Abstract
The icy moons of the outer Solar System harbor potentially habitable environments for life, however, compared to the terrestrial biosphere, these environments are characterized by extremes in temperature, pressure, pH, and other physico-chemical conditions. Therefore, the search for life on these icy worlds is anchored on the study of terrestrial extreme environments (termed “analogue sites”), which harbor microorganisms at the frontiers of polyextremophily. These so-called extremophiles have been found in areas previously considered sterile: hot springs, hydrothermal vents, acidic or alkaline lakes, hypersaline environments, deep sea sediments, glaciers, and arid areas, amongst others. Such model systems and communities in extreme terrestrial environments may provide important information relevant to the astrobiology of icy bodies, including the composition of potential biological communities and the identification of biosignatures that they may produce.
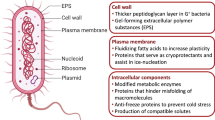
Extremophiles can use either sunlight (phototrophs) or chemical energy (chemotrophs) as energy sources, and different chemical compounds as electron donors or acceptors. Aerobic microorganisms use oxygen (O2) as a terminal electron acceptor, whereas anaerobic microorganisms may use nitrate (\(\mathrm{NO}_{3} ^{-}\)), sulfate (\(\mathrm{SO}_{4} ^{2-}\)), carbon dioxide (CO2), Fe(III), or other organic or inorganic molecules during respiration. The phylogenetic diversity of extremophiles is very high, leading to their broad dispersal across the phylogenetic tree of life together with a wide variety in metabolic diversity.
Some metabolisms are specific to archaea, for example, methanogenesis, an anaerobic respiration during which methane (CH4) is produced. Also sulfur-reduction performed by some bacteria and archaea is considered as a primitive metabolism which is restricted to anoxic sulfur-rich habitats in nature.
Methanogenesis and sulfur reduction are of specific interest for icy moon research as it might be one of the few known terrestrial metabolisms possible on these celestial bodies.
Therefore, the adaptation of these intriguing microorganisms to extreme conditions will be highlighted within this review.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Abe, Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on microbial cell membranes: structural and functional perspectives. Sub-Cell. Biochem. 72, 371–381 (2015)
A. Aertsen, F. Meersman, M.E. Hendrickx, R.F. Vogel, C.W. Michiels, Biotechnology under high pressure: applications and implications. Trends Biotechnol. 27(7), 434–441 (2009)
P.S. Aguilar, D. de Mendoza, Control of fatty acid desaturation: a mechanism conserved from bacteria to humans. Mol. Microbiol. 62, 1507–1514 (2006)
E.E. Allen, D. Facciotti, D.H. Bartlett, Monounsaturated but not polyunsaturated fatty acids are required for growth of the deep-sea bacterium photobacterium profundum SS9 at high pressure and low temperature. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65, 1710–1720 (1999)
A.C. Allwood, M.R. Walter, I.W. Burch, B.S. Kamber, 3.42 billion-year-old stromatolite reef from the Pilbara Craton of Western Australia: ecosystem-scale in- sights to early life on Earth. Precambrian Res. 158, 198–227 (2007)
A.C. Allwood, M.T. Rosing, D.T. Flannery, J.A. Hurowitz, C.M. Heirwegh, Reassessing evidence of life in 3,700-million-year-old rocks of Greenland. Nature 563, 241–244 (2018)
M.A. Amoozegar, A. Makhdoumi-Kakhki, S.A. Shahzadeh Fazeli, R. Azarbaijani, A. Ventosa, Halopenitus persicus gen. nov., sp. nov., an archaeon from an inland salt lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62, 1932–1936 (2012)
J. Antón, R. Rossello-Mora, F. Rodríguez-Valera, R. Amann, Extremely halophilic bacteria in crystallizer ponds from solarsalterns. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 3052–3057 (2000)
J. Antón, A. Oren, S. Benlloch, F. Rodríguez-Valera, R. Amann, R. Rosselló-Mora, Salinibacter ruber gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel extreme halophilic member of the bacteria from saltern crystallizer ponds. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52, 485–491 (2002)
A. Antunes, Extreme Red Sea: life in the deep-sea anoxic brine lakes, in Red Sea VI Proceedings, ed. by A. Agius, E. Khalil, E. Scerri (E.J. Brill, Leiden, 2017)
A. Antunes, D.K. Ngugi, U. Stingl, Microbiology of the Red Sea (and other) deep-sea anoxic brine lakes. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 3, 416–433 (2011)
A. Antunes, S. Kaartvedt, M. Schmidt, Geochemistry and life at the interfaces of brine-filled deeps in the Red Sea, in Oceanography and Environment of the Red Sea II. Springer Earth System Sciences 2018 (Springer, Berlin, 2018)
A. Antunes, K. Olsson-Francis, T. McGenity, Exploring deep-sea brines as potential terrestrial analogues of oceans in the icy moons of the outer solar system. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.21775/9781912530304.06
R.E. Bardavid, L. Mana, A. Oren, Haloplanus natans gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic, gas-vacuolate archaeon isolated from Dead Sea–Red Sea water mixtures in experimental outdoor ponds. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 780–783 (2007)
L.M. Barge, LM. White, Experimentally testing hydrothermal vent origin of life on Enceladus and other icy/ocean worlds. Astrobiology 17, 820–833 (2017)
D.H. Bartlett, Pressure effects on in vivo microbial processes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1595, 367–381 (2002)
F.U. Battistuzzi, A. Feijao, S.B. Hedges, A genomic timescale of prokaryote evolution: insights into the origin of methanogenesis, phototrophy, and the colonization of land. BMC Evol. Biol. 4, 44 (2004)
L.M.F. Baumann, R.-S. Taubner, T. Bauersachs, M. Steiner, C. Schleper, J. Peckmann, S.K.-M.R. Rittmann, D. Birgel, Intact polar lipid and core lipid inventory of the hydrothermal vent methanogens Methanocaldococcus villosus and Methanothermococcus okinawensis. Org. Geochem. 126, 33–42 (2018)
J. Beranova, M. Jemiola-Rzeminska, D. Elhottova et al., Metabolic control of the membrane fluidity in Bacillus subtilis during cold adaptation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Biomembr. 1778, 445–453 (2008)
S. Bernacchi, S. Rittmann, A.H. Seifert, A. Krajete, C. Herwig, Experimental methods for screening parameters influencing the growth to product yield (Y(x/CH4)) of a biological methane production (BMP) process performed with Methanothermobacter marburgensis. AIMS Bioeng. 1, 72–86 (2014)
G. Bernhardt, R. Jaenicke, H.D. Ludemann, High-pressure equipment for growing methanogenic microorganisms on gaseous substrates at high temperature. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53, 1876–1879 (1987)
C.E. Blank, Phylogenomic dating—the relative antiquity of archaeal metabolic and physiological traits. Astrobiology 9, 193–219 (2009)
H. Bolhuis, E.M. Poele, F. Rodriguez-Valera, Isolation and cultivation of Walsby’s square archaeon. Environ. Microbiol. 6, 1287–1291 (2004)
B. Boonyaratanakornkit, J. Córdova, C.B. Park, D.S. Clark, Pressure affects transcription profiles of Methanocaldococcus jannaschii despite the absence of barophilic growth under gas-transfer limitation. Environ. Microbiol. 8, 2031–2035 (2006)
M.D. Brasier, O.R. Green, A.P. Jephcoat, A.K. Kleppe, M.J. Van Kranendonk, J.F. Lindsay, A. Steele, N.V. Grassineau, Questioning the evidence of Earth’s oldest fossils. Nature 416, 76–81 (2002)
M.D. Brasier, O.R. Green, J.F. Lindsay, A. Steele, Earth’s oldest (∼3.5 Ga) fossils and the ‘early Eden hypothesis’: questioning the evidence. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 34, 257–269 (2004)
M.D. Brasier, N. McLoughlin, O.R. Green, D.A. Wacey, Fresh look at the fossil evidence for early Archaean cellular life. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 361, 887–902 (2006)
M.D. Brasier, R. Matthewman, S. McMahon, D. Wacey, Pumice as a remarkable substrate for the origin of life. Astrobiology 11, 725–735 (2011)
M. Brasier, J. Antcliffe, M. Saunders, D. Wacey, Changing the picture of Earth’s earliest fossils (3.5-1.9 Ga) with new approaches and new discoveries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 112, 4859–4864 (2015)
S.L. Bräuer, H. Cadillo-Quiroz, R.J. Ward, J.B. Yavitt, S.H. Zinder, Methanoregula boonei gen. nov., sp. nov., an acidiphilic methanogen isolated from an acidic peat bog. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 61, 45–52 (2011)
C. Brochier-Armanet, P. Forterre, S. Gribaldo, Phylogeny and evolution of the Archaea: one hundred genomes later. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 14, 274–281 (2011)
A.D. Brown, Microbial water stress. Bacteriol. Rev. 40, 803–846 (1976)
A.D. Brown, Microbial Water Stress Physiology. Principles and Perspectives (John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, 1990)
S. Burggraf, H. Fricke, A. Neuner, J. Kristjansson, P. Rouvier, L. Mandelco, C.R. Woese, K.O. Stetter, Methanococcus igneus sp. nov., a novel hyperthermophilic methanogen from a shallow submarine hydrothermal system. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 13, 263–269 (1990)
D.G. Burns, H.M. Camakaris, P.H. Janssen, M. Dyall-Smith, Cultivation of Walsby’s square haloarchaeon. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 238, 469–473 (2004)
D.G. Burns, P.H. Janssen, T. Itoh, M. Kamekura, Z. Li, G. Jensen, F. Rodriguez-Valera, H. Bolhuis, M.L. Dyall-Smith, Haloquadratum walsbyi gen. nov., sp. nov., the square haloarchaeon of Walsby, isolated from saltern crystallizers in Australia and Spain. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 387–392 (2007)
D.G. Burns, P.H. Janssen, T. Itoh, M. Kamekura, A. Echigo, M.L. Dyall-Smith, Halonotius pteroides gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon recovered from a saltern crystallizer. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 60, 1196–1199 (2010)
H. Cadillo-Quiroz, J.B. Yavitt, S.H. Zinder, Methanosphaerula palustris gen. nov., sp. nov., a hydrogenotrophic methanogen isolated from a minerotrophic fen peatland. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 59, 928–935 (2009)
A. Camerlenghi, Anoxic basins of the eastern Mediterranean: geological framework. Mar. Chem. 31, 1–19 (1990)
