Abstract
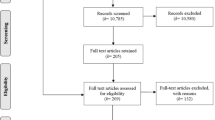
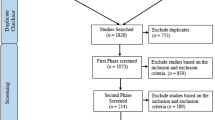
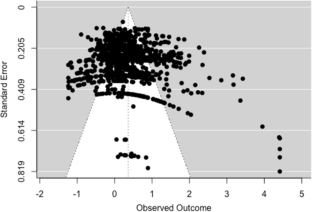
The current best evidence meta-analysis reanalyzed the data from a meta-analysis by Graham et al. (J Educ Psychol 115:1004–1027, 2023). This meta-analysis and the prior one examined if teaching writing improved the writing of students in Grades 6 to 12, examining effects from writing intervention studies employing experimental and quasi-experimental designs (with pretests). In contrast to the prior meta-analysis, we eliminated all N of 1 treatment/control comparisons, studies with an attrition rate over 20%, studies that did not control for teacher effects, and studies that did not contain at least one reliable writing measure (0.70 or greater). Any writing outcome that was not reliable was also eliminated. Across 148 independent treatment/control comparisons, yielding 1,076 writing effect sizes (ESs) involving 22,838 students, teaching writing resulted in a positive and statistically detectable impact on students’ writing (ES = 0.38). Further, six of the 10 writing treatments tested in four or more independent comparisons improved students’ performance. This included the process approach to writing (0.75), strategy instruction (0.59), transcription instruction (0.54), feedback (0.30), pre-writing activities (0.32), and peer assistance (0.59). In addition, the Self-Regulated Strategy Development model for teaching writing strategies yielded a statistically significant ES of 0.84, whereas other approaches to teaching writing strategies resulted in a statistically significant ES of 0.51. The findings from this meta-analysis and the Graham et al. (2023) review which included studies that were methodologically weaker were compared. Implications for practice, research, and theory are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
References marked with an asterisk indicate studies included in the meta-analysis
*Adams, V., (1971). A study of the effects of two methods of teaching composition to twelfth Graders [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Aiken, L., West, S., Schwalm, D., Carroll, J., & Hsiung, S. (1998). Comparison of a randomized and two quasi-experimental designs in a single outcome evaluation. Evaluation Review, 22, 207–244. https://doi.org/10.1177/0193841X9802200203
*Al Shaheb, M. N. A. (n.d.). The effect of self-regulated strategy development on persuasive writing, self-efficacy, and attitude: A mixed-methods, quasi-experimental study in Grade 6 in Lebanon [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Université Saint-Joseph, Beirut, Lebanon.
Applebee, A., & Langer, J. (2011). A snapshot of writing instruction in middle schools and high schools. English Journal, 100, 14–27.
Bangert-Drowns, R. (1993). The word processor as an instructional tool: A meta-analysis of word processing in writing instruction. Review of Educational Research, 63, 69–93. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543063001069
Bangert-Drowns, R., Hurley, M., & Wilkinson, B. (2004). The effects of school-based writing to-learn interventions on academic achievement: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 74(1), 29–58. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543074001029
*Barrot, J. S. (2018). Using the sociocognitive-transformative approach in writing classrooms: Effects on L2 learners’ writing performance. Reading & Writing Quarterly, 34(2), 187–201. https://doi.org/10.1080/10573569.2017.1387631
*Barton, H. (2018). Writing, collaborating, and cultivating: Building writing self-efficacy and skills through a student-centric, student-led writing center. Doctor of Education in Secondary Education Dissertations. 13. https://digitalcommons.kennesaw.edu/seceddoc_etd/13
*Benson, N. L. (1979). The effects of peer feedback during the writing process on writing performance, revision behavior, and attitude toward writing [Unpublished doctoral dissertation] University of Colorado.
*Berman, R. (1994). Learners’ transfer of writing skills between languages. TESL Canada Journal, 12(1), 29–46.
*Black, J. G. (1995). Teaching elements of written composition through use of classical music and art: the effects on high school students' writing [Unpublished doctoral dissertation] University of California, Riverside.
Bloom, B., Engelhart, M., Furst, E., Hill, W., & Krathwohl, D. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives: The classification of educational goals. Handbook I: Cognitive domain. David McKay Company.
*Braaksma, M. (2002). Observational learning in argumentative writing [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Amsterdam: University of Amsterdam.
