Abstract
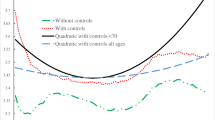
Over the past several decades, the proportion of older adults in the Chinese population has steadily increased during a period of substantial social change; the effect of these changes on older adults warrants examination. The present study explored changes in subjective well-being (SWB) in older adults by birth cohort and the social factors influential in these changes. We performed a cross-temporal meta-analysis using data from 20,713 adults over 60 years of age; data were obtained from 61 studies that used the Memorial University of Newfoundland Scale of Happiness. The dynamics of SWB in older adults were evaluated as a function of time. The mean SWB score decreased by 4.98 over the measured period, indicating a decrease of .52 standard deviations between 1990 and 2010. In addition, SWB in older adults was significantly correlated with high social connectedness and low overall threat. Specifically, urbanization level, Gini coefficient, personal medical expenditure, and birth rate were strong predictors of SWB. Our research demonstrates that social connectedness and overall threat contribute to SWB in Chinese older adults. As SWB is significantly related to the mental and physical health of older adults, the present study may serve as a useful reference for health care agencies and policy-makers.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
“Ecological fallacy”, a logical fallacy, is inherent in making causal inferences from group data to individual behaviors, which is not a problem of the measure of the association but rather one of construct validity.
References (*The Literate Used in Meta-analysis)
Aboa-Éboulé, C., Brisson, C., Maunsell, E., Mâsse, B., Bourbonnais, R., Vézina, M., & Dagenais, G. R. (2007). Job strain and risk of acute recurrent coronary heart disease events. Journal of the American Medical Association, 298(14), 1652–1660.
Ball, R., & Chernova, K. (2008). Absolute income, relative income, and happiness. Social Indicators Research, 88, 497–529.
Bishop, A., Martin, P., & Poon, L. (2006). Happiness and congruence in older adulthood: A structural model of life satisfaction. Aging and Mental Health, 10, 445–453.
Bjørnskov, C. (2008). Healthy and happy in Europe? On the association between happiness and life expectancy over time. Social Science and Medicine, 66, 1750–1759.
Boehm, J. K., & Kubzansky, L. D. (2012). The heart’s content: The association between positive psychological well-being and cardiovascular health. Psychological Bulletin, 138, 655.
Boyce, C. J., Brown, G. D., & Moore, S. C. (2010). Money and happiness rank of income, not income, affects life satisfaction. Psychological Science, 21, 471–475.
Bray, I., & Gunnell, D. (2006). Suicide rates, life satisfaction and happiness as markers for population mental health. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 41(5), 333–337.
Bronsteen, J., Buccafusco, C., & Masur, J. (2010). Welfare as happiness. Georgetown Law Journal, 98, 1583.
Charles, S. T., & Carstensen, L. L. (2007). Emotion regulation and aging. Handbook of Emotion Regulation, 307, 327.
*Chen, R., Chen, W. C., Yu, J. L., Xiong, Y., Liu, J., Han, Q. Z., & Shi, H. Y. (2007). Investigation on older adults’ well-being in Huangshi area. China Journal of Health Psychology, 15(10), 908–910.
*Chen, F., & Zhang, Q. H. (2005). Study on the subjective well-being and influencing factors in older university students. China Journal of Health Psychology, 13(2), 153–154.
Cheng, S. T., & Chan, A. C. (2006). Filial piety and psychological well-being in well older Chinese. The Journals of Gerontology Series B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences, 61, 262–269.
*Cheng, X. (2011). Study on older adults’ mental and physical health and influencing factors in the three gorges reservoir area. Unpublished Master thesis, Chongqing Medical University.
Cohen, J. (1992). A power primer. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 155.
Dai, B., Zhang, B., & Li, J. (2013). Protective factors for subjective well-being in Chinese older adults: The roles of resources and activity. Journal of Happiness Studies, 14(4), 1225–1239.
Davis, J. A. (1984). New money, and old man/lady and ‘two’s company:’ Subjective welfare in the NORC general social surveys, 1972–1982. Social Indicators Research, 15, 319–350.
de Jong Gierveld, J., Dykstra, P. A., & Schenk, N. (2012). Living arrangements, intergenerational support types and older adult loneliness in Eastern and Western Europe. Demographic Research, 27, 167–200.
