Abstract
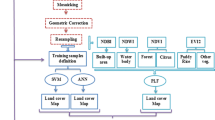
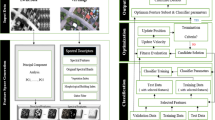
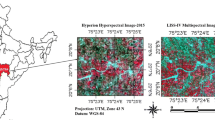
Multi-sensor data fusion has recently received remarkably more attraction in urban land classification. The fusion of multi-resolution and multi-sensor remote sensing data can help in comprehending more information about the same land cover features, thereby, enhancing the classification accuracy. In this field of study, a combination of hyperspectral data in a long-wave infrared range and a very high-resolution data in a visible range has been extensively used for exploring the spectral and spatial features for decision level fusion classification. This paper proposes a novel method of integrating the classifier decisions with the additional ancillary information derived from spectral and spatial features for improvement in the classification accuracy of natural and man-made objects in urban land cover. The paper also presents a detailed performance comparative evaluation of two classifiers i.e., support vector machine (SVM) and artificial neural network (ANN) to show the effectiveness of these classifiers. The results obtained from a decision-based multilevel fusion of spectral and spatial information using hyperspectral and visible data have shown improvement in classification accuracy. The results also reveal that the classification accuracy of the SVM classifier is better than ANN in multi-sensor data using decision level fusion of combined feature set analysis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rodriguez-Galiano, V. F., Ghimire, B., Pardo-Iguzquiza, E., Chica-Olmo, M., & Congalton, R. G. (2012). Incorporating the downscaled Landsat TM thermal band in land-cover classification using random forest. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 78(2), 129–137.
Luo, Xiaoqing, Zhang, Zhancheng, & Xiaojun, Wu. (2016). A novel algorithm of remote sensing image fusion based on shift-invariant Shearlet transform and regional selection. AEU- International Journal of Electronics and Communication., 70(2), 186–197.
Berger, C., Riedel, F., Rosentreter, J., Stein, E., Hese, S., & Schmullius, C. (2015). Fusion of airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR remote sensing data to study the thermal characteristics of urban environments. In Computational Approaches for Urban Environments (pp. 273-292). Springer, Cham.
Ma, Jiayi, Ma, Yong, & Li, Chang. (2018). Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: a survey. Information Fusion, 45, 153–178.
Dianat, R., & Kasaei, S. (2010). Dimension reduction of remote sensing images by incorporating spatial and spectral properties. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communication, 64(8), 729–732.
Zhang, Lefei, & Tao, Dacheng. (2012). On combining multiple features for hyperspectral remote sensing image classification. IEEE Transaction on Geoscience and Remote Sensing., 50(3), 879–893.
Bruzzone, L., & Bovolo, F. (2013). A novel framework for the design of change-detection systems for very-highresolution remote sensing images. Proceedings of the IEEE, 101(3), 609–630.
Huang, X., Zhang, L., & Zhu, T. (2014). Building change detection from multitemporal high-resolution remotely sensed images based on a morphological building index. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing., 7(1), 105–115.
Tian, J., Reinartz, P. (2011). Multitemporal 3D change detection in urban areas using stereo information from different sensors. In International Symposium on Image and Data Fusion (pp. 1–4).
Gao, Jianqiang, & Lizhong, Xu. (2015). An efficient method to solve the classification problem for remote sensing. AEU- International Journal of Electronics and Communication, 69(1), 198–205.
Moser, G., & Serpico, S. B. (2013). Benediktsson. Land cover mapping by markov modelling of spatial contextual information in very high-resolution remote sensing images, Proceedings of IEEE., 101(3), 631–651.
Eslami, M., & Mohammadzadeh, A. (2015). Developing a spectral-based strategy for urban object detection from airborne hyperspectral TIR and visible data. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 9(5), 1808–1816.
Li, J., Zhang, H., Guo, M., Zhang, L., Shen, H., & Du, Q. (2015). Urban classification by the fusion of thermal infrared hyperspectral and visible data. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 81(12), 901–911.
Lu, X., Zhang, J., Li, T., & Zhang, G. (2015). Synergetic classification of long-wave infrared hyperspectral and visible images. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 8(7), 3546–3557.