*Braaksma, M., Rijlaarsdam, G. C. W., & van den Bergh, H. H. (2018). Effects of hypertext writing and observational learning on content knowledge acquisition, self-efficacy, and text quality: Two experimental studies exploring aptitude treatment interactions. Journal of Writing Research, 9(3), 259–300. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2018.09.03.02
*Brantley, H., & Small, D. (1991). Effects of self evaluation on written composition skill in learning disabled children. U.S. Department of Education.
*Brewer, D. (2002). Teaching writing in science through the use of a writing rubric [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Michigan-Flint.
Cheung, A., & Slavin, R. (2016). How methodological features affect effect sizes in education. Educational Researcher, 45, 283–292. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X16656615
*Christensen, C. A. (2004). Relationship between orthographic-motor integration and computer use for the production of creative and well-structured written text. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 74(4), 551–564. https://doi.org/10.1348/0007099042376373
*Chung, H. Q., Chen, V., & Olson, C. B. (2021). The impact of self-assessment, planning and goal setting, and reflection before and after revision on student self-efficacy and writing performance. Reading and Writing, 34, 1885–1913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-021-10186-x
*Combs, W. E. (1976). Further effects of sentence-combining practice on writing ability. Research in the Teaching of English, 10(2), 137–149.
*Combs, W. E. (1977). Sentence-combining practice: Do gains in judgments of writing “quality” persist? The Journal of Educational Research, 70(6), 318–321. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.1977.10885014
*Conklin, E. (2007). Concept mapping: Impact on content and organization of technical writing in science [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Walden University.
*Corey, D. R. (1990). The effects of concurrent instruction in composition and speech upon the composition writing holistic scores and sense of audience of a ninth-grade student population [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The Union for Experimenting Colleges and Universities.
Cortina, J., & Nouri, H. (2000). Effect size for ANOVA design. Sage.
*Couzijn, M., & Rijlaarsdam, G. (2004). Learning to read and write argumentative text by observation of peer learners. In Rijlaarsdam, G. (Series Ed.) & Rijlaarsdam, G., van den Bergh, H., & Couzijn, M. (Vol. 14 Eds.), Effective learning and teaching of writing, (pp. 241–258). Springer.
Couzijn, M., & Rijlaarsdam, G. (2005). Learning to write instructive texts by reader observation and written feedback. In G. Rijlaarsdam, H. van den Bergh, & M. Couzijn (Eds.), Effective learning and teaching of writing (pp. 209–240). Springer.
*Covill, A. E. (1996). Students' revision practices and attitudes in response to surface-related feedback as compared to content-related feedback on their writing [Unpublished doctoral dissertation] University of Washington.
*Cremin, T., Myhill, D., Eyres, I., Nash, T., Wilson, A., & Oliver, L. (2020). Teachers as writers: Learning together with others. Literacy, 54(2), 49–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/lit.12201
*Crook, J. D. (1985). Effects of computer-assisted instruction upon seventh-grade students’ growth in writing performance [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Nebraska.
*Crossley, S. A., Roscoe, R., & McNamara, D. S. (2013). Using automated scoring models to detect changes in student writing in an intelligent tutoring system. Paper presented at Proceedings of the Twenty-sixth International Florida Artificial Intelligence Research Society Conference, Florida.
*Crossley, S. A., Varner, L. K., Roscoe, R. D., & McNamara, D. S. (2013). Using automated indices of cohesion to evaluate an intelligent tutoring system and an automated writing evaluation system. In Artificial intelligence in education: 16th international conference, AIED 2013, Memphis, TN, USA, July 9–13, 2013. Proceedings 16 (pp. 269-278). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
*Dailey, E. M. (1992). The relative efficacy of cooperative learning versus individualized learning on the written performance of adolescent students with writing problems [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The Johns Hopkins University.
*Daiute, C., & Kruidenier, J. (1985). A self-questioning strategy to increase young writers’ revising processes. Applied Psycholinguistics, 6, 307–318. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0142716400006226
*de la Paz, S., & Graham, S. (2002). Explicitly teaching strategies, skills, and knowledge: Writing instruction in middle school classrooms. Journal of Educational Psychology, 94(4), 687. https://doi.org/10.1037//0022-0663.94.4.687
*de la Paz, S., & Wissinger, D. R. (2017). Improving the historical knowledge and writing of students with or at risk for LD. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 50(6), 658–671. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219416659444
*de la Paz, S., Wissinger, D. R., Gross, M., & Butler, C. (in press). Strategies that promote historical reasoning and contextualization: A pilot intervention with urban high school students. Reading and Writing.