*Di, W. J., & Chen, Q. P. (2009). Study on widowed older adults’ subjective well-being and influencing factors. Journal of China Medical University, 5, 372–376.
Diener, E., Oishi, S., & Lucas, R. E. (2003). Personality, culture, and subjective well-being: Emotional and cognitive evaluations of life. Annual Review of Psychology, 54, 403–425.
Ervasti, H., & Venetoklis, T. (2010). Unemployment and subjective well-being: An empirical test of deprivation theory, incentive paradigm and financial strain approach. Acta Sociologica, 53, 119–139.
*Han, S. Q. (2011). Study on older adults’ happiness and psychological contract in Jining rural area. Unpublished Master thesis, Qufu Normal University.
*Hang, R. H., Liu, X. M., Feng, L. P., & Xing, J. (2011). Study on the influence of psychological intervention on the community Empty Nesters’ symptoms of depression, loneliness and happiness. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 31(14), 2723–2725.
Hobfoll, S. E. (2002). Social and psychological resources and adaptation. Review of General Psychology, 6, 307.
Howell, R. T., Kern, M. L., & Lyubomirsky, S. (2007). Health benefits: Meta-analytically determining the impact of well-being on objective health outcomes. Health Psychology Review, 1(1), 83–136.
*Hu, J. S., Xiao, J., & Bai, S. Y. (2005). Study on Jiangxi older adults’ subjective well-being and influencing factors in the rural area. Journal of China Medical University, 19(5), 342.
*Hui, Q. P., & He, A. M. (2013). Study on the older adults left behind in rural areas of their happiness and enhancement strategies. Journal of Guangxi Vocational and Technical College, 2, 66–68.
*Jian, J., & Zhang, H. (2008). Investigation on the retired cadres’ happiness in Chongqing Municipal Administration. Health Medicine Research and Practice in Higher Institutions, 5(4), 10–12.
*Jiang, H. B., & Lin, L. Z. (2008). Investigation on older adults’ influencing factors of subjective well-being of and adjustment. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 28(24), 2461–2462.
Kenny, C. (2005). Does development make you happy? Subjective well-being and economic growth in developing countries. Social Indicators Research, 73(2), 199–219.
Kozma, A., & Stones, M. (1980). The measurement of happiness: Development of the Memorial University of Newfoundland Scale of Happiness (MUNSH). Journal of Gerontology, 35, 906–912.
Li, J. P. (2005). Study on the Influence of physical exercise participation on older adults’ mental health, happiness and quality of life. Suzhou University Journal, 118–120.
Li, J. (2007). Study on the impacts of personality, self-esteem, social support on retired military cadres’ subjective well-being. Unpublished Master thesis, Third Military Medical University.
Li, L. W., & Liang, J. (2007). Social exchanges and subjective well-being among older Chinese: Does age make a difference? Psychology and Aging, 22, 386.
Li, L. W., Liang, J., Toler, A., & Gu, S. (2005). Widowhood and depressive symptoms among older Chinese: Do gender and source of support make a difference? Social Science and Medicine, 60, 637–647.
*Li, J., & Feng, Z. Z. (2008). Study on the relationship among retired cadres’ subjective well-being, self-esteem and social support. Chinese Journal of Health Education, 23(7), 493–495.
*Li, G. L., & Wei, S. J. (2004). Analysis study on factors affecting the retired cadres’ psychological health level. Chinese Journal of Behavioral Medical Science, 3, 335–336.
*Li, J. P., Xu, D. J., & Deng, K. W. (2004). Study on the influence of doing morning exercises on older adults’ mental health. Journal of China Medical University, 18(7), 461–463.
*Liao, X. C. (2010). Study on the relationship between very old adults’ life satisfaction and subjective well-being in old-age care institutions. Applied Journal of General Practice, 5, 627–628.
*Lin, Z. B. (2011). Construction of old cadres’ service system based on investigations of mental health status. Unpublished Doctor thesis, Huaqiao University.
*Liu, R. G., & Gong, Y. X. (2000). Study on older adults’ subjective well-being and influencing factors. Journal of China Medical University, 8(2), 73–78.
*Liu, R. G., & Gong, Y. X. (2001). Correlation study between older adults’ stress level and subjective well-being. Journal of China Medical University, 15(1), 28–30.
*Luo, Y. M., Hu, H., Zhu, Z. H., Chen, J., & Guo, H. M. (2008). Correlation study between older adults’ intergenerational social support and subjective well-being in Hunan province. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 16(2), 173–175.