S. Campanaro, A. Vezzi, N. Vitulo, F.M. Lauro M. D’Angelo, F. Simonato, A. Cestaro, G. Malacrida, G. Bertoloni, G. Valle, D.H. Bartlett, Laterally transferred elements and high pressure adaptation in Photobacterium profundum strains. BMC Genomics 14(6), 122 (2005)
P. Carini, A. White, E. Campbell, S. Giovannoni, Methane production by phosphate-starved SAR11 chemoheterotrophic marine bacteria. Nat. Commun. 5, 4346 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5346
A. Cario, V. Grossi, P. Schaeffer, P.M. Oger, Membrane homeoviscous adaptation in the piezo-hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus barophilus. Front. Microbiol. 6, 1152 (2015)
A. Cario, M. Jebbar, A. Thiel, N. Kervarec, P. Oger, Molecular chaperone accumulation as a function of stress evidences adaptation to high hydrostatic pressure in the piezophilic archaeon Thermococcus barophilus. Sci. Rep. 6, 29483 (2016)
A.M. Castillo, M.C. Gutiérrez, M. Kamekura, Y. Xue, Y. Ma, D.A. Cowan, B.E. Jones, W.D. Grant, A. Ventosa, Halostagnicola larsenii gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from a saline lake in Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 1519–1524 (2006a)
A.M. Castillo, M.C. Gutiérrez, M. Kamekura, Y. Ma, D.A. Cowan, B.E. Jones, W.D. Grant, A. Ventosa, Halovivax asiaticus gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 765–770 (2006b)
B. Cavalazzi, R. Barbieri, F. Gómez, B. Capaccioni, K. Olsson-Francis, M. Pondrelli, A.P. Rossi, K. Hickman-Lewis, A. Agangi, G. Gasparotto, M. Glamoclija, G.G. Ori, N. Rodriguez, M. Hagos, The Dallol geothermal area, Northern Afar (Ethiopia)—an exceptional planetary field analog on Earth. Astrobiology 19, 553–578 (2019)
R. Cavicchioli, Cold-adapted archaea. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4, 331–343 (2006)
S. Chen, H.C. Liu, J. Zhou, H. Xiang, Haloparvum sedimenti gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the family Haloferacaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 66(6), 2327–2334 (2016)
L. Cheng, T.L. Qiu, X.B. Yin, X.L. Wu, G.Q. Hu, Y. Deng, H. Zhang, Methermicoccus shengliensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a thermophilic, methylotrophic methanogen isolated from oil-production water, and proposal of Methermicoccaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 2964–2969 (2007)
S.C. Chong, Y. Liu, M. Cummins, D.L. Valentine, D.R. Boone, Methanogenium marinum sp. nov., a H2-using methanogen from Skan Bay, Alaska, and kinetics of H2 utilization. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 81, 263–270 (2002)
P.L. Chong, U. Ayesa, V.P. Daswani, E.C. Hur, On physical properties of tetraether lipid membranes: effects of cyclopentane rings. Archaea. 2012, 138439 (2012)
C.F. Chyba, C.B. Phillips, Possible ecosystems and the search for life on Europa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 801–804 (2001)
C.E. Cleland, C.F. Chyba, Defining ‘life’. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 32, 387–393 (2002)
D.R. Colman, S. Poudela, B.W. Stamps, E.S. Boyd, J.R. Spear, The deep, hot biosphere: twenty-five years of retrospection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 114, 6895–6903 (2017)
F.S. Colwell, S. D’Hondt, Nature and extent of the deep biosphere. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 75, 547–574 (2013)
J.B. Corliss, J. Dymond, L.I. Gordon, J.M. Edmond, R.P. von Herzen, R.D. Ballard, K. Green, D. Williams, A. Bainbridge, K. Crane, T.H. van Andel, Submarine thermal springs on the Galapagos Rift. Science 203, 1073–1083 (1979)
L. Csonka, Physiological and genetic responses of bacteria to osmotic stress. Microbiol. Rev. 53, 121–147 (1989)
H.L. Cui, X.X. Qiu, Salinarubrum litoreum gen. nov., sp. nov.: a new member of the family Halobacteriaceae isolated from Chinese marine solar salterns. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 105, 135–141 (2014)
H.L. Cui, W.J. Zhang, Salinigranum rubrum gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the family Halobacteriaceae isolated from a marine solar saltern. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 64, 2029–2033 (2014)
H.L. Cui, X. Gao, X. Yang, X.W. Xu, Halorussus rarus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Halobacteriaceae isolated from a marine solar saltern. Extremophiles 14, 493–499 (2010a)
H.L. Cui, X. Gao, F.F. Sun, Y. Dong, X.W. Xu, Y.G. Zhou, H.C. Liu, A. Oren, P.J. Zhou, Halogranum rubrum gen. nov., sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from a marine solar saltern. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 60, 1366–1371 (2010b)
H.L. Cui, X.Y. Li, X. Gao, X.W. Xu, Y.G. Zhou, H.C. Liu, A. Oren, P.J. Zhou, Halopelagius inordinatus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Halobacteriaceae isolated from a marine solar saltern. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 60, 2089–2093 (2010c)
H.L. Cui, X. Yang, Y.Z. Mou, Salinarchaeum laminariae gen. nov., sp. nov.: a new member of the family Halobacteriaceae isolated from salted brown alga Laminaria. Extremophiles 15, 625–631 (2011a)
H.L. Cui, X. Gao, X. Yang, X.W. Xu, Halolamina pelagica gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Halobacteriaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 61, 1617–1621 (2011b)
H.L. Cui, X. Yang, X. Gao, X.W. Xu, Halobellus clavatus gen. nov., sp. nov. and Halorientalis regularis gen. nov., sp. nov., two new members of the family Halobacteriaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 61, 2682–2689 (2011c)
H.L. Cui, Y.Z. Mou, X. Yang, Y.G. Zhou, H.C. Liu, P.J. Zhou, Halorubellus salinus gen. nov., sp. nov. and Halorubellus litoreus sp. nov., novel halophilic archaea isolated from a marine solar saltern. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 35, 30–34 (2012)
H.L. Cui, Z.Z. Lü, Y. Li, Y. Zhou, Salinirussus salinus gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a marine solar saltern. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 67(9), 3622–3626 (2017)
J.C. Cushman, Osmoregulation in plants: implications for agriculture. Am. Zool. 41, 758–769 (2001)
L.E. Cybulski, D. Albanesi, M.C. Mansilla et al., Mechanism of membrane fluidity optimization: isothermal control of the Bacillus subtilis acyl-lipid desaturase. Mol. Microbiol. 45, 1379–1388 (2002)
M.S. da Costa, H. Santos, E.A. Galinski, An overview of the role and diversity of compatible solutes in bacteria and archaea. Adv. Biochem. Biotechnol. 61, 118–153 (1998)
D. Daffonchio, S. Borin, T. Brusa, L. Brusetti, P.W.J.J. van derWielen, H. Bolhuis et al., Stratified prokaryote network in the oxic-anoxic transition of a deep-sea halocline. Nature 440, 203–207 (2006)
C. Dalmasso, P. Oger, G. Selva, D. Courtine, S. L’Haridon, A. Garlaschelli, E. Roussel, J. Miyazaki, J. Reveillaud, M. Jebbar, K. Takai, L. Maignien, K. Alain, Thermococcus piezophilus sp. nov., a novel hyperthermophilic and piezophilic archaeon with a broad pressure range for growth, isolated from a deepest hydrothermal vent at the Mid-Cayman Rise. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 39(7), 440–444 (2016)
O. Dannenmuller, K. Arakawa, T. Eguchi et al., Membrane properties of archaeal macrocyclic diether phospholipids. Chemistry (Easton) 6, 645–654 (2000)
A.V. Dass, M. Jaber, A. Brack, F. Foucher, T.P. Kee, T. Georgelin, F. Westall, Potential role of inorganic confined environments in prebiotic phosphorylation. Life 8, 7 (2018)
S. DasSarma, P. Arora, Halophiles. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences (2001). Macmillan Press
K.S. Dawson, K.H. Freeman, J.L. Macalady, Molecular characterization of core lipids from halophilic archaea grown under different salinity conditions. Org. Geochem. 48, 1–8 (2012)
M. De Rosa, E. Esposito, A. Gambacorta et al., Complex lipids of Caldariella acidophila, a thermoacidophile archaebacterium. Phytochemistry 19, 821–826 (1980a)
M. De Rosa, E. Esposito, A. Gambacorta et al., Effects of temperature on ether lipid composition of Caldariella acidophila. Phytochemistry 19, 827–831 (1980b)
E.F. DeLong, A.A. Yayanos, Adaptation of the membrane-lipids of a deep-sea bacterium to changes in hydrostatic-pressure. Science 228, 1101–1102 (1985)
A. Dereeper, V. Guignon, G. Blanc, S. Audic, S. Buffet, F. Chevenet, J.F. Dufayard, S. Guindon, V. Lefort, M. Lescot, J.M. Claverie, O. Gascuel, Phylogeny.fr: robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, W465–W469 (2008). (Web Server issue)
D. Desmarais, P.E. Jablonski, N.S. Fedarko, Roberts MF: 2-sulfotrehalose, a novel osmolyte in haloalkaliphilic archaea. J. Bacteriol. 179, 3146–3153 (1997)
D. Dianou, T. Miyaki, S. Asakawa, H. Morii, K. Nagaoka, H. Oyaizu, S. Matsumoto, Methanoculleus chikugoensis sp. nov., a novel methanogenic archaeon isolated from paddy field soil in Japan, and DNA-DNA hybridization among Methanoculleus species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51, 1663–1669 (2001)
M.S. Dodd, D. Papineau, T. Grenne, J.F. Slack, M. Rittner, F. Pirajno, J. O’Neil, C.T. Little, Evidence for early life in Earth’s oldest hydrothermal vent precipitates. Nature 543, 60–64 (2017)
X. Dong, Z. Chen, Psychrotolerant methanogenic archaea: diversity and cold adaptation mechanisms. Sci. China Life Sci. 55, 415–421 (2012)
T. Ebisuzaki, S. Maruyama, Nuclear geyser model of the origin of life: driving force to promote the synthesis of building blocks of life. Geosci. Front. 8, 275–298 (2017)
A. Echigo, H. Minegishi, Y. Shimane, M. Kamekura, T. Itoh, R. Usami, Halomicroarcula pellucida gen. nov., sp. nov., a non-pigmented, transparent-colony-forming, halophilic archaeon isolated from solar salt. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 63, 3556–3562 (2013)
B. Elazari-Volcani, Genus XII. Halobacterium Elazari-Volcani, 1940, in Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, ed. by R.S. Breed, E.G.D. Murray, N.R. Smith 7th edn. (Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, 1957), pp. 207–212
N. Empadinhas, M.S. da Costa, Diversity and biosynthesis of compatible solutes in hyper/thermophiles. Int. Microbiol. 9, 199–206 (2006)
M. Ernst, H.J. Freisleben, E. Antonopoulos et al., Calorimetry of archaeal tetraether lipid—indication of a novel metastable thermotropic phase in the main phospholipid from Thermoplasma acidophilum cultured at 59 degrees C. Chem. Phys. Lipids 94, 1–12 (1998)