*de Ment, L. (2008). The Relationship of self-evaluation, writing ability, and attitudes toward writing among gifted grade 7 language arts students [Unpublished master’s thesis] Walden University.
*de Smedt, F., & van Keer, H. (2018). Fostering writing in upper primary grades: A study into the distinct and combined impact of explicit instruction and peer assistance. Reading and Writing, 31, 325–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-017-9787-4
*de Smedt, F., Graham, S., & van Keer, H. (2019). The bright and dark side of writing motivation: Effects of explicit instruction and peer assistance. The Journal of Educational Research, 112(2), 152–167. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2018.1461598
*de Smedt, F., Graham, S., & Van Keer, H. (2020). “It takes two” : The added value of structured peer-assisted writing in explicit writing instruction. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 60, 101835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2019.101835
Drew, S., Olinghouse, N., Luby-Faggella, M., & Welsh, M. (2017). Framework for disciplinary writing in science Grades 6–12: A national survey. Journal of Educational Psychology, 109, 935–955. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000186
Dunnagan, K. L. (1990). Seventh grade students’ audience awareness in writing produced within and without the dramatic mode [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The Ohio State University.
*Eliason, R. G. (1994). The effect of selected word processing adjunct programs on the writing of high school students (Publication No. 0426055) [Doctoral dissertation]. University of South Florida.
*Erickson, D. K. (2009). The effects of blogs versus dialogue journals on open-response writing scores and attitudes of grade eight science students (Publication No. 3393920) [Doctoral dissertation]. University of Massachusetts, Lowell. ProQuest LLC.
*Espinoza, S. F. (1992). The effects of using a word processor containing grammar and spell checkers on the composition writing of sixth graders [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Texas Tech University.
*Festas, I., Oliveira, A. L., Rebelo, J. A., Damião, M. H., Harris, K., & Graham, S. (2015). Professional development in self-regulated strategy development: Effects on the writing performance of eighth grade Portuguese students. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 40, 17–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2014.05.004
Fisher, Z., Tipton, E., & Zhipeng, H. (2017). Package ' robumeta'. Retrieved from http://cran.uni-muenster.de/web/packages/robumeta/robumeta.pdf
*Frank, A. R. (2008). The effect of instruction in orthographic conventions and morphological features on the reading fluency and comprehension skills of high-school freshmen [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The University of San Francisco.
*Franzke, M., Kintsch, E., Caccamise, D., Johnson, N., & Dooley, S. (2005). Summary Street®: Computer support for comprehension and writing. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 33(1), 53–80. https://doi.org/10.2190/DH8F-QJWM-J457-FQVB
*Frost, K. L. (2008). The effects of automated essay scoring as a high school classroom intervention (Publication No. 3352171) [Doctoral dissertation], University of Nevada, Las Vegas. ProQuest LLC.
*Galbraith, J. (2014). The effect of self-regulation writing strategies and gender on writing self-efficacy and persuasive writing achievement for secondary students [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Western Connecticut State University.
*Ganong, F. L. (1974). Teaching writing through the use of a program based on the work of Donald M. Murray [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Boston University.
Goldberg, A., Russell, M., & Cook, A. (2003). The effect of computers on student writing: A meta-analysis of studies from 1992 to 2002. The Journal of Technology, Learning, and Assessment 2(1). Retrived from https://ejournals.bc.edu/index.php/jtla/article/view/1661
*González-Lamas, J., Cuevas, I., & Mateos, M. (2016). Arguing from sources: Design and evaluation of a programme to improve written argumentation and its impact according to students’ writing beliefs. Journal for the Study of Education and Development, 39(1), 49–83. https://doi.org/10.1080/02103702.2015.111160
*Grejda, G. F. (1988). The effects of word processing and revision patterns on the writing quality of sixth-grade students (Publication No. 8909998) [Doctoral dissertation], Pennsylvania State University.
Graham, S. (2019). Changing how writing is taught. Review of Research in Education, 43, 277–303. https://doi.org/10.3102/0091732X18821125
Graham, S. (2018). A revised writer(s)-within-community model of writing. Educational Psychologist, 53, 258–279. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2018.1481406
Graham, S. (2015). Inaugural editorial for the journal of educational psychology. Journal of Educational Psychology, 107, 1–2. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000007
Graham, S., & Harris, K. R. (2018). Evidence-based writing practices: A meta-analysis of existing meta-analyses. In R. Fidalgo, K. R. Harris, & M. Braaksma (Eds.). Design principles for teaching effective writing: Theoretical and empirical grounded principles (pp. 13–37). Hershey, PA: Brill Editions.
