reduces the risk of fistula and meatal stenosis for proximal hypospadias: a report of 63 cases. Int Urol Nephrol 49, 2099–2104 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1725-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1725-5