M. Essendoubi, F. Brhada, J.E. Eljamali, A. Filali-Maltouf, S. Bonnassie, S. Georgeault, C. Blanco, M. Jebbar, Osmoadaptative responses in the rhizobia nodulating Acacia isolated from south-eastern Moroccan Sahara. Environ. Microbiol. 9(3), 603–611 (2007)
G. Feller, C. Gerday, Psychrophilic enzymes: hot topics in cold adaptation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 1, 200–208 (2003)
V. Formisano, S. Atreya, T. Encrenaz, N. Ignatiev, M. Giuranna, Detection of methane in the atmosphere of Mars. Science 306, 1758–1761 (2004)
S. Fox, H. Strasdeit, A possible prebiotic origin on volcanic islands of oligopyrrole-type photopigments and electron transfer cofactors. Astrobiology 13, 578–595 (2013)
P.D. Franzmann, N. Springer, W. Ludwig, E.C. De Macario, M. Rohde, A methanogenic archaeon from Ace Lake, Antarctica: Methanococcoides burtonii sp. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 15, 573–581 (1992)
P.D. Franzmann, Y. Liu, D.L. Balkwill, H.C. Aldrich, E.C.D. Macario, D.R. Boone, Methanogenium frigidum sp. nov., a psychrophilic, H2-using methanogen from Ace Lake, Antarctica. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47, 1068–1072 (1997)
E.A. Galinski, H.G. Trüper, Microbial behaviour in salt-stressed ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 15, 95–108 (1994)
J.M. García-Ruiz, S.T. Hyde, A.M. Carnerup, A.G. Christy, M.J. Van Kranendonk, N.J. Welham, Self-assembled silica-carbonate structures and detection of ancient microfossils. Science 14, 1194–1197 (2003)
E.A. Gaucher, J.T. Kratzer, R.N.R. Deep, Phylogeny—how a tree can help characterize early life on Earth. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2, a002238 (2010)
M.B. Gillett, J.R. Suko, F.O. Santoso, P.H. Yancey, Elevated levels of trimethylamine oxide in muscles of deep-sea gadiform teleosts: a high-pressure adaptation? J. Exp. Zool. 279, 386–391 (1997)
C.R. Glein, J.A. Baross, J. Hunter Waite Jr., The pH of Enceladus’ oceans. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 162, 202–219 (2015)
A. Gliozzi, R. Rolandi, M. De Rosa, A. Gambacorta, Monolayer black membranes from bipolar lipids of archaebacteria and their temperature-induced structural changes. J. Membr. Biol. 75, 45–56 (1983)
I. Gonthier, M.N. Rager, P. Metzger et al., A di-O-dihydrogeranylgeranyl glycerol from Thermococcus S557, a novel ether lipid, and likely intermediate in the biosynthesis of diethers in Archaea. Tetrahedron Lett. 42, 2795–2797 (2001)
N.V. Grassineau, P.W.U. Appel, C.M.R. Fowler, E.G. Nisbet, Distinguishing biological from hydrothermal signatures via sulphur and carbon isotopes in Archaean mineralizations at 3.8 and 2.7 Ga. Geol. Soc. (Lond.) Spec. Publ. 248, 195–212 (2005)
F. Greco, B. Cavalazzi, A. Hofmann, K. Hickman-Lewis, 3.4 Ga biostructures from the barberton greenstone belt of South Africa: new insights into microbial life. Boll. Soc. Paleontol. Ital. 57, 59–74 (2018)
N. Gunde-Cimerman, J. Ramos, A. Plemenitaš, Halotolerant and halophilic fungi. Mycol. Res. 113(11), 1231–1241 (2009)
E. Gunnigle, P. McCay, M. Fuszard, C.H. Botting, F. Abram, V. O’Flaherty, A functional approach to uncover the low-temperature adaptation strategies of the archaeon Methanosarcina barkeri. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 79, 4210–4219 (2013)
R.S. Gupta, S. Naushad, S. Baker, Phylogenomic analyse sand molecular signatures for the class Halobacteria and its two major clades: a proposal for division of the class Halobacteria into an emended order Halobacteriales and two new orders, Haloferacales ord. nov. and Natrialbales ord. nov., containing the novel families Haloferacaceae fam. nov. and Natrialbaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 65, 1050–1069 (2015)
R.S. Gupta, S. Naushad, R. Fabros, M. Adeolu, A phyloge-nomic reappraisal of family-level divisions within the class Halobacteria: proposal to divide the order Halobacteriales into the families Halobacteriaceae, Haloarculaceae fam. nov and Halococcaceae fam. nov., and the order Haloferacales into the families, Haloferacaceae and Halorubraceae fam. nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 109, 565–587 (2016)
M.C. Gutiérrez, A.M. Castillo, M. Kamekura, Y. Ma, D.A. Cowan, B.E. Jones, W.D. Grant, A. Ventosa, Halopiger xanaduensis gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from saline Lake Shangmatala in Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 1402–1407 (2007)
D. Hafenbradl, M. Keller, R. Thiericke, K.O. Stetter, A novel unsaturated archael ether core lipid from the hyperthermophile Methanopyrus kandleri. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 16, 165–169 (1993)
J.B.S. Haldane, Origin of life. Ration. Annu. 148, 3–10 (1929)
T. Harding, A.G. Simpson, Recent advances in halophilic protozoa research. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 65(4), 556–570 (2018)
T. Hassenkam, M.P. Andersson, K.N. Dalby, D.M.A. Mackenzie, M.T. Rosing, Elements of Eoarchean life trapped in mineral inclusions. Nature 548(3), 78–81 (2017)
J.M. Hayes, Global methanotrophy at Archean-Proterozoic transition, in Early Life on Earth, ed. by S. Bengtsen. Nobel Symposium 84 (Columbia University Press, New York, 1994)
R.M. Hazen, D.A. Sverjensky, Mineral surfaces, geochemical complexities, and the origins of life. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2, a002162 (2010)
R.M. Hazen, N. Boctor, J.A. Brandes, G.D. Cody, R.J. Hemley, A. Sharma, H.S. Yoder Jr., High pressure and the origin of life. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 14, 11489–11494 (2002)
F.F. Hezayen, B.J. Tindall, A. Steinbüchel, B.H.A. Rehm, Characterization of a novel halophilic archaeon, Halobiforma haloterrestris gen. nov., sp. nov., and transfer of Natronobacterium nitratireducens to Halobiforma nitratireducens comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52, 2271–2280 (2002)
K. Hickman-Lewis, R.J. Garwood, M.D. Brasier, T. Goral, H. Jiang, N. McLoughlin, D. Wacey, Carbonaceous microstructures of the 3.46 Ga stratiform ‘Apex chert’, Chinaman Creek locality, Pilbara, Western Australia. Precambrian Res. 278, 161–178 (2016)
K. Hickman-Lewis, B. Cavalazzi, F. Foucher, F. Westall, Most ancient evidence for life in the Barberton Greenstone Belt: microbial mats and biofabrics of the ∼3.47 Ga Middle Marker horizon. Precambrian Res. 312, 45–67 (2018)
K. Hickman-Lewis, P. Gautret, L. Arbaret, S. Sorieul, R. De Wit, F. Foucher, B. Cavalazzi, F. Westall, Mechanistic morphogenesis of organo-sedimentary structures growing under geochemically stressed conditions: keystone to proving the biogenicity of some Archaean stromatolites? Geosciences 9, 359 (2019)
A. Hofmann, R. Bolhar, Carbonaceous cherts in the Barberton greenstone belt and their significance for the study of early life in the archean record. Astrobiology 7(2), 355–388 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1089/ast.2005.0288
H.J. Hofmann, A.H. Grey, A.H. Hickman, R.I. Thorpe, Origin of 3.45 Ga coniformstromatolites in Warrawoona Group, Western Australia. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 111, 1256–1262 (1999)
G. Holtmann, E. Bremer, Thermoprotection of Bacillus subtilis by exogenously provided glycine betaine and structurally related compatible solutes: Involvement of Opu transporters. J. Bacteriol. 186, 1683–1693 (2004)
J. Hou, Y.J. Zhao, L. Zhu, H.L. Cui, Salinirubellus salinus gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a marine solar saltern. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 68(6), 1874–1878 (2018)
C.H. House, D.Z. Oehler, K. Sugitani, K. Mimura, Carbon isotopic analyses of ca. 3.0 Ga microstructures imply planktonic autotrophs inhabited Earth’s early oceans. Geology 41(6), 651–654 (2013)
H.W. Hsu, F. Postberg, Y. Sekine, T. Shibuya, S. Kempf, M. Horányi, A. Juhász, N. Altobelli, K. Suzuki, Y. Masaki et al., Ongoing hydrothermal activities within Enceladus. Nature 519, 207–210 (2015)
R. Huber, M. Kurr, H.W. Jannasch, K.O. Stetter, A novel group of abyssal methanogenic archaebacteria (Methanopyrus) growing at 110 C. Nature 342, 833–834 (1989)
T. Iino, H. Tamaki, S. Tamazawa, Y. Ueno, M. Ohkuma, K.i. Suzuki, Y. Igarashi, S. Haruta, Candidatus methanogranum caenicola: a novel methanogen from the anaerobic digested sludge, and proposal of methanomassiliicoccaceae fam. Nov. And methanomassiliicoccales ord. nov., for a methanogenic lineage of the class thermoplasmata. Microbes Environ. 28, 244–250 (2013)
K. Inoue, T. Itoh, M. Ohkuma, K. Kogure, Halomarina oriensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from a seawater aquarium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 61, 942–946 (2011)
T. Itoh, T. Yamaguchi, P. Zhou, T. Takashina, Natronolimnobius baerhuensis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Natronolimnobius innermongolicus sp. nov., novel haloalkaliphilic archaea isolated from soda lakes in Inner Mongolia, China. Extremophiles 9, 111–116 (2005)
H.W. Jannasch, C.D. Taylor, Deep-sea microbiology. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 38, 487–514 (1984)
C. Jeanthon, S. L’Haridon, A.L. Reysenbach, M. Vernet, P. Messner, U.B. Sleytr, D. Prieur, Methanococcus infernus sp. nov., a novel hyperthermophilic lithotrophic methanogen isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 4(8 Pt 3), 913–919 (1998)
C. Jeanthon, S. L’Haridon, A.L. Reysenbach, E. Corre, M. Vernet, P. Messner, U.B. Sleytr, D. Prieur, Methanococcus vulcanius sp. nov., a novel hyperthermophilic methanogen isolated from East Pacific Rise, and identification of Methanococcus sp. DSM 4213T as Methanococcus fervens sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49, 583–589 (1999)
M. Jebbar, R. Talibart, K. Gloux, T. Bernard, C. Blanco, Osmoprotection of Escherichia coli by ectoine: uptake and accumulation characteristics. J. Bacteriol. 174(15), 5027–5035 (1992)
M. Jebbar, B. Franzetti, E. Girard, P. Oger, Microbial diversity and adaptation to high hydrostatic pressure in deep-sea hydrothermal vents prokaryotes. Extremophiles 19(4), 721–740 (2015)
B. Jiang, S.N. Parshina, W.V. Doesburg, B.P. Lomans, A.J.M. Stams, Methanomethylovorans thermophila sp. nov., a thermophilic, methylotrophic methanogen from an anaerobic reactor fed with methanol. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55, 2465–2470 (2005)