Graham, S., & Harris, K. R. (1997). It can be taught, but it does not develop naturally: Myths and realities in writing instruction. School Psychology Review, 26, 414–424. https://doi.org/10.1080/02796015.1997.12085875
Graham, S., & Harris, K. R. (2014). Conducting high quality writing intervention research: Twelve recommendations. Journal of Writing Research 6, 89–123. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2014.06.02.1
Graham, S., & Hebert, M. (2011). Writing-to-read: A meta-analysis of the impact of writing and writing instruction on reading. Harvard Educational Review, 81, 710–744. https://doi.org/10.17763/haer.81.4.t2k0m13756113566
Graham, S., Hebert, M., & Harris, K. R. (2015). Formative assessment and writing: A meta-analysis. Elementary School Journal, 115, 524–547. https://doi.org/10.1086/681947
Graham, S., Kim, Y., Cao, Y., Lee, W., Tate, T., Collins, T., Cho, M., Moon, Y., Chung, H., & Olson, C. (2023). A meta-analysis of writing treatments for students in Grades 6 to 12. Journal of Educational Psychology, 115, 1004–1027. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000819
Graham, S., Kiuhara, S., & MacKay, M. (2020). The effects of writing on learning in science, social studies, and mathematics: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 90, 179–226. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654320914744
Graham, S., Kiuhara, S., McKeown, D., & Harris, K. R. (2012). A meta-analysis of writing instruction for students in the elementary grades. Journal of Educational Psychology, 104, 879–896. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0029185
Graham, S., & Perin, D. (2007). A meta-analysis of writing instruction for adolescent students. Journal of Educational Psychology, 99, 445–476. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.99.3.445
Graham, S., & Rijlaarsdam, G. (2016). Writing education around the globe: Introduction and call for a new global analysis. Reading & Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 29, 781–792. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-016-9640-1
*Hamilton, H. (1960). A combined auditory-visual syllabification approach to the study of spelling [Unpublished master’s thesis]. Texas Technological College.
*Hammar, D. D. (1986). The effectiveness of computer-assisted writing instruction for juniors who have failed the Regents competency test in writing (Publication No. 8704355) [Doctoral dissertation]. University of Rochester.
Harris, K. R., & Graham, S. (1992). Self-regulated strategy development: A part of the writing process. In M. Pressley, K. R. Harris, & J. Guthrie (Eds.), Promoting academic competence and literacy in school (pp. 277–309). Academic Press.
*Harville, M. L. (2001). A study of computer-assisted expository writing of middle school students with special learning needs [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Columbia University
Hedges, L. V., Tipton, E., & Johnson, M. C. (2010). Robust variance estimation in meta-regression with dependent effect size estimates. Research Synthesis Methods, 1(1), 39–65. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.5
*Hickerson, B. L. (1987). Critical thinking, reading, and writing: developing a schema for expository text through direct instruction in analysis of text structure (metacognition, webbing, mapping) [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. North Texas State University.
*Higgins, P. D. (2013). The effects of using a critical thinking graphic organizer to improve Connecticut academic performance test interdisciplinary writing assessment scores [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Western Connecticut State University.
*Hill, B. G. (1990). A comparison of the writing quality of paired and unpaired students composing at the computer [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Texas at Austin.
Hillocks, G. (2008). Writing in secondary schools. In C. Bazerman (Ed.), Handbook of research on writing: History, society, school, individual, text (pp. 311–329). Routledge.
Hillocks, G. J. (1986). Research on written composition: New directions for teaching. National Council of Teachers of English.
*Hillocks, G. (1982). The interaction of instruction, teacher comment, and revision in teaching the composing process. Research in the Teaching of English, 16(3), 261–278.
*Hisgen, S., Barwasser, A., Wellmann, T., & Grünke, M. (2020). The effects of a multicomponent strategy instruction on the argumentative writing performance of low-achieving secondary students. Learning Disabilities: A Contemporary Journal, 18(1), 93–110.
Higgins, J. P. T., & Green, S. (Eds.). (2011). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions (Version 5.1.0). Retrieved from http://handbook.cochrane.org
*Holley, C. A. B. (1990). The effects of peer editing as an instructional method on the writing proficiency of selected high school students in Alabama [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Alabama.