*Luo, S. X., Xiao, S. N., & Luo, S. X. (2005). Study on the influence of stress state on older adults’ happiness. Chinese General Practice, 8(15), 1251–1252.
*Ma, Y. (2007). Study on older adults’ subjective well-being and influencing factors in social organizations for the aged in Xi’an city. Unpublished Master thesis, Fourth Military Medical University.
*Ma, Y., Hua, Q. Z., Fan, S. H., & Fu, J. F. (2007). Research on older adults’ subjective well-being and related factors in old-age care institutions. Journal of Nursing Science, 22(4), 5–8.
Marsland, A. L., Pressman, S., & Cohen, S. (2007). Positive affect and immune function. In R. Ader (Ed.), Psychoneuroimmunology (4th ed., Vol. 2, pp. 761–779). San Diego, CA: Elsevier.
Mhaoláin, A. M., Gallagher, D., Connell, H. O., Chin, A., Bruce, I., Hamilton, F., & Lawlor, B. A. (2012). Subjective well-being amongst community-dwelling elders: What determines satisfaction with life? Findings from the Dublin Healthy Aging Study. International Psychogeriatrics, 24, 316–323.
Ministry of Civil Affairs. (2011). Social service development statistical bulletin. Beijing: China Statistic Press.
Ministry of Health. (2011). China health statistical yearbook. Beijing: China Statistic Press.
Napier, J. L., Thorisdottir, H., & Jost, J. T. (2010). The joy of sexism? A multinational investigation of hostile and benevolent justifications for gender inequality and their relations to subjective well-being. Sex Roles, 62, 405–419.
National Bureau of Statistics of China. (2011). China statistical yearbook. Beijing: China Statistic Press.
National Bureau of Statistics of China. (2012). China statistical yearbook. Beijing: China Statistic Press.
Ogunseitan, O. A. (2005). Topophilia and the quality of life. Environmental Health Perspectives, 113, 143.
Oliver, M. B., & Hyde, J. S. (1993). Gender differences in sexuality: a meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 114, 29.
Ostir, G. V., Berges, I. M., Markides, K. S., & Ottenbacher, K. J. (2006). Hypertension in older adults and the role of positive emotions. Psychosomatic Medicine, 68(5), 727–733.
*Pan, J. (2009). Study on the relationship between older adults’ attachment style, social support and subjective well-being. Unpublished Doctor thesis, Jiangxi Normal University.
Patton, G. C., Tollit, M. M., Romaniuk, H., Spence, S. H., Sheffield, J., & Sawyer, M. G. (2011). A prospective study of the effects of optimism on adolescent health risks. Pediatrics, 127, 308–316.
Sacks, D. W., Stevenson, B., & Wolfers, J. (2010). Subjective well-being, income, economic development and growth (NBER Working Paper Series, No. 16441) Retrieved from the National Bureau of Economic Research website: http://www.nber.org/papers/w16441.pdf.
Segerstrom, S. C., & Sephton, S. E. (2010). Optimistic expectancies and cell-mediated immunity the role of positive affect. Psychological Science, 21(3), 448–455.
Shao, J. J., Li, D., Zhang, D. J., Zhang, L., Zhang, Q., & Qi, X. (2013). Birth cohort changes in the depressive symptoms of Chinese older adults: A cross-temporal meta-analysis. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry,. doi:10.1002/gps.3942.
*Sun, M. X., Li, G. P., Li, J. H., & Liao, G. X. (2011). Path analysis on Influencing Factors of subjective well-being of the elderly in nursing home. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 31(16), 3140–3143.
*Suo, H. M., Tian, J. Q., & Ji, L. (2009). Correlation study between retired people’s self-efficacy and subjective well-being. Practical Journal of Medicine & Pharmacy, 26(11), 69–70.
*Tan, H. Y. (2010). Comparison study of the influence of social endowment and family endowment on older adults’ quality of life and subjective well-being. Unpublished Master thesis, Gannan Normal University.
Thomas, P. A. (2010). Is it better to give or to receive? Social support and the well-being of older adults. The Journals of Gerontology Series B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences, 65, 351–357.
Tian, W. (2002). The collapse of traditional large family system. Zhejiang Academic Journal, 3, 97–98.