W.J. Jones, M.J.B. Paynter, R. Gupta, Characterization of Methanococcus maripaludis sp. nov., a new methanogen isolated from salt marsh sediment. Arch. Microbiol. 135, 91–97 (1983a)
W.J. Jones, J.A. Leigh, F. Mayer, C.R. Woese, R.S. Wolfe, Methanococcus jannaschii sp. nov., an extremely thermophilic methanogen from a submarine hydrothermal vent. Arch. Microbiol. 136, 254–261 (1983b)
M. Kamekura, Diversity of extremely halophilic bacteria. Extremophiles 2, 289–295 (1998)
M. Kamekura, M.L. Dyall-Smith, Taxonomy of the family Halobacteriaceae and the description of two new genera Halorubrobacterium and Natrialba. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 41, 333–350 (1995)
M. Kamekura, M.L. Dyall-Smith, V. Upasani, A. Ventosa, M. Kates, Diversity of alkaliphilic halobacteria: proposals for transfer of Natronobacterium vacuolatum, Natronobacterium magadii, and Natronobacterium pharaonic to Halorubrum, Natrialba, and Natronomonas gen. nov., respectively, as Halorubrum vacuolatum comb. nov., Natrialba magadii comb. nov., and Natronomonas pharaonic comb. nov., respectively. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47, 853–857 (1997)
J.S. Kargel, J.Z. Kaye, J.W. Head III., G.M. Marion, R. Sassen, J.K. Crowley, O.P. Ballesteros, S.A. Grant, D.L. Hogenboom, Europa’s crust and ocean: origin, composition, and the prospects for life. Icarus 148, 226–265 (2000)
D.M. Karl, L. Beversdorf, K. Björkman, M.J. Church, A. Martinez, E.F. Delong, Aerobic production of methane in the sea. Nat. Geosci. 1, 473–478 (2008)
R. Kasahara, T. Sato, H. Tamegai, K.C. Piezo-adapted, 3-isopropylmalate dehydrogenase of the obligate piezophile Shewanella benthica DB21MT-2 isolated from the 11,000-m depth of the Mariana Trench. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 73(11), 2541–2543 (2009)
R. Kasai, Y. Kitajima, C.E. Martin et al., Molecular control of membrane properties during temperature acclimatation—membrane fluidity regulation of fatty acid desaturase action. Biochemistry 15, 5228–5233 (1976)
J.Z. Kaye, J.A. Baross, Synchronous effects of temperature, hydrostatic pressure, and salinity on growth, phospholipid profiles, and protein patterns of four Halomonas species isolated from deep-sea hydrothermal-vent and sea surface environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70, 6220–6229 (2004)
R.H. Kelly, P.H. Yancey, High contents of trimethylamine oxide correlating with depth in deep-sea teleost fishes, skates, and decapod crustaceans. Biol. Bull. 196, 18–25 (1999)
B. Kempf, E. Bremer, Uptake and synthesis of compatible solutes as microbial stress responses to high-osmolality environments. Arch. Microbiol. 170(5), 319–330 (1998)
C. Koeberl, The record of impact processes on the early Earth—a review of the first 2.5 billion years, in Processes of the Early Earth, Geological Society of America Special Paper 405, ed. by W.U. Reimold, R.L. Gibson. (Geological Society of America, Boulder, 2006), pp. 1–22
Y. Koga, Thermal adaptation of the archaeal and bacterial lipid membranes. Archaea (Vanc. B. C.) 2012, 789652 (2012)
T. Kozawa, K. Sugitani, D.Z. Oehler, C.H. House, I. Saito, T. Watanabe, G.T. Early, Archean planktonic mode of life: Implications from fluid dynamics of lenticular microfossils. Geobiol., 17 (2018)
T.A. Kral, S.T. Altheide, Methanogen survival following exposure to desiccation, low pressure and martian regolith analogs. Planet. Space Sci. 89, 167–171 (2013)
T.A. Kral, T.S. Altheide, A.E. Lueders, A.C. Schuerger, Low pressure and desiccation effects on methanogens: implications for life on Mars. Planet. Space Sci. 59, 264–270 (2011)
A.U. Kuhlmann, J. Bursy, S. Gimpel, T. Hoffmann, E. Bremer, Synthesis of the compatible solute ectoine in Virgibacillus pantothenticus is triggered by high salinity and low growth temperature. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74, 4560–4563 (2008)
H.J. Kunte, H.G. Trüper, S.-L.H. Halophilic, Microorganisms, in Astrobiology, ed. by G. Horneck, C. Baumstark-Khan (Springer, Berlin, 2002)
M.C. Lai, K.R. Sowers, D.E. Robertson, M.F. Roberts, R.P. Gunsalus, Distribution of compatible solutes in the halophilic methanogenic archaebacteria. J. Bacteriol. 173, 5352–5358 (1991)
M.C. Lai, T.Y. Hong, R.P. Gunsalus, Glycine betaine transport in the obligate halophilic archaeon Methanohalophilus portucalensis. J. Bacteriol. 182, 5020–5024 (2000)
D. Lai, J.R. Springstead, H.G. Monbouquette, Effect of growth temperature on ether lipid biochemistry in Archaeoglobus fulgidus. Extremophiles 12, 271–278 (2008)
H. Lammer, J.H. Bredehöft, A. Coustenis, M.L. Khodachenko, L. Kaltenegger, O. Grasset, D. Prieur, F. Raulin, P. Ehrenfreund, M. Yamauchi, J.-E. Wahlund, J.-M. Grießmeier, G. Stangl, C.S. Cockell, Y. Kulikov, J.L. Grenfell, H. Rauer, What makes a planet habitable? Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 17, 181–249 (2009)
N. Lane, W.F. Martin, The origin of membrane energetics. Cell 151, 1406–1416 (2012)
F.M. Lauro, K. Tran, A. Vezzi, N. Vitulo, G. Valle, B.DH. Large-Scale, Transposon mutagenesis of Photobacterium profundum SS9 reveals new genetic loci important for growth at low temperature and high pressure. J. Bacteriol. 190, 1699–1709 (2008)
A.G. Lee, Lipid–protein interactions in biological membranes: a structural perspective. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1612, 1–40 (2003)
A.G. Lee, How lipids affect the activities of integral membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Biomembr. 1666, 62–87 (2004)
K. Lepot, K.H. Williford, P. Philippot, C. Thomazo, T. Ushikubo, K. Kitajima, S. Mostefaoui, J.W. Valley, Extreme 13C-depletions and organic sulfur content argue for S-fueled anaerobic methane oxidation in 2.72 Ga old stromatolites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 244, 522–547 (2019)
S. L’Haridon, A.L. Reysenbach, A. Banta, P. Messner, P. Schumann, E. Stackebrandt, C. Jeanthon, Methanocaldococcus indicus sp. nov., a novel hyperthermophilic methanogen isolated from the Central Indian Ridge. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 53, 1931–1935 (2003)
J. Lim, T. Thomas, R. Cavicchioli, Low temperature regulated DEAD-box RNA helicase from the antarctic archaeon, Methanococcoides burtonii. J. Mol. Biol. 297, 553–567 (2000)
J.F. Lindsay, M.D. Brasier, N. McLoughlin, O.R. Green, M. Fogel, A. Steele, S.A. Mertzman, The problem of deepcarbon—an Archean paradox. Precambrian Res. 143, 1–22 (2005)
Y. Liu, W.B. Whitman, Metabolic, phylogenetic, and ecological diversity of the methanogenic archaea. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1125, 171–189 (2008)
Q. Liu, M. Ren, L.L. Zhang, Natribaculum breve gen. nov., sp. nov. and Natribaculum longum sp. nov., halophilic archaea isolated from saline soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 65(2), 604–608 (2015)
J.E. Lovelock, L. Margulis, Homeostatic tendencies of the Earth’s atmosphere. Orig. Life 5(1), 93–103 (1974)
D.R. Lowe, Abiological origin of described stromatolites older than 3.2 Ga. Geology 22, 387–390 (1994)
D.R. Lowe, G.R. Byerly, Stratigraphy of the west-central part of the Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa, in Geologic Evolution of the Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa, Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap., vol. 329, ed. by D.R. Lowe, G.R. Byerly (1999), pp. 1–36
D.R. Lowe, G.R. Byerly, Geologic record of partial ocean evaporation triggered by giant asteroid impacts, 3.29–3.23 billion years ago. Geology 43, 6 (2015)
D.R. Lowe, G.R. Byerly, F.T. Kyte, Recently discovered 3.42–3.23 Ga impact layers, Barberton Belt, South Africa: 3.8 Ga detrital zircons, Archean impact history, and tectonic implications. Geology 42, 747–750 (2014)
Z. Lü, Y. Lu, Methanocella conradii sp. nov., a thermophilic, obligate hydrogenotrophic methanogen, isolated from Chinese rice field soil. PLoS ONE 7, e35279 (2012)
K. Ma, X. Liu, X. Dong, Methanosaeta harundinacea sp. nov., a novel acetate-scavenging methanogen isolated from a UASB reactor. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 127–131 (2006)
G.M. Maestrojuán, D.R. Boone, L. Xun, R.A. Mah, L. Zhang, Transfer of Methanogenium bourgense, Methanogenium marisnigri, Methanogenium olentangyi, and Methanogenium thermophilicum to the Genus Methanoculleus gen. nov., Emendation of Methanoculleus marisnigri and Methanogenium, and Description of New Strains of Methanoculleus bourgense and Methanoculleus marisnigri. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 40, 117–122 (1990)
C. Magnabosco, L. Lin, H. Dong, M. Bomberg, W. Ghiorse, H. Stan-Lotter, K. Pedersen, T.L. Kieft, E. van Heerden, T.C. Onstott, The biomass and biodiversity of the continental subsurface. Nat. Geosci. 11, 707–717 (2018)
A. Makhdoumi-Kakhki, M.A. Amoozegar, M. Bagheri, M. Ramezani, A. Ventosa, Haloarchaeobius iranensis gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from a saline lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62, 1021–1026 (2012a)
A. Makhdoumi-Kakhki, M.A. Amoozegar, A. Ventosa, Halovenus aranensis gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from Aran-Bidgol salt lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62, 1331–1336 (2012b)
K. Mangelsdorf, K.G. Zink, J.L. Birrien, L. Toffin, A quantitative assessment of pressure dependent adaptive changes in the membrane lipids of piezosensitive deep sub-seafloor bacterium. Org. Geochem. 36, 1459–1479 (2005)
A.G. Marr, J.L. Ingraham, Effect of temperature on the composition of fatty acids in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 84, 1260–1267 (1962)
C.P. Marshall, G.D. Love, C.E. Snape, A.C. Hill, A.C. Allwood, M.R. Walter, M.J. Van Kranendonk, S.A. Bowden, S.P. Sylva, R.E. Summons, Structural characterization of kerogen in 3.4 Ga Archaean cherts from the Pilbara Craton, Western Australia. Precambrian Res. 155, 1–23 (2007)
W. Martin, M.J. Russell, On the origins of cells: a hypothesis for the evolutionary transitions from abiotic geochemistry to chemoautotrophic prokaryotes, and from prokaryotes to nucleated cells. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B, Biol. Sci. 358, 59 (2003)
W. Martin, M.J. Russell, On the origin of biochemistryat an alkaline hydrothermal vent. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B, Biol. Sci. 362, 1887–1926 (2007)