Holliway, D., & McCutchen, D. (2004). Audience perspective in young writers’ composing and revising. In L. Allal, L. Chanquoy, & P. Largy (Eds.), Revision: Cognitive and instructional processes (pp. 87–101). Kluwer.
*Hoogeveen, M. C. E. J. (2013). Writing with peer response using genre knowledge: A classroom intervention study [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Twente.
*Hoogeveen, M., & van Gelderen, A. (2015). Effects of peer response using genre knowledge on writing quality: A randomized control trial. The Elementary School Journal, 116(2), 265–290. https://doi.org/10.1086/684129
*Hoogeveen, M., & van Gelderen, A. (2018). Writing with peer response using different types of genre knowledge: Effects on linguistic features and revisions of sixth-grade writers. The Journal of Educational Research, 111(1), 66–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2016.1190913
Hopewell, S., Loudon, K., Clarke, M. J., Oxman, A. D., & Dickersin, K. (2009). Publication bias in clinical trials due to statistical significance or direction of trial results. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 1, 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.MR000006.pub3
*Iordanou, K., & Constantinou, C. P. (2015). Supporting use of evidence in argumentation through practice in argumentation and reflection in the context of SOCRATES learning environment. Science Education, 99(2), 282–311. https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.21152
*Jacoby, K. E. (1990). Remove the dust covers and let the children play: An investigation into the effectiveness of computers in spelling drill and practice in the classroom [Unpublished master’s thesis]. University of New England.
*Jeroski, S. (1982). Competence in written expression: Interactions between instruction and individual differences among junior high school students [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of British Columbia.
*Jones, J. L. (1966). Effects of spelling instruction in eighth grade biological science upon scientific spelling, vocabulary, and reading comprehension; general spelling, vocabulary and reading comprehension; science progress; and science achievement [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Maryland.
*Jones, S., Myhill, D., & Bailey, T. (2013). Grammar for writing? An investigation of the effects of contextualised grammar teaching on students’ writing. Reading and Writing, 26(8), 1241–1263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-012-9416-1
*Kaffar, B. (1993). Exploring the effects of online instructional models on the writing achievement of high school students with and without disabilities [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Nevada.
*Kasparek, R. F. (1994). Effects of integrated writing on attitude and algebra performance of high school students [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The University of North Carolina at Greensboro.
*Kelley, K. R. (1984). The effect of writing instruction on reading comprehension and story writing ability [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Pittsburgh.
*Kennedy, K. A. (2008). Validating FOLA: A randomized writing experiment [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Southern California.
*Kim, J. S., Olson, C. B., Scarcella, R., Kramer, J., Pearson, M., van Dyk, D., Collins, P., & Land, R. E. (2011). A randomized experiment of a cognitive strategies approach to text-based analytical writing for mainstreamed Latino English language learners in grades 6 to 12. Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness, 4(3), 231–263. https://doi.org/10.1080/19345747.2010.523513
Koster, M., Tribushinina, E., de Jong, P. F., & van den Bergh, H. (2015). Teaching children to write: A meta-analysis of writing intervention research. Journal of Writing Research, 7(2), 249–274. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2015.07.02.2
*Kuscenko, D. (2018). Supporting collaborative writing in secondary Language Arts: A revision decision method intervention [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Lehigh University.
*Lane, R. A. J. (2003). “Keep cool and DECIDE”: Using discussion and writing instruction to improve the problem-solving skills of adolescent, urban students, labeled learning disabled [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Columbia University.
*Lange, A. A., Mulhern, G., & Wylie, J. (2009). Proofreading using an assistive software homophone tool. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 42(4), 322–335. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219408331035
*Laysears-Smith, R. R. (2005). Students' attitudes about structured journal writing and their perceptions of their self-esteem in an urban career and technical classroom [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Temple University.
*Lee, J., & Schallert, D. L. (2016). Exploring the reading-writing connection: A yearlong classroom-based experimental study of middle school students developing literacy in a new language. Reading Research Quarterly, 51(2), 143–164. https://doi.org/10.1002/rrq.132
*Limpo, T., & Alves, R. A. (2014). Implicit theories of writing and their impact on students’ response to a SRSD intervention. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 84(4), 571–590. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12042
Lipskey, M., & Wilson, D. (2001). Practical meta-analysis. Sage.
*López, P., Torrance, M., Rijlaarsdam, G., & Fidalgo, R. (2021). Evaluating effects of different forms of revision instruction in upper-primary students. Reading and Writing, 34, 1741–1767. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-021-10156-3
*Lott, C. J. (1986). The effects of the microcomputer word processor on the composition skills of seventh-grade students [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Montana.
