Abstract
Introduction
Soil pollution caused by toxic elements such as lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd) induces environmental stress on vegetable plants and soil microbial communities, reducing crop yield and disrupting ecosystem functions.
Methodology
In this study, nanoscale zerovalent iron supported with eggshell biochar and activated carbon (nZVI-ESB/AC) was synthesized using carbothermal reduction synthesis and evaluated the effectiveness in minimizing the toxicity of lead and cadmium in soil and alleviating the toxic effects of these metals on Brassica chinensis L. and soil microbial communities.
Results
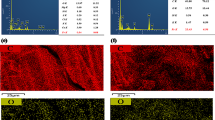
The nZVI-ESB/AC immobilized Pb and Cd in the soil more than ordinary eggshell biochar, resulting in their lower bioaccumulation in the edible part of Brassica chinensis L. The nZVI-ESB/AC treatments were significantly more effective than biochar treatments in enhancing plant growth, reducing oxidative stress indicators by 1.5–2 folds, and increasing the relative abundance level of Bacilli and Clostridia by 52–67% and 10–15%, respectively. The presence of iron in nZVI-ESB/AC enhanced the activities of antioxidant enzymes, leading to the decreased generation of reactive oxygen species and lipid peroxidation in the plants.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates the potential of nZVI-ESB/AC as an effective adsorbent for soil remediation, alleviating stress induced by toxic metals on vegetable plants and promoting bacterial community diversity. The successful application of nZVI-ESB/AC presents promising prospects for sustainable agriculture, mitigating the environmental impact of lead and cadmium pollution and improving crop yield.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Research data are available only by the corresponding author based on reasonable request.
References
Aborisade MA, Feng A, Oba BT et al (2022a) Pyrolytic synthesis and performance efficacy comparison of biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron on soil polluted with toxic metals. Arch Agron Soil Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2022.2146100
Aborisade MA, Feng A, Zheng X et al (2022b) Carbothermal reduction synthesis of eggshell-biochar modified with nanoscale zerovalent iron/activated carbon for remediation of soil polluted with lead and cadmium. Environ Nanotechnology Monit Manag 18:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2022.100726
Aborisade MA, Geng H, Oba BT et al (2023) Remediation of soil polluted with Pb and Cd and alleviation of oxidative stress in Brassica rapa plant using nanoscale zerovalent iron supported with coconut-husk biochar. J Plant Physiol 287:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2023.154023
Ahmad S, Liu X, Tang J, Zhang S (2022) Biochar-supported nanosized zero-valent iron (nZVI/BC) composites for removal of nitro and chlorinated contaminants. Chem Eng J 431:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133187
Alazaiza MYD, Albahnasawi A, Copty NK et al (2022) Nanoscale zero-valent iron application for the treatment of soil, wastewater and groundwater contaminated with heavy metals: a review. Desalin Water Treat 253:194–210. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2022.28302
Azeem M, Hayat R, Hussain Q et al (2019) Effects of biochar and NPK on soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity during 2 years of application in the arid region. Arab J Geosci 12:. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4482-1
Baragano D, Forjan R, Alvarez N et al (2022) Zero valent iron nanoparticles and organic fertilizer assisted phytoremediation in a mining soil: Arsenic and mercury accumulation and effects on the antioxidative system of Medicago sativa L. J Hazard Mater 433:128748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128748
Basegio TM, Garcia AP, Bergmann CP (2022) Nanostructured zero-valent iron: from synthesis to application. In: Kopp Alves, A (eds) Environmental applications of nanomaterials. Engineering materials. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-86822-2_12
Cao L, Ding Q, Liu M et al (2021) Biochar-supported Cu2+/Cu+Composite as an electrochemical ultrasensitive interface for ractopamine detection. ACS Appl Bio Mater 4:1424–1431. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.0c01314
Chen Y, Ho S-H, Wang D et al (2018) Lead removal by a magnetic biochar derived from persulfate-ZVI treated sludge together with one-pot pyrolysis. Bioresour Technol 247:463–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.125
Chen D, Wei Z, Wang Z et al (2022a) Long-term exposure to nanoplastics reshapes the microbial interaction network of activated sludge. Environ Pollut 314:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120205
Chen D, Zhao L, Wang Z et al (2022b) Successional dynamics of low C/N activated sludge system under salinity shock: Performance, nitrogen removal pathways, microbial community, and assembly. Chemosphere 307:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135703
Dionisio-Sese ML, Tobita S (1998) Antioxidant responses of rice seedlings to salinity stress. Plant Sci 135:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(98)00025-9