D.D. Martin, D.H. Bartlett, M.F. Roberts, Solute accumulation in the deep-sea bacterium Photobacterium profundum. Extremophiles 6, 507–514 (2002)
W. Martin, J. Baross, D. Kelley, M.J. Russell, Hydrothermal vents and the origin of life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 805–814 (2008)
J.C. Mathai, G.D. Sprott, M.L. Zeidel, Molecular mechanisms of water and solute transport across archaebacterial lipid membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 27266–27271 (2001)
Y. Matsuno, A. Sugai, H. Higashibata et al., Effect of growth temperature and growth phase on the lipid composition of the archaeal membrane from Thermococcus kodakaraensis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 73, 104–108 (2009)
T.J. McGenity, W.D. Grant, Transfer of Halobacterium sacchurovorum, Hulobacterium sodomense, Halobacterium trupanicum NRC34021 and Halobacterium lucusprofundi to the genus Halorubrum gen. nov., as Halorubmm saccharovorurn comb. nov., Halorubrum sodomense comb. nov., Halorubnun trupanicum comb. nov., and Halonibrum lacusprofundi comb. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 18, 237–243 (1995)
T.J. McGenity, R.T. Gemmell, W.D. Grant, Proposal of a new halobacterial genus Natrinema gen. nov., with two species Natrinema pellirubrum nom. nov. and Natrinema pallidum nom. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 48, 1187–1196 (1998)
C.P. McKay, C.C. Porco, T. Altheide, W.L. Davis, T.A. Kral, The possible origin and persistence of life on Enceladus and detection of biomarkers in the plume. Astrobiology 8, 909–919 (2008)
C.P. McKay, B.N. Khare, R. Amin, M. Klasson, T.A. Kral, Possible sources for methane and C2–C5 organics in the plume of Enceladus. Planet. Space Sci. 71, 73–79 (2012)
C.P. McKay, A. Davila, C.R. Glein, K. Hand, A.M. Stockton, Enceladus astrobiology, habitability, and the origin of life, in Enceladus and the Icy Moons of Saturn, ed. by P.M. Schenk, R.N. Clark, C.J.A. Howett, A.J. Verbiscer, J.H. Waite (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 2018), pp. 437–452
M. Mehrshad, M.A. Amoozegar, A. Makhdoumi, M. Rasooli, B. Asadi, P. Schumann, A. Ventosa, Halovarius luteus gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from a Salt Lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 65(8), 2420–2425 (2015)
M. Mehrshad, M.A. Amoozegar, A. Makhdoumi, S.A.S. Fazeli, H. Farahani, B. Asadi, P. Schumann, A. Ventosa, Halosiccatus urmianus gen. nov., sp. nov., a haloarchaeon from a Salt Lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 66(2), 725–730 (2016)
W.W. Metcalf, B.M. Griffin, R.M. Cicchillo, J. Gao, S.C. Janga, H.A. Cooke, B.T. Circello, B.S. Evans, W. Martens-Habbena, D.A. Stahl et al., Synthesis of methylphosphonic acid by marine microbes: a source for methane in the Aerobic ocean. Science 337, 1104–1107 (2012)
S.L. Miller, A production of amino acids under possible primitive Earth conditions. Science 117, 528–529 (1953)
J.F. Miller, N.N. Shah, C.M. Nelson, J.M. Ludlow, D.S. Clark, Pressure and temperature effects on growth and methane production of the extreme thermophile Methanococcus jannaschii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54, 3039–3042 (1988)
H. Minegishi, A. Echigo, S. Nagaoka, M. Kamekura, R. Usami, Halarchaeum acidiphilum gen. nov., sp. nov., a moderately acidophilic haloarchaeon isolated from commercial solar salt. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 60, 2513–2516 (2010)
H. Minegishi, A. Echigo, A. Kuwahara, Y. Shimane, M. Kamekura, T. Itoh, M. Ohkuma, R. Usami, Halocalculus aciditolerans gen. nov., sp. nov., an acid-tolerant haloarchaeon isolated from commercial salt. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 65(5), 1640–1645 (2015)
R. Montalvo-Rodríguez, R.H. Vreeland, A. Oren, M. Kessel, C. Betancourt, J. López-Garriga, Halogeometricum borinquense, gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel halophilic archaeon from Puerto Rico. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 48, 1305–1312 (1998)
K. Mori, D.A. Nurcahyanto, H. Kawasaki, P. Lisdiyanti, K.I. Suzuki, Halobium palmae gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from a solar saltern. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 66(10), 3799–3804 (2016)
D. Morozova, D. Wagner, Stress response of methanogenic archaea from Siberian permafrost compared with methanogens from nonpermafrost habitats. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 61, 16–25 (2007)
Y.Z. Mou, X.X. Qiu, M.L. Zhao, H.L. Cui, D. Oh, M.L. Dyall-Smith, Halohasta litorea gen. nov. sp. nov., and Halohasta litchfieldiae sp. nov., isolated from the Daliang aquaculture farm, China and from Deep Lake, Antarctica, respectively. Extremophiles 16, 895–901 (2012)
M.J. Mumma, G.L. Villanueva, R.E. Novak, T. Hewagama, B.P. Bonev, M.A. DiSanti, A.M. Mandell, M.D. Smith, Strong release of methane on Mars in northern summer 2003. Science 323, 1041–1045 (2009)
K. Nakamura, A. Takahashi, C. Mori, H. Tamaki, H. Mochimaru, K. Nakamura, K. Takamizawa, Y. Kamagata, Methanothermobactertenebrarum sp. nov., a hydrogenotrophic, thermophilic methanogen isolated from gas-associated formation water of a natural gas field. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 63, 715–722 (2013)
C. Neves, M.S. da Costa, H. Santos, Compatible solutes of the hyperthermophile Palaeococcus ferrophilus: osmoadaptation and thermoadaptation in the order thermococcales. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 8091–8098 (2005)
D.S. Nichols, M.R. Miller, N.W. Davies, A. Goodchild, M. Raftery, R. Cavicchioli, Cold adaptation in the Antarctic Archaeon Methanococcoides burtonii involves membrane lipid unsaturation. J. Bacteriol. 186, 8508–8515 (2004)
P. Nielsen, D. Fritze, F.G. Priest, Phenetic diversity of alkaliphilic Bacillus strains: proposal for nine new species. Microbiology 141, 1745–1761 (1995)
H.B. Niemann, S.K. Atreya, S.J. Bauer, G.R. Carignan, J.E. Demick, R.L. Frost, D. Gautier, J.A. Haberman, D.N. Harpold, D.M. Hunten et al., The abundances of constituents of Titan’s atmosphere from the GCMS instrument on the Huygens probe. Nature 438, 779–784 (2005)
E. Nisbet, C. Fowler, Some liked it hot. Nature 382, 404–405 (1996)
E.G. Nisbet, C.M.R. Fowler, Archaean metabolic evolution of microbial mats. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B, Biol. Sci. 266, 2375–2382 (1999)
N. Nishimura, S. Kitaura, A. Mimura, Y. Takahara, Cultivation of thermophilic methanogen KN-15 on H2-CO2 under pressurized conditions. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 73, 477–480 (1992)
A.P. Nutman, V.C. Bennett, C.R.L. Friend, M.J. Van Kranendonk, A.R. Chivas, Rapid emergence of life shown by discovery of 3,700-million-year-old microbial structures. Nature 537, 535–538 (2016)
D.Z. Oehler, M.M. Walsh, K. Sugitani, M.-C. Liu, C.H. House, Large and robust lenticular microorganisms on the young Earth. Precambrian Res. 296, 112–119 (2017)
P.M. Oger, A. Cario, Adaptation of the membrane in Archaea. Biophys. Chem. 183, 42–56 (2013)
P. Oger, M. Jebbar, The many ways of coping with pressure. Res. Microbiol. 161, 799–809 (2010)
B. Ollivier, P. Caumette, J.-L. Garcia, R.A. Mah, Anaerobic bacteria from hypersaline environments. Microbiol. Rev. 58, 27–38 (1994)
A.I. Oparin, Proiskhozhdenic Zhizny (Izd. Moskovski Rabochii, Moscow, 1924)
A. Oren, Bioenergetic aspects of halophilism. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 63, 334–348 (1999)
A. Oren, Diversity of halophilic microorganisms: environments, phylogeny, physiology, and applications. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotech. 28, 56–63 (2002a)
A. Oren, Molecular ecology of extremely halophilic archaea and bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 39, 1–7 (2002b)
A. Oren, Convergent evolution in extremely halophilic prokaryotes: a comparison between Salinibacter ruber (Bacteria) and the Halobacteriaceae (Archaea), in Evolutionary Theory and Processes: Modern Horizons. Papers in Honour of Eviatar Nevo, ed. by S.P. Wasser (Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 2004), pp. 53–64
A. Oren, The family methanosarcinaceae, in The Prokaryotes, ed. by E. Rosenberg, E.F. DeLong, S. Lory, E. Stackebrandt, F. Thompson (Springer, Berlin, 2014)
A. Oren, P. Gurevich, R.T. Gemmell, A. Teske, Halobaculum gomorrense gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel extremelyhalophilic archaeon from the Dead Sea. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 45, 747–754 (1995)
A. Oren, The order Halobacteriales, in The Prokaryotes: Anevolving Electronic Resource for the Microbiological Community [Online], ed. by M. Dworkin et al. 3rd edn. (Springer, New York, 2000)
A. Oren, R. Elevi, S. Watanabe, K. Ihara, A. Corcelli, Halomicrobium mukohataei gen. nov., comb. nov., and emended description of Halomicrobium mukohataei. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52, 1831–1835 (2002)
P. Pappenreiter, S. Zwirtmayr, L.-M. Mauerhofer, S.K.-M.R. Rittmann, C. Paulik, Development of a simultaneous bioreactor system for characterization of gas production kinetics of methanogenic archaea at high pressure. Eng. Life Sci. 19, 537–544 (2019)
C.B. Park, D.S. Clark, Rupture of the cell envelope by decompression of the deep-sea methanogen Methanococcus jannaschii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 1458–1463 (2002)
S.N. Parshina, A.V. Ermakova, M. Bomberg, E.N. Detkova, Methanospirillum stamsii sp. nov., a psychrotolerant, hydrogenotrophic, methanogenic archaeon isolated from an anaerobic expanded granular sludge bed bioreactor operated at low temperature. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 64, 180–186 (2014)
I. Parsons, M.R. Lee, J.V. Smith, Biochemical evolution II: origin of life in tubular microstructures on weathered feldspar surfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 15173–15176 (1998)
B.K.D. Pearce, A.S. Tupper, R.E. Pudritz, P.G. Higgs, Constraining the time interval for the origin of life on Earth. Astrobiology 18(3), 343–364 (2018)
B. Poolman, E. Glaasker, Regulation of compatible solute accumulation in bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 29, 397–407 (1998)