*Lyons, H. L. K. (2002). The effects of technology use on student writing proficiency and student attitudes toward written assignments in a ninth-grade language arts classroom [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Idaho State University.
*Lytle, M. J. (1987). Word processors and writing: The relation of seventh grade students’ learner characteristics and revision behaviors (Publication No. 8800537) [Doctoral dissertation], University of Oregon.
Matuchniak, T., Olson, C. B., & Scarcella, R. (2014). Examining the text-based, on-demand, analytical writing of mainstreamed Latino English learners in a randomized field trial of the Pathway Project intervention. Reading and Writing, 27, 973–994. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-013-9490-z
*Mayo, N. B. (1976). The effects of discussion and assignment questions on the quality of descriptive writing of tenth grade students [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Memphis State University.
*McCarty, R. P. (2016). Leveraging historical thinking heuristics as warrants in historical argumentative writing [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Illinois at Chicago.
*McCreight, C. K. (1995). Computer-assisted process writing: A cooperative-pairs approach [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Baylor University.
*McDermott, M. A. (2009). The impact of embedding multiple modes of representation on student construction of chemistry knowledge [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The University of Iowa.
*McNeill, K. L., Lizotte, D. J., Krajcik, J., & Marx, R. W. (2006). Supporting students’ construction of scientific explanations by fading scaffolds in instructional materials. The Journal of the Learning Sciences, 15(2), 153–191. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327809jls1502_1
Morphy, P., & Graham, S. (2012). Word processing programs and weaker writers/readers: A meta-analysis of research findings. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 25, 641–678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-010-9292-5
*Moseley, D. S. (2003). Vocabulary instruction and its effects on writing quality [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Louisiana Tech University.
National Center for Educational Statistics (2012). The nation’s report card: Writing 2011 (NCES 2012-470). Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Educational Sciences.
*Niemi, D., Wang, J., Steinberg, D. H., Baker, E. L., & Wang, H. (2007). Instructional sensitivity of a complex language arts performance assessment. Educational Assessment, 12(3–4), 215–237. https://doi.org/10.1080/10627190701578271
Nunnally, J. (2017). Psychometric theory. McGraw-Hill.
*Olina, Z., & Sullivan, H. J. (2004). Student self-evaluation, teacher evaluation, and learner performance. Educational Technology Research and Development, 52(3), 5–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02504672
*Olson, C. B., Kim, J. S., Scarcella, R., Kramer, J., Pearson, M., van Dyk, D. A., Collins, P., & Land, R. E. (2012). Enhancing the interpretive reading and analytical writing of mainstreamed English learners in secondary school: Results from a randomized field trial using a cognitive strategies approach. American Educational Research Journal, 49(2), 323–355. https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831212439434
*Olson, C. B., Matuchniak, T., Chung, H. Q., Stumpf, R., & Farkas, G. (2017). Reducing achievement gaps in academic writing for Latinos and English learners in Grades 7–12. Journal of Educational Psychology, 109(1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000095
*Page-Voth, V., & Graham, S. (1999). Effects of goal setting and strategy use on the writing performance and self-efficacy of students with writing and learning problems. Journal of Educational Psychology, 91(2), 230–240. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.91.2.230
*Palumbo, D. B., & Prater, D. L. (1992). A comparison of computer-based prewriting strategies for basic ninth-grade writers. Computers in Human Behavior, 8(1), 63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/0747-5632(92)90019-B
*Pedersen, E. L. (1977). Improving syntactic and semantic fluency in writing of language arts students through extended practice in sentence combining [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The University of Minnesota.
*Pittman, R. T. (2007). Improving spelling ability among speakers of African American vernacular English: An intervention based on phonological, morphological, and orthographic principle [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Texas A&M University.
*Pivarnik, B. A. (1985). The effect of training in word processing on the writing of eleventh grade students [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Connecticut.
*Prata, M. J., de Sousa, B., Festas, I., & Oliveira, A. L. (2019). Cooperative methods and self-regulated strategies development for argumentative writing. The Journal of Educational Research, 112(1), 12–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2018.1427037
Pressley, M., Graham, S., & Harris, K. R. (2006). The state of educational intervention research. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 76, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1348/000709905x66035
*Rapanta, C. (2021). Can teachers implement a student-centered dialogical argumentation method across the curriculum? Manuscript submitted for publication.