*Tian, J. Q., Ji, L., & Suo, H. M. (2009). Study on the influence of exercise on pla retirees’ subjective well-being. Chinese Journal of Convalescent Medicine, 18(6), 573–574.
Twenge, J. M. (2000). The age of anxiety? The birth cohort change in anxiety and neuroticism, 1952–1993. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 79, 1007.
Twenge, J. M., Gentile, B., DeWall, C. N., Ma, D., Lacefield, K., & Schurtz, D. R. (2010). Birth cohort increases in psychopathology among young Americans, 1938–2007: A cross-temporal meta-analysis of the MMPI. Clinical Psychology Review, 30, 145–154.
Twenge, J. M., & Im, C. (2007). Changes in the need for social approval, 1958–2001. Journal of Research in Personality, 41, 171–189.
VanderWeele, T. J., Hawkley, L. C., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2012). On the reciprocal association between loneliness and subjective well-being. American Journal of Epidemiology, 176, 777–784.
*Wang, Y. M. (2008). Successful aging: study on the relationship between resources, SOC life management strategies, self-efficacy and subjective well-being[D]. East China Normal University.
*Wang, C. (2011). Study on the relationship between social participation and subjective well-being among older adults in different healthy states. Unpublished Master thesis, Hunan Normal University.
*Wang, Y. M., & Chen, C. P. (2010). Study on the influence of resources, SOC life management strategies on older adult’ subjective well-being. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 30(16), 2339–2341.
*Wang, X., & Wang, T. (2012). Research on older adults’ subjective well-being and influencing factors in the well-off background. Journal of Jiangsu Teachers University of Technology, 18(1), 66–71.
*Wang, F. X., Xu, F. F., & Li, H. (2011). Study on the current states of older adults’ subjective well-being and loneliness. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 31(13), 2533–2535.
Wiesmann, U., & Hannich, H. J. (2008). A salutogenic view on subjective well-being in active elderly persons. Aging and Mental Health, 12, 56–65.
Winkelmann, R. (2009). Unemployment, social capital, and subjective well-being. Journal of Happiness Studies, 10, 421–430.
Wu, X., Ip, C. Y., & Li, Y. (2012). Economic growth, income inequality and subjective well-being: Evidence from China. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the population association of America, San Francisco, CA.
*Wu, J. H. (2007). Investigation on older adults’ happiness and coping style living in different areas of senior houses. Chinese Journal of Geriatrics, 26(7), 536–538.
*Wu, J. (2010). Study on the relationship among middle aged people’ needs, social support and psychological health in cities. Unpublished Doctor thesis, Nankai University.
*Wu, J. F. (2010). Correlation study on older adults’ intergenerational support and subjective well-being in urban and suburban areas. China Journal of Health Psychology, 7, 822–824.
*Wu, H. J., Shen, J. Q., & Wang, X. (2011). Correlation study on older citizens’ happiness and social support. Chinese Rural Health Service Administration, 31(10), 1039–1040.
*Wu, Y. Q., Yu, C. M., Jiang, L. P., Zhu, X. H., Li, P., Zhu, X. L., & Wang, Y. X. (2008). Study on the empty nesters’ happiness and influencing factors in the urban area of Wenzhou city. Journal of Nursing Science, 23(2), 63–66.
Xin, Z., Niu, J., & Chi, L. (2012). Birth cohort changes in Chinese adolescents’ mental health. International Journal of Psychology, 47, 287–295.
Xin, Z., Zhang, L., & Liu, D. (2010). Birth cohort changes of Chinese adolescents’ anxiety: A cross-temporal meta-analysis, 1992–2005. Personality and Individual Differences, 48, 208–212.
Xu, J., & Roberts, R. E. (2010). The power of positive emotions: It’s a matter of life or death—subjective well-being and longevity over 28 years in a general population. Health Psychology, 29, 9.
Xu, A., Xie, X., Liu, W., Xia, Y., & Liu, D. (2007). Chinese family strengths and resiliency. Marriage & Family Review, 41, 143–164.
*Xu, S. S. (2011). Study on the relationship among life events, coping style and subjective well-being. Unpublished Master thesis, Qufu Normal University.
*Xu, J. (2012). Study on the influence of support model and social support on older adults’ subjective well-being. Unpublished Master thesis, Shanxi Normal University.
*Xu, S. L., Wang, C. H., & Jiang, L. (1993). Study of retired cadres on their life quality, subjective well-being and influencing factors. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 7(2), 63–66.