L.M. Proctor, R. Lai, R.P. Gunsalus, The methanogenic archaeon Methanosarcina thermophila TM-1 possesses a high-affinity glycine betaine transporter involved in osmotic adaptation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63, 2252–2257 (1997)
C. Quast, E. Pruesse, P. Yilmaz, J. Gerken, T. Schweer, P. Yarza, J. Peplies, F.O. Glöckner, The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, 590–596 (2013)
F.A. Rainey, T.N. Zhilina, E.S. Boulygina, E. Stackebrandt, T.P. Tourova, G.A. Zavarzin, The taxonomic status of the fermentative halophilic anaerobic bacteria: description of Haloanaerobiales ord. nov., Halobacteroidaceae fam. nov., Orenia gen. nov. and further taxonomic rearrangements at the genus and species level. Anaerobe 1, 185–199 (1995)
S. Rea, J.P. Bowman, S. Popovski, C. Pimm, A.D.G. Wright, Methanobrevibacter millerae sp. nov. and Methanobrevibacter olleyae sp. nov., methanogens from the ovine and bovine rumen that can utilize formate for growth. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 450–456 (2007)
F. Reith, Life in the deep subsurface. Geology 39, 287–288 (2011)
S. Rittmann, A. Seifert, C. Herwig, Essential prerequisites for successful bioprocess development of biological CH4 production from CO2 and H2. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 35, 141–151 (2015)
D.E. Robertson, D. Noll, M.F. Roberts, J.A. Menaia, D.R. Boone, Detection of the osmoregulator betaine in methanogens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56, 563–565 (1990)
F. Rodríguez-Valera, Characteristics and microbial ecology of hyper-saline environments, in Halophilicbacteria, vol. 1, ed. by F. Rodriguez-Valera (CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, 1988), pp. 3–30
M. Roeßler, K. Pflüger, H. Flach, T. Lienard, G. Gottschalk, V. Müller, Identification of a salt-induced primary transporter for glycine betaine in the methanogen Methanosarcina mazei Gö1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 2133–2139 (2002)
L.A. Romanenko, N. Tanaka, G.M. Frolova, V.V. Mikhailov, Psychrobacter fulvigenes sp. nov., isolated from a marine crustacean from the Sea of Japan. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 59(Pt 6), 1480-6 (2009)
J.A. Romesser, R.S. Wolfe, F. Mayer, E. Spiess, A. Walther-Mauruschat, Methanogenium, a new genus of marine methanogenic bacteria, and characterization of Methanogenium cariaci sp. nov. and Methanogenium marisnigri sp. nov. Arch. Microbiol. 121, 147–153 (1979)
M.T. Rosing, C-13-depleted carbon microparticles in >3700-Ma sea-floor sedimentary rocks from west Greenland. Science 283, 674–676 (1999)
J. Rouillard, J.M. García-Ruiz, J. Gong, M.A.A. van Zuilen, Morphogram for silica–witherite biomorphs and its application to microfossil identification in the early Earth rock record. Geobiology 16, 279–296 (2018)
A. Rudolph, J. Crowe, Membrane stabilization during freezing: the role of two natural cryoprotectants, trehalose and proline. Cryobiology 22, 367–377 (1985)
N.J. Russell, D.S. Nichols, Polyunsaturated fatty acids in marine bacteria–a dogma rewritten. Microbiology 145(Pt 4), 767–779 (1999)
M.J. Russell, A.J. Hall, W. Martin, Serpentinization as a source of energy at the origin of life. Geobiology 8, 355–371 (2010)
H. Santos, M.S. da Costa, Compatible solutes of organisms that live in hot saline environments. Environ. Microbiol. 4, 501–509 (2002)
N.F.W. Saunders, T. Thomas, P.M.G. Curmi, J.S. Mattick, E. Kuczek, R. Slade, J. Davis, P.D. Franzmann, D. Boone, K. Rusterholtz et al., Mechanisms of thermal adaptation revealed from the genomes of the Antarctic archaea methanogenium frigidum and Methanococcoides burtonii. Genome Res. 13, 1580–1588 (2003)
K.N. Savage, L.R. Krumholz, A. Oren, M.S. Elshahed, Haladaptatus paucihalophilus gen. nov., sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from a low-salt, sulfide-rich spring. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 19–24 (2007)
M. Schidlowski, A 3,800-million-year isotopic record of life from carbon in sedimentary rocks. Nature 333, 313–318 (1988)
J. Schirmack, K. Mangelsdorf, L. Ganzert, W. Sand, A. Hillebrand-Voiculescu, D. Wagner, Methanobacterium movilense sp. nov., a hydrogenotrophic, secondary-alcohol-utilizing methanogen from the anoxic sediment of a subsurface lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 64, 522–527 (2014)
C. Schleper, G. Puehler, I. Holz, A. Gambacorta, D. Janekovic, U. Santarius, H.P. Klenk, W. Zillig, Picrophilus gen. nov., fam. nov.: a novel aerobic, heterotrophic, thermoacidophilic genus and family comprising archaea capable of growth around pH 0. J. Bacteriol. 177(24), 7050–7059 (1995)
G. Schoop, Obligat halophile Mikroben. Zentr Bakteriol Parasitenk Orig, Abt I. (1935), pp. 14–23
J.W. Schopf, Paleobiology of the Archean, in The Proterozoic Biosphere, ed. by J.W. Schopf, C. Klein (Cambridge University Press, New York, 1992), pp. 25–39
J.W. Schopf, B.M. Packer, Early Archean (3.3-billion to 3.5-billion-year-old) microfossils from Warrawoona Group, Australia. Science 237, 70–73 (1987)
J.W. Schopf, A.B. Kudryavtsev, J.T. Osterhout, K.H. Williford, K. Kitajima, J.W. Valley, K. Sugitani, An anaerobic ∼3400 Ma shallow-water microbial consortium: presumptive evidence of Earth’s Paleoarchean anoxic atmosphere. Precambrian Res. 299, 309–318 (2017)
A.H. Seifert, S. Rittmann, S. Bernacchi, C. Herwig, Method for assessing the impact of emission gasses on physiology and productivity in biological methanogenesis. Bioresour. Technol. 136, 747–751 (2013)
A.H. Seifert, S. Rittmann, C. Herwig, Analysis of process related factors to increase volumetric productivity and quality of biomethane with Methanothermobacter marburgensis. Appl. Energy 132, 155–162 (2014)
H. Shimada, N. Nemoto, Y. Shida et al., Effects of pH and temperature on the composition of polar lipids in Thermoplasma acidophilum HO-62. J. Bacteriol. 190, 5404–5411 (2008)
Y. Shimane, Y. Hatada, H. Minegishi, T. Mizuki, A. Echigo, M. Miyazaki, Y. Ohta, R. Usami, W.D. Grant, K. Horikoshi, Natronoarchaeum mannanilyticum gen. nov., sp. nov., an aerobic, extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from commercial salt. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 60, 2529–2534 (2010)
Y. Shimane, Y. Hatada, H. Minegishi, A. Echigo, S. Nagaoka, M. Miyazaki, Y. Ohta, T. Maruyama, R. Usami, W.D. Grant, K. Horikoshi, Salarchaeum japonicum gen. nov., sp. nov., an aerobic, extremely halophilic member of the Archaea isolated from commercial salt. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 61, 2266–2270 (2011)
K.S. Siddiqui, R. Cavicchioli, Cold-adapted enzymes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 75, 403–433 (2006)
K. Siddiqui, R. Cavicchioli, T. Thomas, Thermodynamic activation properties of elongation factor 2 (EF-2) proteins from psychrotolerant and thermophilic Archaea. Extremophiles 6, 143–150 (2002)
M.V. Simankova, S.N. Parshina, T.P. Tourova, T.V. Kolganova, A.J. Zehnder, A.N. Nozhevnikova, Methanosarcina lacustris sp. nov., a new psychrotolerant methanogenic archaeon from anoxic lake sediments. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 24, 362–367 (2001)
M. Sinensky, Temperature control of phospholipid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 106, 449–455 (1971)
M. Sinensky, Homeoviscous adaptation—homerostatic process that regulates viscosity of membrane lipids in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 71, 522–525 (1974)
M.A. Singer, S. Lindquist, Multiple effects of trehalose on protein folding in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cell 1, 639–648 (1998)
N. Singh, M.M. Kendall, Y. Liu, D.R. Boone, Isolation and characterization of methylotrophic methanogens from anoxic marine sediments in Skan Bay, Alaska: description of Methanococcoides alaskense sp. nov., and emended description of Methanosarcina baltica. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55, 2531–2538 (2005)
V.B.D. Skerman, V. McGowan, P.H.A. Sneath, W.E.C. Moore, L.V. Moore, Approved lists. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 30, 225–420 (1980)
N.H. Sleep, Geological and geochemical constraints on the origin and evolution of life. Astrobiology 18, 1199–1219 (2018)
H.S. Song, I.T. Cha, K.J. Yim, H.W. Lee, D.W. Hyun, S.J. Lee, S.K. Rhee, K.N. Kim, D. Kim, J.S. Choi, M.J. Seo, H.J. Choi, J.W. Bae, J.K. Rhee, Y.D. Nam, S.W. Roh, Halapricum salinum gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from non-purified solar salt. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 105, 979–986 (2014)
H.S. Song, I.T. Cha, J.K. Rhee, K.J. Yim, A.Y. Kim, J.S. Choi, S.J. Baek, M.J. Seo, S.J. Park, Y.D. Nam, S.W. Roh, Halostella salina gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from solar salt. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 66(7), 2740–2746 (2016)
D.Y. Sorokin, B. Abbas, A.Y. Merkel, W.I. Rijpstra, J.S. Damsté, M.V. Sukhacheva, M.C. van Loosdrecht, Methanosalsum natronophilum sp. nov., and Methanocalculus alkaliphilus sp. nov., haloalkaliphilic methanogens from hypersaline soda lakes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 65(10), 3739–3745 (2015)
D.Y. Sorokin, I.V. Kublanov, M.M. Yakimov, W.I.C. Rijpstra, J.S.S. Damsté, Halanaeroarchaeum sulfurireducens gen. nov., sp. nov., the first obligately anaerobic sulfur-respiring haloarchaeon, isolated from a hypersaline lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 66(6), 2377–2381 (2016)
D.Y. Sorokin, E. Messina, F. Smedile, P. Roman, J.S.S. Damsté, S. Ciordia, M.C. Mena, M. Ferrer, P.N. Golyshin, I.V. Kublanov, N.I. Samarov, Discovery of anaerobic lithoheterotrophic haloarchaea, ubiquitous in hypersaline habitats. ISME J. 11(5), 1245 (2017)
D.Y. Sorokin, T.V. Khijniak, N.A. Kostrikina, A.G. Elcheninov, S.V. Toshchakov, N.J. Bale, J.S.S. Damsté, I.V. Kublanov, Natronobiforma cellulositropha gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel haloalkaliphilic member of the family Natrialbaceae (class Halobacteria) from hypersaline alkaline lakes. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 41(4), 355–362 (2018a)
D.Y. Sorokin, A.Y. Merkel, B. Abbas, K.S. Makarova, W.I.C. Rijpstra, M. Koenen, J.S. Sinninghe Damsté, E.A. Galinski, E.V. Koonin, M.C.M. van Loosdrecht, Methanonatronarchaeum thermophilum gen. nov., sp. nov. and ‘Candidatus Methanohalarchaeum thermophilum’, extremely halo(natrono)philic methyl-reducing methanogens from hypersaline lakes comprising a new euryarchaeal class Methanonatronarchaeia classis nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 68(7), 2199–2208 (2018b)