Elstner EF, Heupel A (1976) Inhibition of nitrite formation from hydroxylammoniumchloride: a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. Anal Biochem 70:616–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90488-7
Erkan M, Wang SY, Wang CY (2008) Effect of UV treatment on antioxidant capacity, antioxidant enzyme activity and decay in strawberry fruit. Postharvest Biol Technol 48:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2007.09.028
Fan X, He L, Meng Y et al (2015) α-MMC and MAP30, two ribosome-inactivating proteins extracted from Momordica charantia, induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in A549 human lung carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep 11:3553–3558. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3176
Fielding JL, Hall JL (1978) A biochemical and cytochemical study of peroxidase activity in roots of Pisum sativum: II. Distribution of enzymes in relation to root development. J Exp Bot 29:983–991. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/29.4.983
He H, Li W, Yu R, Ye Z (2017) Illumina-based analysis of bulk and rhizosphere soil bacterial communities in paddy fields under mixed heavy metal contamination. Pedosphere 27:569–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60352-7
Hu J, Guo H, Li J et al (2017) Comparative impacts of iron oxide nanoparticles and ferric ions on the growth of Citrus maxima. Environ Pollut 221:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.11.064
Igalavithana AD, Lee S-E, Lee YH et al (2017) Heavy metal immobilization and microbial community abundance by vegetable waste and pine cone biochar of agricultural soils. Chemosphere 174:593–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.148
Iqbal N, Tanzeem-ul-Haq HS, Gull-e-Faran et al (2023) Soil amendments and foliar melatonin reduced Pb uptake, and oxidative stress, and improved spinach quality in Pb-Contaminated soil. Plants 12:. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12091829
Irfan M, Hussain Q, Khan KS et al (2019) Response of soil microbial biomass and enzymatic activity to biochar amendment in the organic carbon deficient arid soil: a 2-year field study. Arab J Geosci 12:. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4239-x
Irshad MK, Chen C, Noman A et al (2020) Goethite-modified biochar restricts the mobility and transfer of cadmium in soil-rice system. Chemosphere 242:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125152
Islam E, Liu D, Li T et al (2008) Effect of Pb toxicity on leaf growth, physiology and ultrastructure in the two ecotypes of Elsholtzia argyi. J Hazard Mater 154:914–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.121
Jia Z, Deng J, Chen N et al (2017) Bioremediation of cadmium-dichlorophen co-contaminated soil by spent Lentinus edodes substrate and its effects on microbial activity and biochemical properties of soil. J Soils Sediments 17:315–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1562-7
Jin Y, Wang Y, Li X et al (2023) Remediation and its biological responses to Cd(II)-Cr(VI)-Pb(II) multi-contaminated soil by supported nano zero-valent iron composites. Sci Total Environ 867:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.161344
Jungklang J, Saengnil K, Uthaibutra J (2017) Effects of water-deficit stress and paclobutrazol on growth, relative water content, electrolyte leakage, proline content and some antioxidant changes in Curcuma alismatifolia Gagnep. cv. Chiang Mai Pink. Saudi J Biol Sci 24:1505–1512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.09.017
Kumar A, Kumar A, Cabral-Pinto MMS et al (2020) Lead toxicity: health hazards, influence on food chain, and sustainable remediation approaches. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072179
Kumar R, Verma A, Rakib MRJ et al (2023) Adsorptive behavior of micro(nano)plastics through biochar: Co-existence, consequences, and challenges in contaminated ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 856:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159097
Lee S-H, Kim M-S, Kim J-G, Kim S-O (2020) Use of soil enzymes as indicators for contaminated soil monitoring and sustainable management. Sustain 12:. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12198209
Li C, Zhou K, Qin W et al (2019) A review on heavy metals contamination in soil: effects, sources, and remediation techniques. Soil Sediment Contam 28:380–394. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2019.1592108
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(87)48036-1
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:421–428. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1978.03615995004200030009x
Liu Z, Bao H, Cai J et al (2014) A novel thylakoid ascorbate peroxidase from jatrophacurcas enhances salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Int J Mol Sci 15:171–185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010171
Liu H, Xu F, Xie Y et al (2018) Effect of modified coconut shell biochar on availability of heavy metals and biochemical characteristics of soil in multiple heavy metals contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 645:702–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.115