Melgani, F., & Serpico, S. B. (2002). A statistical approach to the fusion of spectral and spatio-temporal contextual information for the classification of remote-sensing images. Pattern Recognition Letters, 23(9), 1053–1061.
Bardossy, A., & Samaniego, L. (2002). Fuzzy rule-based classification of remotely sensed imagery. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 40(2), 362–374.
Bruzzone, L., & Cossu, R. (2002). A multiple-cascade-classifier system for a robust and partially unsupervised updating of land-cover maps. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 40(9), 1984–1996.
Lu, D., & Weng, Q. (2007). A survey of image classification methods and techniques for improving classification Performance. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 28(5), 823–870.
Won Hee Lee. (2015). Object-oriented classification of urban areas using lidar and aerial images. Journal of the Korean Society of Surveying, Geodesy, Photogrammetry and Cartography., 33(3), 173–179.
IEEE GRSS Data Fusion Contest, Presented to Image Analysis and Data Fusion Technical Committee, IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Society (GRSS) (2014).
Haboudane, Driss. (2004). Hyperspectral vegetation indices and novel algorithms for predicting green LAI of crop canopies: Modeling and validation in the context of precision agriculture. Remote Sensing of Environment, 90, 337–352.
Huang, Xin, & Zhang, Liangpei. (2012). Morphological building/shadow index for building extraction from high- resolution imagery over urban areas. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing., 5(1), 161–172.
Liao, Wenzhi, & Bellens, Rik. (2012). Classification of hyperspectral data over urban areas using directional morphological profiles and semi-supervised feature extraction. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing., 5(4), 1177–1190.
Marceau, D., Howarth, P., Dubois, J., & Gratton, D. (1990). Evaluation of the grey-level co-occurrence matrix method for land-cover classification using Spot imagery. IEEE Transaction of Geoscience Remote Sensing., 28(4), 513–519.
Askarpour, S., Anari, M. S., Brumandnia, A., & Javidi, M. M. (2014). The analysis of connected components and clustering in segmentation of persian texts. Research Journal of Recent Sciences, 3(4), 71–72.
XinHuang, Liangpei Zhang. (2013). An SVM ensemble approach combining spectral, structural, and semantic features for the classification of high-resolution remotely sensed imagery. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 51(1), 257–272.
Luo, Shezhou, Wang, Cheng, Xi, Xiaohuan, Zeng, Hongcheng, Li, Dong, Xia, Shaobo, et al. (2015). Fusion of airborne discrete-return LiDAR and hyperspectral data for land cover classification. Remote Sensing, 8(1), 3–12.
Melgani, Farid. (2004). Classification of hyperspectral remote sensing images with support vector machines. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 42(8), 1778–1790.
Yuan, Hui, & Van Der Wiele, Cynthia F. (2009). An automated artificial neural network system for land use/land cover classification from LANDSAT TM imagery. Journal of Remote Sensing. ISSN, 2072–4292, 243–265.
Madsen, K., Neilsen, H. B. (2004) Methods for non-linear least squares problems. 2nd Edition.
Licciardi, G. (2009). Decision fusion for the classification of hyperspectral data: outcome of the 2008 GRS-S data fusion contest. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 47(11), 3857–3865.
Santra, A. K., & Christy, C. J. (2012). Genetic algorithm and confusion matrix for document clustering. International Journal of Computer Science Issues., 9(1), 322–328.
Singh, Kunwar K., Vogler, John B., Shoemaker, Douglas A., & Meentemeyer, Ross K. (2014). LiDAR-Landsat data fusion for large-area assessment of urban land cover: Balancing spatial resolution, data volume and mapping accuracy. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing., 74, 110–121.
Liao, W., et al. (2014). IEEE data fusion best paper contest.
Momeni, R., Aplin, P., & Boyd, D. (2016). Mapping complex urban land cover from spaceborne imagery: the influence of spatial resolution, spectral band set and classification approach. Remote Sensing, 8(2), 88.
Rees, D. G. (1987). Foundations of statistics. London: Chapman & Hall.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vohra, R., Tiwari, K.C. Comparative Analysis of SVM and ANN Classifiers using Multilevel Fusion of Multi-Sensor Data in Urban Land Classification. Sens Imaging 21, 17 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11220-020-00280-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11220-020-00280-9