D.Y. Sorokin, T.V. Khijniak, A.G. Elcheninov, S.V. Toshchakov, N.A. Kostrikina, N.J. Bale, J.S.S. Damsté, I.V. Kublanov, Halococcoides cellulosivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic cellulose-utilizing haloarchaeon from hypersaline lakes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 69(5), 1327–1335 (2019a)
D.Y. Sorokin, M.M. Yakimov, E. Messina, A.Y. Merkel, N.J. Bale, J.S.S. Damsté, Natronolimnobius sulfurireducens sp. nov. and Halalkaliarchaeum desulfuricum gen. nov., sp. nov., the first sulfur-respiring alkaliphilic haloarchaea from hypersaline alkaline lakes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 69(9), 2662–2673 (2019b)
K.R. Sowers, J.E. Boone, R.P. Gunsalus, Disaggregation of Methanosarcina spp. and growth as single cells at elevated osmolarity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59, 3832–3839 (1993)
G.D. Sprott, M. Meloche, J.C. Richards, Proportions of diether, macrocyclic diether, and tetraether lipids in Methanococcus jannaschii grown at different temperatures. J. Bacteriol. 173, 3907–3910 (1991)
L.C. Stewart, M. Kates, I.H. Ekiel, I.CP. Smith, Molecular order and dynamics of diphytanylglycerol phospholipids—a 2H NMR and 31P NMR study. Chem. Phys. Lipids 54, 115–129 (1990)
K. Sugitani, Early Archaean (pre-3.0 Ga) cellularly preserved microfossils and microfossil-like structures frm the Pilbara craton, Western Australia–a review, in Earth’s Oldest Rocks, ed. by M.J. Van Kranendonk, V.C. Bennett, J.E. Hofmann 2nd edn. (2018), pp. 1007–1028
K. Sugitani, K. Grey, A. Allwood, T. Nagaoka, K. Mimura, M. Minami, C.P. Marshall, M.J. Van Kranendonk, M.R. Walter, Diverse microstructures from Archaean chert from the mount goldsworthy-mount grant area, pilbara craton, western Australia: microfossils, dubiofossils, or pseudofossils? Precambrian Res. 158, 228–262 (2007)
K. Sugitani, K. Mimura, M. Takeuchi, T. Yamaguchi, K. Suzuki, R. Senda, Y. Asahara, S. Wallis, M.J. Van Kranendonk, A Paleoarchean coastal hydrothermal field inhabited by diverse microbial communities: the Strelley Pool Formation, Pilbara Craton Western Australia. Geobiology 13, 522–545 (2015)
W. Sunda, D.J. Kieber, R.P. Kiene, S. Huntsman, An antioxidant function for DMSP in marine algae. Nature 418, 317–320 (2002)
K. Takai, A. Inoue, K. Horikoshi, Methanothermococcus okinawensis sp. nov., a thermophilic, methane-producing archaeon isolated from a Western Pacific deep-sea hydrothermal vent system. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52, 1089–1095 (2002)
K. Takai, K. Nakamura, T. Toki, U. Tsunogai, M. Miyazaki, J. Miyazaki, H. Hirayama, S. Nakagawa, T. Nunoura, K. Horikoshi, Cell proliferation at 122 degrees C and isotopically heavy CH4 production by a hyperthermophilic methanogen under high-pressure cultivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 10949–10954 (2008)
H. Tamegai, L. Li, N. Masui, C. Kato, A denitrifying bacterium from the deep sea at 11,000-m depth. Extremophiles 1997(1), 207–211 (1997)
T. Tashiro, A. Ishida, M. Hori, M. Igisu, M. Koike, P. Méjean, N. Takahata, Y. Sano, T. Komiya, Early trace of life from 3.95 Ga sedimentary rocks in Labrador, Canada. Nature 549, 516–518 (2017)
R.S. Taubner, S.K.M.R. Rittmann, Method for indirect quantification of CH4 production via H2O production using hydrogenotrophic methanogens. Front. Microbiol. 7, 532 (2016a)
R.-S. Taubner, J. Leitner, M. Firneis, R. Hitzenberger, Modelling the interior structure of Enceladus based on the 2014’s Cassini gravity data. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 46, 283–288 (2016b)
R.-S. Taubner, P. Pappenreiter, J. Zwicker, D. Smrzka, C. Pruckner, P. Kolar, S. Bernacchi, A.H. Seifert, A. Krajete, W. Bach, J. Peckmann, C. Paulik, M.G. Firneis, C. Schleper, S.K.-M.R. Rittmann, Biological methane production under putative Enceladus-like conditions. Nat. Commun. 9, 748 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-02876-y
R.-S. Taubner, L.M.F. Baumann, T. Bauersachs, E.L. Clifford, B. Mähnert, B. Reischl, R. Seifert, J. Peckmann, S.K.-M.R. Rittmann, D. Birgel, Membrane lipid composition and amino acid excretion patterns of Methanothermococcus okinawensis grown in the presence of inhibitors detected in the Enceladian plume. Life 9, 85 (2019)
R.K. Thauer, A.K. Kaster, H. Seedorf, W. Buckel, R. Hedderich, Methanogenic archaea: ecologically relevant differences in energy conservation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 579–591 (2008)
T. Thomas, R. Cavicchioli, Effect of temperature on stability and activity of elongation factor 2 proteins from Antarctic and thermophilic methanogens. J. Bacteriol. 182, 1328–1332 (2000)
T. Thomas, N. Kumar, R. Cavicchioli, Effects of ribosomes and intracellular solutes on activities and stabilities of elongation factor 2 proteins from psychrotolerant and thermophilic methanogens. J. Bacteriol. 183, 1974–1982 (2001)
M.M. Tice, Environmental controls on photosynthetic microbial mat distribution and 728 morphogenesis on a 3.42 Ga clastic-starved platform. Astrobiology 9, 989–1000 (2009)
M.M. Tice, D.R. Lowe, Photosynthesis microbial mats in the 3.416-Myr-old ocean. Nature 431, 549–552 (2004)
B.J. Tindall, H.N.M. Ross, W.D. Grant, Natronobacterium gen. nov., and Natronococcus gen. nov., two new genera of haloalkaliphilic archaebacteria. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 5, 41–57 (1984)
M. Torreblanca, F. Rodriguez-Valera, G. Juez, A. Ventosa, M. Kamekura, M. Kates, Classification of non-alkaliphilic halobacteria based onnumerical taxonomy and polar lipid composition, and description of Halo-arculagen nov. and Haloferaxgen. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 8, 89–99 (1986)
E.J. Trower, D.R. Lowe, Sedimentology of the ∼3.3 Ga upper Mendon Formation, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Precambrian Res. 281, 473–494 (2016)
H.G. Trüper, E.A. Galinski, Concentrated brines as habitats for microorganisms. Experientia 42, 1182–1187 (1986)
I. Uda, A. Sugai, Y.H. Itoh, T. Itoh, Variation in molecular species of polar lipids from Thermoplasma acidophilum depends on growth temperature. Lipids 36, 103–105 (2001)
Y. Uda, A. Sugai, Y.H. Itoh, T. Itoh, Variation in molecular species of core lipids from the order Thermoplasmales strains depends on the growth temperature. J. Oleo Sci. 53, 399–404 (2004)
Y. Ueno, S. Maruyama, Y. Isozaki, H. Yurimoto, Early Archean (ca. 3.5 Ga) microfossils and 13C-depleted carbonaceous matter in the North Pole area, Western Australia: field occurrence and geochemistry, in Geochemistry and the Origin of Life, ed. by S. Nakashima, S. Maruyama, A. Brack, B.F. Windley (Universal Academy Press Inc., Tokyo, 2001), pp. 201–236
Y. Ueno, K. Yamada, N. Yoshida, S. Maruyama, Y. Isozak, Evidence from fluid inclusions for microbial methanogenesis in the early Archaean era. Nature 440, 516–519 (2006)
H.C. Urey, The origin and development of the Earth and other terrestrial planets. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1, 209–277 (1951)
M.J. Van Kranendonk, A.H. Hickman, R.H. Smithies, I.R. Williams, L. Bagas, T.R. Farrell, Revised Lithostratigraphy of Archaean Supracrustal and Intrusive Rocks in the Northern Pilbara Craton, Western Australia Geol. Surv. West. Austral. Rec., vol. 15 (2006), pp. 1–55
M.J. Van Kranendonk, R.H. Smithies, A.H. Hickman, D.C. Champion, Paleoarchean development of a continental nucleus: the East Pilbara Terrane of the Pilbara Craton, Western Australia, in Earth’s Oldest Rocks (2007), pp. 307–337
M.J. Van Kranendonk, D. Deamer, T. Djokic, Life springs. Sci. Am. 317, 28–35 (2017)
M.A. van Zuilen, Proposed early signs of life not set in stone. Nature 563, 190–191 (2018)
M.A. van Zuilen, M. Chaussidon, C. Rollion-Bard, B. Marty, Carbonaceous cherts of the Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa: isotopic, chemical and structural characteristics of individual microstructures. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 71, 655–669 (2007)
P. Vannier, G. Michoud, P. Oger, V.T. Marteinsson, M. Jebbar, Genome expression of Thermococcus barophilus and Thermococcus kodakarensis in response to different hydrostatic pressure conditions. Res. Microbiol. 166(9), 717–725 (2015)
A. Ventosa, J.J. Nieto, Biotechnological applications and potentialities of halophilic microorganisms. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 11, 85–94 (1995)
A. Ventosa, A. Oren, Halobacterium salinarum nom. corrig., a name to replace Halobacterium salinarium (Elazari-Volcani) and to include Halobacterium halobium and Halobacterium cutirubrum. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 46, 347 (1996)
A. Ventosa, J.J. Nieto, A. Oren, Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 62, 504–544 (1998)
A. Ventosa, M.C. Gutiérrez, M. Kamekura, M.L. Dyall-Smith, Proposal to transfer Halococcus turkmenicus, Halobacterium trapanicum JCM 9743 and strain GSL-11 to Haloterrigena turkmenica gen. nov., comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49, 131–136 (1999)
A. Ventosa, M.C. Márquez, C. Sánchez-Porro, R. Rafael, Taxonomy of halophilic archaea and bacteria, in Advances in Understanding the Biology of Halophilic Microorganisms (Springer, Dordrecht, 2012), pp. 59–80
H.C. Ver Eecke, D.A. Butterfield, J.A. Huber, M.D. Lilley, E.J. Olson, K.K. Roe, L.J. Evans, A.Y. Merkel, H.V. Cantin, J.F. Holden, Hydrogen-limited growth of hyperthermophilic methanogens at deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 13674–13679 (2012)
H.C. Ver Eecke, N.H. Akerman, J.A. Huber, D.A. Butterfield, J.F. Holden, Growth kinetics and energetics of a deep-sea hyperthermophilic methanogen under varying environmental conditions. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 5, 665–671 (2013)
A. Vezzi, S. Campanaro, M. D’Angelo, F. Simonato, N. Vitulo, F.M. Lauro, A. Cestaro, G. Malacrida, B. Simionati, N. Cannata, C. Romualdi, D.H. Bartlett, G. Valle, Life at depth: photobacterium profundum genome sequence and expression analysis. Science 307, 1459–1461 (2005)
A. Vieth, H. Wilkes, Stable isotopes in understanding origin and degradation processes of petroleum, in Handbook of Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology, ed. by K. Timmis (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2010), pp. 97–111