*Xue, X. B., & Zhang, X. B. (1998). Analysis of happiness and its related factors for the elderly in community. Journal of China Medical University, 12(1), 34–35.
Yang, K., & Victor, C. R. (2008). The prevalence of and risk factors for loneliness among older people in China. Ageing and Society, 28, 305–328.
*Yang, G. F., Song, J. H., Lin, R., Peng, Y. Z., Li, Y., & Luo, L. Q. (2011). Study on the influencing factors of older adults’ subjective well-being in old-age care institution of Fuzhou city. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 31(11), 2062–2064.
*Yi, J. C., Yang, H. H., Lu, Z. Z., & Po, J. Q. (2006). Correlation study between older adults’ subjective well-being and levels of physical training in Subei small towns. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 12(26), 1634–1635.
*Yu, M. J., & Ou, A. H. (1996). Exploration on older adults’ well-being and influencing factors in Guiyang city. Journal of Guiyang Medical University, 21(2), 108–110.
*Yu, Y. Q., Fan L. F., Wang, H. L., Xie, S. Y., Li, S., Yao, H., & Chen, Z. G. (1993). Study of older adults’ well-being and influencing factors. Journal of China Medical University, 1.
*Zeng, T. (1989). Comparison study of the Hui, Han elderly happiness in Ji’nan area. Shandong Psychiatry, 1, 005.
*Zhang, K. P. (2008). Study on older adults’ mental health problems and intervention living in senior houses in Chongqing City. Unpublished Master thesis, ChongQing Medical University.
*Zhang, J. Y. (2010). Study on the impacts of physical exercise on older adults’ social support, coping strategies and subjective well-being. Unpublished Master thesis, Xinjia Normal University.
*Zhang, Y. L., Feng, Z. Z., Shan, L. Y., & Xiong, C. (2009). Longitudinal study on the relationship between Self esteem, social support and subjective well-being of retired old cadres. Chinese Journal of Health Education, 25(7), 519–521.
*Zhang, L. L., Liang, Y. D., & Chen, P. Y. (2008). Investigation study on older adults’ happiness in old-age care institutions in Guangzhou City. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 28(15), 1513–1515.
*Zhang, S. Q., & Tao, M. (2001). Study on the retired cadres’ subjective well-being and related factors. China Journal of Health Psychology, 9(1), 38–39.
*Zhao, Y. P. (2005). Investigation on older adults’ mental health and quality of life in Ji’nan city. Unpublished Master thesis, Shandong University.
*Zhao, A. J., & Zhang, J. Q. (2011). Retrospective study on influencing factors of older adults’ life quality living in senior houses in Tangshan city. Modern Preventive Medicine, 38(18), 3681–3682.
*Zheng, H. Z., & Chen, H. Z. (2005). Correlation study between subjective well-being and social support among 314 older residents. Chinese Journal of Behavioral Medical Science, 14(9), 820–821.
*Zhong, W. G., Li, W. G., Li, S. M., Wu, J. P., Ao, H. B., & Qiu, W. (1998). A preliminary study on the elderly’s well-being and depression. Journal of China Medical University, 12(6), 346.
*Zhou, X. M., Li, J. P., Gu, Q. F., Xu, D. J., & Song, S. H. (2002). Investigation study on older adults’ well-being and its influence factors in retired cadres university. Journal of Jiangsu Clinical Medicine, 3, 037.
*Zhou, D. M., & Pan, X. G. (1999). Study on older adults’ subjective well-being and related social factors in Qingdao city. Orient Forum (Journal of Qiingdao University), 4, 021.
*Zhou, R. S., Pan, Z. D., Xie, B., & Cai, J. (2009). Comparison study on empty nest and non-Empty Nesters’mental health and subjective well-being in Shanghai Huangpu District city. Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 21(6), 336–339.
*Zhou, J., Tang, D., Wang, D. H., Peng, H. M., & Shen, J. L. (2006). Study of older adults’ positive emotion and negative emotion and related factors. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 14(2), 194–196.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L., Yan, Z., Yang, X. et al. Impact of Social Changes and Birth Cohort on Subjective Well-Being in Chinese Older Adults: A Cross-Temporal Meta-analysis, 1990–2010. Soc Indic Res 126, 795–812 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-015-0907-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-015-0907-8