Abstract
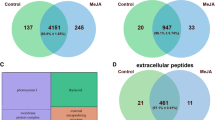
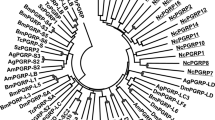
Plants utilize a plethora of peptide signals to regulate their immune response. Peptide ligands and their cognate receptors involved in immune signaling share common motifs among many species of vascular plants. However, the origin and evolution of immune peptides is still poorly understood. Here, we searched for genes encoding small secreted peptides in the genomes of three bryophyte lineages—mosses, liverworts and hornworts—that occupy a critical position in the study of land plant evolution. We found that bryophytes shared common predicted small secreted peptides (SSPs) with vascular plants. The number of SSPs is higher in the genomes of mosses than in both the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha and the hornwort Anthoceros sp. The synthetic peptide elicitors—AtPEP and StPEP—specific for vascular plants, triggered ROS production in the protonema of the moss Physcomitrella patens, suggesting the possibility of recognizing peptide ligands from angiosperms by moss receptors. Mass spectrometry analysis of the moss Physcomitrella patens, both the wild type and the Δcerk mutant secretomes, revealed peptides that specifically responded to chitosan treatment, suggesting their role in immune signaling.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the manuscript. The mass spectrometry data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE (Perez-Riverol et al. 2019) partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD021721.
References
Beike AK, Spagnuolo V, Lüth V, Steinhart F, Ramos-Gómez J, Krebs M, Adamo P, Rey-Asensio AI, Angel Fernández J, Giordano S, Decker EL, Reski R (2015) Clonal in vitro propagation of peat mosses (Sphagnum L.) as novel green resources for basic and applied research. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult PCTOC 120:1037–1049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0658-2
Bigeard J, Colcombet J, Hirt H (2015) Signaling mechanisms in pattern-triggered immunity (PTI). Mol Plant 8:521–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2014.12.022
Boschiero C, Dai X, Lundquist PK, Roy S, de Bang TC, Zhang S, Zhuang Z, Torres-Jerez I, Udvardi MK, Scheible W-R, Zhao PX (2020) MtSSPdb: the medicago truncatula small secreted peptide database. Plant Physiol 183:399–413. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.01088
Boutrot F, Zipfel C (2017) Function, discovery, and exploitation of plant pattern recognition receptors for broad-spectrum disease resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 55:257–286. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-080614-120106
Bowles AMC, Bechtold U, Paps J (2020) The origin of land plants is rooted in two bursts of genomic novelty. Curr Biol 30:530-536.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2019.11.090
Bowman JL, Kohchi T, Yamato KT, Jenkins J, Shu S, Ishizaki K, Yamaoka S, Nishihama R, Nakamura Y, Berger F, Adam C, Aki SS, Althoff F, Araki T, Arteaga-Vazquez MA, Balasubrmanian S, Barry K, Bauer D, Boehm CR, Briginshaw L, Caballero-Perez J, Catarino B, Chen F, Chiyoda S, Chovatia M, Davies KM, Delmans M, Demura T, Dierschke T, Dolan L, Dorantes-Acosta AE, Eklund DM, Florent SN, Flores-Sandoval E, Fujiyama A, Fukuzawa H, Galik B, Grimanelli D, Grimwood J, Grossniklaus U, Hamada T, Haseloff J, Hetherington AJ, Higo A, Hirakawa Y, Hundley HN, Ikeda Y, Inoue K, Inoue S, Ishida S, Jia Q, Kakita M, Kanazawa T, Kawai Y, Kawashima T, Kennedy M, Kinose K, Kinoshita T, Kohara Y, Koide E, Komatsu K, Kopischke S, Kubo M, Kyozuka J, Lagercrantz U, Lin S-S, Lindquist E, Lipzen AM, Lu C-W, Luna ED, Martienssen RA, Minamino, N., Mizutani, Masaharu, Mizutani, Miya, Mochizuki, Monte N, Mosher I, Nagasaki R, Nakagami H, Naramoto H, Nishitani S, Ohtani K, Okamoto M, Okumura T, Phillips M, Pollak J, Reinders B, Rövekamp A, Sano M, Sawa R, Schmid S, Shirakawa MW, Solano M, Spunde R, Suetsugu A, Sugano N, Sugiyama S, Sun A, Suzuki R, Takenaka Y, Takezawa M, Tomogane D, Tsuzuki H, Ueda M, Umeda T, Ward M, Watanabe JM, Yazaki Y, Yokoyama K, Yoshitake R, Yotsui Y, Zachgo I, Schmutz S, J (2017) . Cell 171:287–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.030