Liu H, Yin H, Tang S et al (2019) Effects of benzo [a] pyrene (BaP) on the composting and microbial community of sewage sludge. Chemosphere 222:517–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.01.180
Liu Q, Sheng Y, Wang W et al (2020) Remediation and its biological responses of Cd contaminated sediments using biochar and minerals with nanoscale zero-valent iron loading. Sci Total Environ 713:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136650
Medina S, Collado-González J, Ferreres F et al (2017) Quantification of phytoprostanes – bioactive oxylipins – and phenolic compounds of Passiflora edulis Sims shell using UHPLC-QqQ-MS/MS and LC-IT-DAD-MS/MS. Food Chem 229:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.02.049
Meyghan N, Moradi P (2018) The effect of nitrogen and phosphorous fertilizers on morphophysiological properties of Althaea officinalis. Iran J Plant Physiol 8:2563–2571. https://doi.org/10.22034/ijpp.2018.543509
Naeem MA, Abdullah M, Imran M et al (2022) Iron oxide nanoparticles doped biochar ameliorates trace elements induced phytotoxicity in tomato by modulation of physiological and biochemical responses: Implications for human health risk. Chemosphere 289:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133203
Nath H, Sarkar B, Mitra S, Bhaladhare S (2022) Biochar from biomass: a review on biochar preparation its modification and impact on soil including soil microbiology. Geomicrobiol J 39:373–388. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2022.2028942
Navazas A, Thijs S, Feito I et al (2021) Arsenate-reducing bacteria affect As accumulation and tolerance in Salix atrocinerea. Sci Total Environ 769:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144648
Noman A, Aqeel M (2017) miRNA-based heavy metal homeostasis and plant growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:10068–10082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8593-5
Noman A, Ali Q, Naseem J et al (2018) Sugar beet extract acts as a natural bio-stimulant for physio-biochemical attributes in water stressed wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Acta Physiol Plant 40:. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-018-2681-0
Oba BT, Zheng X, Aborisade MA et al (2021a) Environmental opportunities and challenges of utilizing unactivated calcium peroxide to treat soils co-contaminated with mixed chlorinated organic compounds. Environ Pollut 291:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118239
Oba BT, Zheng X, Aborisade MA et al (2021b) Remediation of trichloroethylene contaminated soil by unactivated peroxymonosulfate: Implication on selected soil characteristics. J Environ Manage 285:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112063
Paithankar JG, Saini S, Dwivedi S et al (2021) Heavy metal associated health hazards: An interplay of oxidative stress and signal transduction. Chemosphere 262:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128350
Patel K, Chaurasia M, Rao KS (2022) Impacts of Pb-Induced oxidative stress on morphological, physiological and biochemical properties of tree species. Environ Process 9:. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-022-00616-5
Peng D, Wu B, Tan H et al (2019) Effect of multiple iron-based nanoparticles on availability of lead and iron, and micro-ecology in lead contaminated soil. Chemosphere 228:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.106
Saed-Moucheshi A, Shekoofa A, Pessarakli M (2014) Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) generation and detoxifying in plants. J Plant Nutr 37:1573–1585. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2013.868483
Shahid M, Dumat C, Pourrut B et al (2014) Assessing the effect of metal speciation on lead toxicity to Vicia faba pigment contents. J Geochem Explor 144:290–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.01.003
Song P, Ma W, Gao X et al (2022) Remediation mechanism of Cu, Zn, As, Cd, and Pb contaminated soil by biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron and its impact on soil enzyme activity. J Clean Prod 378:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134510
Sun L, Guo D, Liu K et al (2019) Levels, sources, and spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils from a typical coal industrial city of Tangshan, China. CATENA 175:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.12.014
Sun T, Xu Y, Sun Y et al (2021) Cd immobilization and soil quality under Fe–modified biochar in weakly alkaline soil. Chemosphere 280:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130606
Tafa B, Zheng X, Akintayo M et al (2023) Science of the Total Environment Application of KHSO 5 for remediation of soils polluted by organochlorides : A comprehensive study on the treatment ’ s ef fi cacy , environmental implications , and phytotoxicity. 871:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162023
Turan V, Khan SA, Mahmood-ur-Rahman et al (2018a) Promoting the productivity and quality of brinjal aligned with heavy metals immobilization in a wastewater irrigated heavy metal polluted soil with biochar and chitosan. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 161:409–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.05.082
