Abstract
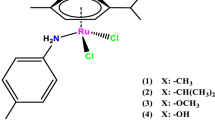
Three half-sandwich Ru(II) complexes with the general formulae of [Ru(\(\eta\) 6-p-cymene)(L)Cl2] (where L: 2a (diethyl-4-aminobenzylphosphonate), 2b (4-aminoethylbenzoate) and 2c (4-methoxybenzylamine) containing an aniline ligands were synthesized and their structures were characterized. The Crystal structure of complex [Ru(\(\eta\) 6-p-cymene)(2c)Cl2] was investigated by single crystal X-ray diffraction studies. Each Ru(II) ion in both complexes is coordinated with a 6-p-cymene nitrogen atom, two chloride and aniline derivatives. This results in a distorted piano-stool geometry. The catalytic performances of the complexes were investigated in transfer hydrogenation reactions. The complexes catalyze the transfer hydrogenation of cyclohexanone and 2-hexanone in the presence of a base. For 2-hexanone to 2-hexanol reduction, complex [Ru(\(\eta\) 6-p-cymene)(2a)Cl2] showed the highest conversion rate (at the end of 6 h) with 97% conversion. The complexes were found to be more active catalysts in the transfer hydrogenation of cyclohexanone than that of 2-hexanone.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Erdem A, Kılınçarslan R, Şahin Ç et al (2020) Synthesis, thermal, electrochemical and catalytic behavior toward transfer hydrogenation investigations of the half-sandwich RuII complexes with 2-(2′-quinolyl)benzimidazoles. J Mol Struct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128556
Wang D, Astruc D (2015) The Golden Age of Transfer Hydrogenation. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00203
Structures MB (2008) Modern Reduction Methods
Johnstone RAW, Wilby AH, Entwistle ID (1985) Heterogeneous catalytic transfer hydrogenation and its relation to other methods for reduction of organic compounds. Chem Rev 85:129–170. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00066a003
Zassinovich G, Mestroni G (1992) Asymmetric hydrogen transfer reactions promoted by homogeneous transition metal catalysts. Chem Rev 92:1051–1069
Poz F (2016) Metal-catalysed transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Top Curr Chem 374:1–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41061-016-0015-5
Pandiarajan D, Ramesh R (2013) Ruthenium(II) half-sandwich complexes containing thioamides: synthesis, structures and catalytic transfer hydrogenation of ketones. J Organomet Chem 723:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jorganchem.2012.10.003
Moya SA, Negrete-Vergara C, Brown K et al (2017) Transfer hydrogenation of N-benzylideneaniline catalyzed by ruthenium complexes with pincer-type phosphorus nitrogen ligands using propan-2-ol as the hydrogen source. Catal Commun 99:150–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2017.04.026
Morris RH (2008) Ruthenium and osmium. Handb Homog Hydrog. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527619382.ch3
Çirali DE, Dayan O (2015) Synthesis of tetranuclear ruthenium (II) complex of pyridyloxy-substituted 2,2′-dioxybiphenyl-cyclotriphosphazene platform and its catalytic application in the transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Phosphorus, Sulfur Silicon Relat Elem 190:1100–1107. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426507.2014.966190
Carrion MC, Sepúlveda F, Jalón FA et al (2009) Base-free transfer hydrogenation of ketones using arene ruthenium(II) complexes. Organometallics 28:3822–3833. https://doi.org/10.1021/om9001268
Bacchi A, Pelagatti P, Pelizzi C, Rogolino D (2009) Diastereomeric half-sandwich Ru(II) cationic complexes containing amino amide ligands. Synthesis, solution properties, crystal structure and catalytic activity in transfer hydrogenation of acetophenone. J Organomet Chem 694:3200–3211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jorganchem.2009.05.010
Raja MU, Raja N, Ramesh R (2010) Transfer hydrogenation of ketones using recyclable (η 6-arene) ruthenium(II) naphthylazo-p-methyl phenolate complex. Open Catal J 3:30–33. https://doi.org/10.2174/1876214X01003010030
Dolomanov OV, Bourhis LJ, Gildea RJ et al (2009) OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J Appl Crystallogr 42:339–341. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889808042726
Sheldrick GM (2015) SHELXT - Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr Sect A Found Crystallogr 71:3–8. https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053273314026370
Sheldrick GM (2015) Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr Sect C Struct Chem 71:3–8
Sadık M, Karabork M, Sahin I, Kose M (2021) Half-sandwich ruthenium(II) complexes containing 4-substituted aniline derivatives: structural characterizations and catalytic properties in transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Transit Met Chem 46:457–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-021-00461-9
Cheng B, Tehrani AA, Hu ML, Morsali A (2014) Supramolecular assemblies of Ru(ii) organometallic half-sandwich complexes. CrystEngComm 16:9125–9134. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ce01214c
Bacchi A, Pelagatti P (2016) Organometallic chemistry meets crystal engineering to give responsive crystalline materials. Chem Commun 52:1327–1337. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cc09427e
Tyagi D, Binnani C, Rai RK et al (2016) Ruthenium-catalyzed oxidative homocoupling of arylboronic acids in water: ligand tuned reactivity and mechanistic study. Inorg Chem 55:6332–6343. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.6b01115
Bacchi A, Balordi M, Cammi R et al (2008) Mechanistic insights into acetophenone transfer hydrogenation catalyzed by half-sandwich ruthenium (II) complexes containing 2-(diphenylphosphanyl) aniline-a combined experimental and theoretical study. Eur J Inorg Chem 2008(28):4462–4473. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.200800509
Schlatter A, Woggon WD (2008) Enantioselective transfer hydrogenation of aliphatic ketones catalyzed by ruthenium complexes linked to the secondary face of β-cyclodextrin. Adv Synth Catal 350:995–1000. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.200700558
Agac A, Karakaya I, Sahin I et al (2016) Synthesis of aminomethyl quinazoline based ruthenium (II) complex and its application in asymmetric transfer hydrogenation under mild conditions. J Organomet Chem 819:189–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jorganchem.2016.07.001
Ritleng V, de Vries JG (2021) Ruthenacycles and iridacycles as transfer hydrogenation catalysts. Molecules https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134076
Higuera-Padilla AR, Batista AA, Colina-Vegas L et al (2017) Synthesis of the [(η6-p-cymene)Ru(dppb)Cl]PF6 complex and catalytic activity in the transfer hydrogenation of ketones. J Coord Chem 70:3541–3551. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2017.1390226
Çalik HS, Ispir E, Karabuga Ş, Aslantas M (2015) Ruthenium (II) complexes of NO ligands: Synthesis, characterization and application in transfer hydrogenation of carbonyl compounds. J Organomet Chem 801:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jorganchem.2015.10.028
Cavallo M, Arnodo D, Mannu A et al (2021) Deep eutectic solvents as H2-sources for Ru(II)-catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of carbonyl compounds under mild conditions. Tetrahedron 83:131997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2021.131997
Acknowledgements
The author thanks to Research Coordination Unit of Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam University for financial support (project number: 2018/2-9 YLS) and postdoc (DOSAP) Scholarship (İrfan Şahin).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şahin, İ., Sevim, S. & Köse, M. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic transfer hydrogenation properties of Ru(II) complexes. Transit Met Chem 47, 77–84 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-021-00488-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-021-00488-y