R Core Team (2018). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Retrieved from https://www.r-project.org/
*Reynolds, C. J., Hill, D. S., Swassing, R. H., & Ward, M. E. (1988). The effects of revision strategy instruction on the writing performance of students with learning disabilities. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 21(9), 540–545. https://doi.org/10.1177/002221948802100904
*Reynolds, G. A., & Perin, D. (2009). A comparison of text structure and self-regulated writing strategies for composing from sources by middle school students. Reading Psychology, 30(3), 265–300. https://doi.org/10.1080/02702710802411547
*Rice, D. P. (1968). A study of a linguistically-based spelling program in grade six [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Temple University.
*Rijlaarsdam, G., & Schoonen, R. (1988). Effects of a teaching program based on peer evaluation on written composition and some variables related to writing apprehension. SCO Cahier Nr. 47. Stichting Centrum voor Onderwijsonderzoek (SCO), Grote Bickersstraat 72, 1013 KS Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
*Rijlaarsdam, G., Couzijn, M., Janssen, T., Braaksma, M., & Kieft, M. (2006). Writing experiment manuals in science education: The impact of writing, genre, and audience. International Journal of Science Education, 28(2–3), 203–233. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500690500336932
Rogers, L., & Graham, S. (2008). A meta-analysis of single subject design writing intervention research. Journal of Educational Psychology, 100, 879–906. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.100.4.879
*Rolfe, A. B. (1991). The effects of an identify-generate-test sequence on the spelling performance of learning disabled and normally-achieving students (Publication No. 0121204) [Doctoral dissertation]. Columbia University.
*Roscoe, R. D., Allen, L. K., & McNamara, D. S. (2019). Contrasting writing practice formats in a writing strategy tutoring system. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 57(3), 723–754. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633118763429
Roscoe, R. D., Brandon, R., Snow, E., & McNamara, D. S. (2013). Game-based writing strategy practice with the Writing Pal. In K. Pytash & R. Ferdig (Eds.), Exploring technology for writing and writing instruction (pp. 1–20). IGI Global.
*Rosenbluth, G. S., & Reed, W. M. (1992). The effects of writing-process-based instruction and word processing on remedial and accelerated 11th graders. Computers in Human Behavior, 8, 71–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0747-5632(92)90020-F
RStudio Team (2016). RStudio: Integrated Development for R. Retrieved from http://www.rstudio.com/.
Sandmel, K., & Graham, S. (2011). The process writing approach: A meta-analysis. Journal of Educational Research, 104, 396–407. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2010.488703
Schulz, K., & Grimes, D. (2002). Sample size slippages in randomized trials: Exclusions and the lost and wayward. Lancet, 359, 781–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(02)07882-0
*Segers, E., & Verhoeven, L. (2009). Learning in a sheltered Internet environment: The use of WebQuests. Learning and Instruction, 19, 423–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2009.02.017
Slavin, R. E., & Madden, N. A. (2011). Measures inherent to treatments in program effectiveness reviews. Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness, 4, 370–380. https://doi.org/10.1080/19345747.2011.558986
*Sloan, C. C. (2017). Types of feedback in peer review and the effect on student motivation and writing quality (Publication No. 10281143) [Doctoral dissertation]. Michigan State University. ProQuest LLC.
*Spilton, R. (1986). The effects of individualized language arts, sentence-combining, and traditional grammar on the syntactic maturity and quality of writing of a select group of eighth graders (Publication No. 8703964) [Doctoral dissertation]. Georgia State University.
Swanson, L., Harris, K. R., & Graham, S. (2013). Handbook of learning disabilities (Second Edition). Guilford.
Tanner-Smith, E. E., Tipton, E., & Polanin, J. R. (2016). Handling complex meta-analytic data structures using robust variance estimates: A tutorial in R. Journal of Developmental and Life-Course Criminology, 2(1), 85–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40865-016-0026-5
*Tezler, E. G. (1993). The effects of modeled strategies and attributions on students' self-regulated learning and spelling achievement (Publication No. 9325155) [Doctoral dissertation]. The City University of New York.
*Thibodeau, A. E. (1964). Improving composition writing with grammar and organization exercises utilizing differentiated group patterns [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Boston University.
*Thomas, M-L. (1995). The effect of genre-specific story grammar instruction on recall, comprehension, and writing of tenth-grade English students (Publication No. 9626945) [Doctoral dissertation]. Marquette University.