D.V. von Klein, H. Arab, H. Völker, M. Thomm, Methanosarcina baltica, sp. nov., a novel methanogen isolated from the Gotland Deep of the Baltic Sea. Extremophiles 6, 103–110 (2002)
R.H. Vreeland, Mechanisms of halotolerance in microorganisms. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 14, 311–356 (1987)
R.H. Vreeland, S. Straight, J. Krammes, K. Dougherty, W.D. Rosenzweig, M. Kamekura, Halosimplex carlsbadense gen. nov., sp. nov., a unique halophilic archaeon, with three 16S rRNA genes, that grows only indefined medium with glycerol and acetate or pyruvate. Extremophiles 6, 445–452 (2002)
D. Wacey, Early life on Earth, a practical guide, in Topics in Geobiology, vol. 31, ed. by N.H. Landman, P.J. Harries (Springer, Heidelberg, 2009)
D. Wacey, M. Saunders, C. Kong, A. Brasier, M. Brasier, 3.46 Ga Apex chert ‘microfossils’ reinterpreted as mineral artefacts produced during phyllosilicate exfoliation. Gondwana Res. 36, 296–313 (2016)
D. Wacey, N. Noffke, M. Saunders, P. Guagliardo, D.M. Pyle, Volcanogenic pseudo-fossils from the ∼3.48 Ga dresser formation, Pilbara, Western Australia. Astrobiology 18(5), 539–555 (2018)
G. Wächtershäuser, Before enzymes and templates: theory of surface metabolism. Microbiol. Rev. 52(4), 452–484 (1988)
D. Wagner, J. Schirmack, L. Ganzert, D. Morozova, K. Mangelsdorf, Methanosarcina soligelidi sp. nov., a desiccation- and freeze-thaw-resistant methanogenic archaeon from a Siberian permafrost-affected soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 63, 2986–2991 (2013)
M. Wainø, B.J. Tindall, K. Ingvorsen, Halorhabdus utahensis en. nov., sp. nov., an aerobic, extremely halophilic member of the Archaea from Great Salt Lake, Utah. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50, 183–190 (2000)
J.H. Waite Jr., W.S. Lewis, B.A. Magee, J.I. Lunine, W.B. McKinnon, C.R. Glein, O. Mousis, D.T. Young, T. Brockwell, J. Westlake et al., Liquid water on Enceladus from observations of ammonia and 40Ar in the plume. Nature 460, 487–490 (2009)
J.H. Waite, T. Brockwell, W.S. Lewis, B. Magee, W.B. McKinnon, O. Mousis, A. Bouquet, Enceladus plume composition. LPI Contrib. 1774, 4013 (2014)
J.H. Waite, C.R. Glein, R.S. Perryman, B.D. Teolis, B.A. Magee, G. Miller, J. Grimes, M.E. Perry, K.E. Miller, A. Bouquet, J.I. Lunine, T. Brockwell, S.J. Bolton, Cassini finds molecular hydrogen in the Enceladus plume: evidence for hydrothermal processes. Science 356, 155–159 (2017)
A.E. Walsby, A square bacterium. Nature (London) 283, 69–71 (1980)
M.M. Walsh, Microfossils and possible microfossils from the Early Archean Onverwacht Group, Barberton mountain land, South Africa. Precambrian Res. 54, 271–293 (1992)
M.M. Walsh, D.R. Lowe, Modes of accumulation of carbonaceous matter in the early Archaean: a petrographic and geochemical study of the carbonaceous cherts of the Swaziland Supergroup, in Geologic Evolution of the Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa, ed. by D.R. Lowe, G.R. Byerly. Geological Society of America Special Paper, vol. 329, Boulder, CO (1999), pp. 115–132
M.R. Walter, R. Buick, J.S.R. Dunlop, Stromatolites 3400–3500 Myr old from the North Pole area, Western Australia. Nature 284, 443–445 (1980)
C.R. Webster, P.R. Mahaffy, S.K. Atreya, G.J. Flesch, M.A. Mischna, P.Y. Meslin, K.A. Farley, P.G. Conrad, L.E. Christensen, A.A. Pavlov et al., Mars methane detection and variability at Gale crater. Science 347, 415–417 (2015)
F. Westall, R.L. Folk, Exogenous carbonaceous microstuctures in Early Archaean cherts and BIFs from the Isua Greenstone Belt: implications for the search for life in ancient rocks. Precambrian Res. 126, 313–330 (2003)
F. Westall, M.J. de Wit, J. Dann, S. van der Gaast, C.E.J. de Ronde, D. Gerneke, Early Archean fossil bacteria and biofilms in hydrothermally-influenced sediments from the Barberton greenstone belt, South Africa. Precambrian Res. 106, 93–116 (2001)
F. Westall, S.T. de Vries, J.N. Nijman, D. Marchesini, A. Severine, The 3.446 Ga “Kittys Gap Chert”, an early Archean microbial ecosystem, in Processes on the Early, ed. by W.U. Reimold, R.L. Gibson. Earth. Geol. Soc. Amer. Spec. Pap., vol. 405 (2006), pp. 105–131
F. Westall, B. Cavalazzi, L. Lemelle, Y. Marrocchi, J.N. Rouzaud, A. Simionovici, M. Salomé, S. Mostefaoui, C. Andreazza, F. Foucher, J. Toporski, A. Jauss, V. Thiel, G. Southam, L. MacLean, S. Wirick, A. Hofmann, A. Meibom, F. Robert, C. Défarge, Implications of in situ calcification for photosynthesis in a ∼3.3 Ga-old microbial biofilm from the Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 310, 468–479 (2011)
F. Westall, K. Hickman-Lewis, N. Hinman, P. Gautret, K.A. Campbell, J.G. Bréhéret, F. Foucher, A. Hubert, S. Sorieul, A.V. Dass, T.P. Kee, T. Georgelin, A. Brack, A hydrothermal-sedimentary context for the origin of life. Astrobiology 18, 259–293 (2018)
M.J. Whitehouse, D.J. Dunkley, M.A. Kusiak, S.A. Wilde, On the true antiquity of Eoarchean chemofossils—assessing the claim for Earth’s oldest biogenic graphite in the Saglek Block of Labrador. Precambrian Res. 323, 70–81 (2019)
W.B. Whitman, D.C. Coleman, W.J. Wiebe, Prokaryotes: the unseen majority. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6578–6583 (1998)
R.J.P. Williams, J.J.R. Fraústo Da Silva, Evolution was chemically constrained. J. Theor. Biol. 220, 323–343 (2003)
R. Winter, Effect of lipid chain length, temperature, pressure and composition on the lateral organisation and phase behavior of lipid bilayer/gramicidin mixtures. Biophys. J. 82, 153A–153A (2002)
R. Winter, C. Jeworrek, Effect of pressure on membranes. Soft Matter 5, 3157–3173 (2009)
C.R.A. Woese, Proposal concerning the origin of life on the planet Earth. J. Mol. Evol. 13, 95–101 (1979)
J.M. Wolfe, G.P. Fournier, Horizontal gene transfer constrains the timing of methanogen evolution. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2, 897–903 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-018-0513-7
J.M. Wood, E. Bremer, L.N. Csonka, R. Krämer, B. Poolman, T. van der Heide, L.T. Smith, Osmosensing and osmoregulatory compatible solute accumulation by bacteria. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., Part A 130, 437–460 (2001)
Y. Xu, P. Zhou, X. Tian, Characterization of two novel haloalkaliphilic archaea Natronorubrum bangense gen. nov., sp.nov., and Natronorubrum tibetense gen. nov., sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49, 261–266 (1999)
Y. Xue, H. Fan, A. Ventosa, W.D. Grant, B.E. Jones, D.A. Cowan, Y. Ma, Halalkalicoccus tibetensis gen. nov., sp. nov., representing a novel genus of haloalkaliphilic archaea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55, 2501–2505 (2005)
K. Yamauchi, K. Doi, Y. Yoshida, M. Kinoshita, Archaebacterial lipids: highly proton-impermeable membranes from 1, 2-diphytanyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1146, 178–182 (1993)
P.H. Yancey, Organic osmolytes as compatible, metabolic and counteracting cytoprotectants in high osmolarity and other stresses. J. Exp. Biol. 208, 2819–2830 (2005)
Y. Yano, A. Nakayama, K. Ishihara, H. Saito, Adaptive changes in membrane lipids of barophilic bacteria in response to changes in growth pressure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 479–485 (1998)
A.A. Yayanos, A.S. Dietz, R. Van Boxtel, Obligately barophilic bacterium from the Mariana trench. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78(8), 5212–5215 (1981)
X.Q. Yin, B.B. Liu, X. Chu, N. Salam, X. Li, Z.W. Yang, Y. Zhang, M. Xiao, W.J. Li, Saliphagus infecundisoli gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from a saline soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 67(10), 4154–4160 (2017)
J. Zajc, P. Zalar, N. Gunde-Cimerman, Yeasts in hypersaline habitats, in Yeasts in Natural Ecosystems: Diversity (Springer, Cham, 2017), pp. 293–329
N.E.B. Zellner, Cataclysm no more: new views on the timing and delivery of lunar impactors. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 47, 261–280 (2017)
G. Zhang, N. Jiang, X. Liu, X. Dong, Methanogenesis from Methanol at Low Temperatures by a Novel Psychrophilic Methanogen, “Methanolobus psychrophilus” sp. nov., Prevalent in Zoige Wetland of the Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74, 6114–6120 (2008)
G. Zhang, J. Gu, R. Zhang, M. Rashid, M.F. Haroon, W. Xun, Z. Ruan, X. Dong, U. Stingl, Haloprofundus marisrubri gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from a brine–seawater interface. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 67(1), 9–16 (2017)
T.N. Zhilina, G.A. Zavarzin, Methanohalobium evestigatus, n. gen., n. sp. The extremely halophilic methanogenic Archaebacterium. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, vol. 293 (1987), pp. 464–468
T.N. Zhilina, D.G. Zavarzina, V.V. Kevbrin, T.V. Kolganova, Methanocalculus natronophilus sp. nov., a new alkaliphilic hydrogenotrophic methanogenic archaeon from a soda lake, and proposal of the new family Methanocalculaceae. Microbiology 82, 698–706 (2013)
L. Zhou, X. Liu, X. Dong, Methanospirillum psychrodurum sp. nov., isolated from wetland soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 64, 638–641 (2014)
C.E. Zobell, F.H. Johnson, The influence of hydrostatic pressure on the growth and viability of terrestrial and marine bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 57, 179–189 (1949)
M.Y. Zolotov, J.S. Kargel, On the chemical composition of Europa’s icy shell, ocean, and underlying rocks, in Europa, ed. by R.T. Pappalardo, W.B. McKinnon, K.K. Khurana. The University of Arizona Space Science Series (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 2009), p. 431
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Ocean Worlds
Edited by Athena Coustenis, Tilman Spohn, Rafael Rodrigo, Kevin P. Hand, Alexander Hayes, Karen Olsson-Francis, Frank Postberg, Christophe Sotin, Gabriel Tobie, Francois Raulin and Nicolas Walter
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jebbar, M., Hickman-Lewis, K., Cavalazzi, B. et al. Microbial Diversity and Biosignatures: An Icy Moons Perspective. Space Sci Rev 216, 10 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-019-0620-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-019-0620-z