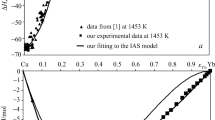
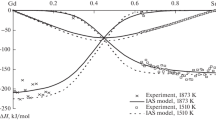
In the framework of the CALPHAD method, a thermodynamic database was developed for calculating the thermodynamic properties of liquid alloys in the Co–Cr–Cu–Fe–Ni system and its quaternary subsystems. The thermodynamic mixing functions of the melts were calculated at 1873 and 1500 K. The calculated excess integral mixing functions showed positive values in a major part of the composition space of the four-component systems with copper and the Co–Cr–Cu–Fe–Ni system. The ideal contribution to the Gibbs energy of mixing for four- and five-component melts of the Co–Cr–Cu–Fe–Ni system was predominant. The excess Gibbs energy of mixing for equiatomic liquid alloys of the four-component systems with copper and the Co–Cr–Cu–Fe–Ni system was lower in magnitude than the ideal component of the Gibbs mixing energy. With decreasing temperature, the positive deviations from the ideal behavior of the excess Gibbs mixing energy increased and the magnitude of the ideal Gibbs mixing energy decreased, resulting in lower thermodynamic stability of the liquid phase. The calculated separation temperatures for four- and five-component equiatomic Co–Cr–Cu–Fe–Ni melts varied in the 1370–1770 K range. The highest liquid-phase separation temperatures were observed in the melts containing both copper and chromium.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Cantor, J. Chang, P. Knight, and A. Vincent, “Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 375, 213–218 (2004).
J.-W. Yeh, S.-K. Chen, S.-J. Lin, J.-Y. Gan, T.-S. Chin, T.-T. Shun, C.-H. Tsau, and S.-Y. Chang, “Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes,” Adv. Eng. Mater., 6, No. 5, 299–303 (2004).
J.-W. Yeh, “Alloy design strategies and future trends in high-entropy alloys,” JOM, 65, No. 12, 1759–1771 (2013).
F. Otto, Y. Yang, H. Bei, and E.P. George, “Relative effects of enthalpy and entropy on the phase stability of equiatomic high-entropy alloys,” Acta Mater., 61, No. 7, 2628–2638 (2013).
D.B. Miracle, J.D. Miller, O.N. Senkov, C. Woodward, M.D. Uchic, and J. Tiley, “Exploration and development of high entropy alloys for structural applications,” Entropy, 16, No. 1, 494–525 (2014).
M.-H. Tsai and J.-W. Yeh, “High-entropy alloys: A critical review,” Mater. Res. Lett., 2, No. 3, 107–123 (2014).
O.N. Senkov, J. Miller, D. Miracle, and C. Woodward, “Accelerated exploration of multi-principal element alloys for structural applications,” Calphad, 50, 32–48 (2015).
B.S. Murty, J.-W. Yeh, and S. Ranganathan, “High-entropy alloys,” Mater. Res. Lett., 2, No. 3, 107–123(2014).
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Z. Tang, M.C. Gao, K.A. Dahmen, P.K. Liaw, and Z.P. Lu, “Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys,” Prog. Mater. Sci., 61, 1–93 (2014).
X. Yang and Y. Zhang, “Prediction of high-entropy stabilized solid-solution in multi-component alloys,” Mater. Chem. Phys., 132, No. 2, 233–238 (2012).
O.N. Senkov and C. Woodward, “Microstructure and properties of a refractory NbCrMo0.5Ta0.5TiZr alloy,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 529, 311–320 (2011).
Y. Zhang, Y.J. Zhou, J.P. Lin, G.L. Chen, and P.K. Liaw, “Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys,” Adv. Eng. Mater., 10, No. 6, 534–538 (2008).
R. Raghavan, K.H. Kumar, and B. Murty, “Analysis of phase formation in multi-component alloys,” J. Alloys Compd., 544, 152–158 (2012).
G. Arzpeyma, A.E. Gheribi, and M. Medraj, “On the prediction of Gibbs free energy of mixing of binary liquid alloys,” J. Chem. Therm., 57, 82–91 (2013).
C.-J. Tong, Y.-L. Chen, J.-W. Yeh, S.-J. Lin, S.-K. Chen, T.-T. Shun, C.-H. Tsau, and S.-Y. Chang, “Microstructure characterization of AlxCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy system with multiprincipal elements,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 36, No. 4, 881–893 (2005).
X.F. Wang, Y. Zhang, Y. Qiao, and G. Chen, “Novel microstructure and properties of multicomponent CoCrCuFeNiTix alloys,” Intermetallics, 15, No. 3, 357–362 (2007).
C. Li, J. Li, M. Zhao, and Q. Jiang, “Effect of alloying elements on microstructure and properties of multiprincipal elements high-entropy alloys,” J. Alloys Compd., 475, No. 1, 752–757 (2009).
N. Park, I. Watanabe, D. Terada, Y. Yokoyama, P.K. Liaw, and N. Tsuji, “Recrystallization behavior of CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 46, No. 4, 1481–1487 (2015).