Turan V, Ramzani PMAPMA, Ali Q et al (2018b) Alleviation of nickel toxicity and an improvement in zinc bioavailability in sunflower seed with chitosan and biochar application in pH adjusted nickel contaminated soil. Arch Agron Soil Sci 64:1053–1067. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2017.1410542
Turan V (2020) Potential of pistachio shell biochar and dicalcium phosphate combination to reduce Pb speciation in spinach, improved soil enzymatic activities, plant nutritional quality, and antioxidant defense system. Chemosphere 245:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125611
Turan V (2021) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and pistachio husk biochar combination reduces Ni distribution in mungbean plant and improves plant antioxidants and soil enzymes. 173:418–429. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13490
Turan V (2022) Calcite in combination with olive pulp biochar reduces Ni mobility in soil and its distribution in chili plant. 24:166–176. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2021.1929826
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000) Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants protective role of exogenous polyamines. Plant Sci 151:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(99)00197-1
Wang L, Li X, Tsang DCW et al (2020) Green remediation of Cd and Hg contaminated soil using humic acid modified montmorillonite: Immobilization performance under accelerated ageing conditions. J Hazard Mater 387:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.122005
Wang A, He M, Ouyang W et al (2021) Effects of antimony (III/V) on microbial activities and bacterial community structure in soil. Sci Total Environ 789:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148073
Wu B, Hou S, Peng D et al (2018) Response of soil micro-ecology to different levels of cadmium in alkaline soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 166:116–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.076
Xie X, He Z, Chen N et al (2019) The roles of environmental factors in regulation of oxidative stress in plant. Biomed Res Int 2019:. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9732325
Yang Z-H, Xu R, Zheng Y et al (2016) Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances and microbial diversity in anaerobic co-digestion reactor treated sewage sludge with fat, oil, grease. Bioresour Technol 212:164–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.04.046
Yang Q, Li Z, Lu X et al (2018) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: pollution and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 642:690–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.068
Yang D, Wang L, Li Z et al (2020) Simultaneous adsorption of Cd(II)andAs(III)by a novel biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron in aqueous systems. Sci Total Environ 708:134823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134823
Yang D, Yang S, Yuan H et al (2021) Co-benefits of biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron in simultaneously stabilizing soil heavy metals and reducing their bioaccessibility. J Hazard Mater 418:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126292
Zand AD, Tabrizi AM, Heir AV (2020) Incorporation of biochar and nanomaterials to assist remediation of heavy metals in soil using plant species. Environ Technol Innov 20:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101134
Zhang S, Lu J, Zhu Y et al (2022) Rapeseed as a previous crop reduces rice N fertilizer input by improving soil fertility. F Crop Res 281:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2022.108487
Zou Z, Wang Y, Huang J et al (2020) A study on the mixture repairing effect of biochar and nano iron oxide on toxicity of Cd toward muskmelon. Environ Pollut 266:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115371
Funding
Authors appreciate the support received from Tianjin key Scientific and Technological Project (Grant No. 18ZXSZSF00240).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Moses Akintayo Aborisade: Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, data curation, analysis, writing the original draft, editing, and visualization.. Belay Tafa Oba & Akash Kumar: Software, review writing, and visualization. Jiashu Liu & Chen Daying: Resources and validation. Oluwaseun Princess Okimiji: Writing – review, editing, and validation. Lin Zhao: Administration, conceptualization, funding, resources, supervision, and validation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Animal research
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Antony Van der Ent.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aborisade, M.A., Oba, B.T., Kumar, A. et al. Remediation of metal toxicity and alleviation of toxic metals-induced oxidative stress in Brassica chinensis L using biochar-iron nanocomposites. Plant Soil 493, 629–645 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06256-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06256-4