Tipton, E., & Pustejovsky, J. E. (2015). Small-sample adjustments for tests of moderators and model fit using robust variance estimation in meta-regression. Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics, 40(6), 604–634. https://doi.org/10.3102/1076998615606099
Tolchinsky, L. (2016). From text to language and back again: The emergence of written language. In C. A. MacArthur, S. Graham, & J. Fitzgerald (Eds.), Handbook of writing research (2nd ed., pp. 144–159). Guilford Press.
Tukey, J. W. (1977). Exploratory data analysis. Addison Wesley.
*Vahidi, A., Karimi, L., & Mahmoodi, M. H. (2016). The effect of reconstruction as a noticing strategy on Iranian female first grade high school students’ writing ability. Theory and Practice in Language Studies, 6(2), 310–324. https://doi.org/10.17507/tpls.0602.12
*van Beuningen, C., G., de Jong, N. H., & Kuiken, F. (2012). Evidence on the effectiveness of comprehensive error correction in second language writing. Language Learning, 62(1), 1–41. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9922.2011.00674.x
*van Drie, J., van Boxtel, C., Erkens, G., & Kanselaar, G. (2005). Using representational tools to support historical reasoning in computer-supported collaborative learning. Technology, Pedagogy and Education, 14(1), 25–42.
*van Drie, J., van Driel, J., & van Weijen, D. (2021). Developing students’ writing in History: Effects of a teacher-designed domain-specific writing instruction. Journal of Writing Research, 13(2), 201–229. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2021.13.02.01
*van Driel, J., van Drie, J., & van Boxtel, C. (2022). Writing about historical significance: The effects of a reading-to-write instruction. International Journal of Educational Research, 122, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2022.101924
*van Wagenen, D. A. (1988). Computerized prewriting activities and the writing performance of high school juniors [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The George Washington University.
*Vinson, L. L. N. (1971). The effects of two prewriting activities upon the overall quality of ninth graders’ descriptive paragraphs [Unpublished doctoral dissertation] University of South Carolina.
*Wagner, J. H. (1978). Peer teaching in spelling: An experimental study in selected Seventh-day Adventist high schools (Publication No. 7.913326) [Doctoral dissertation]. University of Florida.
*Walker, R. R. (1970). A comparison of an individualized and a group-directed system for teaching spelling in the eighth grade [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Columbia University.
*Widvey, L. I. H. (1971). A study of the use of a problem-solving approach to composition in high school English [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
*Wilson, J., & Czik, A. (2016). Automated essay evaluation software in English Language Arts classrooms: Effects on teacher feedback, student motivation, and writing quality. Computers & Education, 100, 94–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.05.004
*Wilson, J., & Roscoe, R. D. (2019). Automated writing evaluation and feedback: Multiple metrics of efficacy. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 58(1), 87–125. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633119830764
*Wise, W. G., & Slater, W. H. (1992). The effects of revision instruction on eighth graders’ persuasive writing (Publication No. 9304422) [Doctoral dissertation]. University of Maryland College Park.
*Wissinger, D. R., & de la Paz, S. (2016). Effects of critical discussions on middle school students’ written historical arguments. Journal of Educational Psychology, 108(1), 43–59. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000043
*Wissinger, D. R., De La Paz, S., & Jackson, C. (2021). The effects of historical reading and writing strategy instruction with fourth-through sixth-grade students. Journal of Educational Psychology, 113(1), 49–67. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000463
*Wong, B. Y. L., Hoskyn, M., Jai, D., Ellis, P., & Watson, K. (2008). The comparative efficacy of two approaches to teaching sixth graders opinion essay writing. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 33(4), 757–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2007.12.004
*Yeh, S. S. (1998). Empowering education: Teaching argumentative writing to cultural minority middle-school students. Research in the Teaching of English, 33(1), 49–83.
*Zellermayer, M., Salomon, G., Globerson, T., & Givon, H. (1991). Enhancing writing-related metacognitions through a computerized writing partner. American Educational Research Journal, 28(2), 373–391. https://doi.org/10.3102/00028312028002373
Acknowledgements
The research reported here was supported by the Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education, through Grant R305C190007 to the University of California – Irvine for the WRITE Center. The opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not represent views of the Institute or the U.S. Department of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have a conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Graham, S., Cao, Y., Kim, YS.G. et al. Effective writing instruction for students in grades 6 to 12: a best evidence meta-analysis. Read Writ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-024-10539-2
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-024-10539-2