J.-W. Yeh, S.-J. Lin, T.-S. Chin, J.-Y. Gan, S.-K. Chen, T.-T. Shun, C.-H. Tsau, and S.-Y. Chou, “Formation of simple crystal structures in Cu–Co–Ni–Cr–Al–Fe–Ti–V alloys with multiprincipal metallic elements,” Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 35, No. 8, 2533–2536 (2004).
C.-M. Lin and H.-L. Tsai, “Equilibrium phase of high-entropy FeCoNiCrCu0.5 alloy at elevated temperature,” J. Alloys Compd., 489, No. 1, 30–35 (2010).
C.-M. Lin, H.-L. Tsai, and H.-Y. Bor, “Effect of aging treatment on microstructure and properties of high-entropy Cu0.5CoCrFeNi alloy,” Intermetallics, 18, No. 6, 1244–1250 (2010).
P.H. Wu, N. Liu, P.J. Zhou, Z. Peng, W.D. Du, X J. Wang, and Y. Pan, “Microstructures and liquid phase separation in multicomponent CoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloys,” Mater. Sci. Technol., 32, No. 6, 576–580 (2016).
W.L. Wang, L. Hu, S.B. Luo, L.J. Meng, D.L. Geng, and B. Wei, “Liquid phase separation and rapid dendritic growth of high-entropy CoCrCuFeNi alloy,” Intermetallics, 77, 41–45 (2016).
N. Liu, P.H. Wu, P.J. Zhou, Z. Peng, X.J. Wang, and Y.P. Lu, “Rapid solidification and liquid-phase separation of undercooled CoCrCuFexNi high-entropy alloy,” Intermetallics, 72, 44–52 (2016).
M.A. Turchanin and P.G. Agraval, “Phase equilibria and thermodynamics of binary copper systems with 3d-metals. V. Copper–cobalt system,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 46, No. 1–2, 77–89 (2007).
M.A. Turchanin, L.A. Dreval, A.R. Abdulov, and P.G. Agraval, “Mixing enthalpies of liquid alloys and thermodynamic assessment of the Cu–Fe–Co system,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 50, No. 1–2, 98–116 (2011).
M.A. Turchanin, “Phase equilibria and thermodynamics of binary copper systems with 3d-metals. III. Copper–chromium system,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 45, No. 9–10, 457–467 (2006).
M.A. Turchanin and P.G. Agraval, “Thermodynamics of liquid alloys, and stable and metastable phase equilibria in the copper–iron system,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 40, No. 7–8, 337–353 (2001).
M.A. Turchanin, P.G. Agraval, and A.R. Abdulov, “Phase equilibria and thermodynamics of binary copper systems with 3d-metals. VI. Copper–nickel system,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 46, No. 9–10, 467–477 (2007).
M.A. Turchanin, A.A. Bondar, L.A. Dreval, A.R. Abdulov, and P.G. Agraval, “Mixing enthalpies of melts and thermodynamic assessment of the Cu–Fe–Cr system,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 53, No. 1–2, 70–90 (2014).
L.A. Dreval, M.A. Turchanin, and P.G. Agraval, “Thermodynamic assessment of the Cu–Fe–Ni system,” J. Alloys Compd., 587, 533–543 (2014).
L.A. Dreval, P.G. Agraval, M.A. Turchanin, A.I. Dovbenko, S.M. Ilienko, and G. Effenberg, “Thermodynamic database for directional search for promising compositions of precipitation-hardened HEAs,” Visn. Donbas. Derzh. Mashinobud. Akad., 41, No. 2, 24–29 (2017).
X.J. Liu, Z.P. Jiang, C.P. Wang, and K. Ishida, “Experimental determination and thermodynamic calculation of the phase equilibria in the Cu–Cr–Nb and Cu–Cr–Co systems,” J. Alloys Compd., 478, No. 1–2, 287–296 (2009).
S. Curiotto, L. Battezzati, E. Johnson, and N. Pryds, “Thermodynamics and mechanism of demixing in undercooled Cu–Co–Ni alloys,” Acta Mater., 55, No. 19, 6642–6650 (2007).
A. Kusoffsky and B. Jansson, “A thermodynamic evaluation of the Co–Cr and the C–Co–Cr systems,” Calphad, 21, No. 3, 321–333 (1997).
F. Guillermet, “Assessment of the thermodynamic properties of the Ni–Co system,” Z. Metallkd., 78, No. 9, 639–647 (1987).
B.J. Lee, “Revision of thermodynamic descriptions of the Fe–Cr & Fe–Ni liquid phases,” Calphad, 17, No. 3, 251–268 (1993).
B.J. Lee, “On the stability of Cr carbides,” Calphad, 16, No. 2, 121–149 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Poroshkova Metallurgiya, Vol. 59, Nos. 11–12 (536), pp. 113–126, 2020. Original article submitted October 8, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agraval, P., Dreval, L.O., Turchanin, M. et al. Temperature–Composition Dependence of Thermodynamic Mixing Functions of Co–Cr–Cu–Fe–Ni Melts. Powder Metall Met Ceram 59, 703–714 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-021-00205-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-021-00205-5