Breiden M, Simon R (2016) Q&A: How does peptide signaling direct plant development? BMC Biol 14:58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-016-0280-3
Bressendorff S, Rasmussen MW, Petersen M, Mundy J (2017) Chitin-induced responses in the moss physcomitrella patens. In: Shan L, He P (eds) Plant pattern recognition receptors: methods and protocols. methods in molecular biology. Springer, New York, pp 317–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6859-6_27
Bressendorff S, Azevedo R, Kenchappa CS, Ponce de León I, Olsen JV, Rasmussen MW, Erbs G, Newman M-A, Petersen M, Mundy J (2016) An innate immunity pathway in the moss Physcomitrella patens. Plant Cell 28:1328–1342. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.15.00774
Butenko MA, Vie AK, Brembu T, Aalen RB, Bones AM (2009) Plant peptides in signalling: looking for new partners. Trends Plant Sci 14:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2009.02.002
Carella P, Gogleva A, Hoey DJ, Bridgen AJ, Stolze SC, Nakagami H, Schornack S (2019) Conserved biochemical defenses underpin host responses to oomycete infection in an early-divergent land plant lineage. Curr Biol 29:2282-2294.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2019.05.078
Campbell L, Turner SR (2017) A comprehensive analysis of RALF proteins in green plants suggests there are two distinct functional groups. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.000372017.00037
Chae K, Lord EM (2011) Pollen tube growth and guidance: roles of small, secreted proteins. Ann Bot 108:627–636. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcr015
Chen Y-L, Fan K-T, Hung S-C, Chen Y-R (2020) The role of peptides cleaved from protein precursors in eliciting plant stress reactions. New Phytol 225:2267–2282. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16241
Chen Y-L, Lee C-Y, Cheng K-T, Chang W-H, Huang R-N, Nam HG, Chen Y-R (2014) Quantitative peptidomics study reveals that a wound-induced peptide from PR-1 regulates immune signaling in tomato. Plant Cell 26:4135–4148. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.131185
Couto D, Zipfel C (2016) Regulation of pattern recognition receptor signalling in plants. Nat Rev Immunol 16:537–552. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.77
Cui H, Shi M-J, Meng R, Zhou J, Lai C-Z, Lin X-Q (2004) Effect of pH on inhibition and enhancement of luminol–H2O2–Co2 chemiluminescence by phenolic compounds and amino acids. Photochem Photobiol 79:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1562/BE-03-28.1
Czyzewicz N, Yue K, Beeckman T, De Smet I (2013) Message in a bottle: small signalling peptide outputs during growth and development. J Exp Bot 64:5281–5296. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert283
de Bang TC, Lundquist PK, Dai X, Boschiero C, Zhuang Z, Pant P, Torres-Jerez I, Roy S, Nogales J, Veerappan V, Dickstein R, Udvardi MK, Zhao PX, Scheible W-R (2017) Genome-wide identification of medicago peptides involved in macronutrient responses and nodulation. Plant Physiol 175:1669–1689. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.01096
de Vries J, de Vries S, Slamovits CH, Rose LE, Archibald JM (2017) How embryophytic is the biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids and their derivatives in streptophyte algae? Plant Cell Physiol 58:934–945. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcx037
De la Concepcion JC, Franceschetti M, MacLean D, Terauchi R, Kamoun S, Banfield MJ (2019) Protein engineering expands the effector recognition profile of a rice NLR immune receptor. eLife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47713
Delaux P-M, Radhakrishnan GV, Jayaraman D, Cheema J, Malbreil M, Volkening JD, Sekimoto H, Nishiyama T, Melkonian M, Pokorny L, Rothfels CJ, Sederoff HW, Stevenson DW, Surek B, Zhang Y, Sussman MR, Dunand C, Morris RJ, Roux C, Wong GK-S, Oldroyd GED, Ané J-M (2015) Algal ancestor of land plants was preadapted for symbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112:13390–13395. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1515426112
Delaux P-M, Hetherington AJ, Coudert Y, Delwiche C, Dunand C, Gould S, Kenrick P, Li F-W, Philippe H, Rensing SA, Rich M, Strullu-Derrien C, Vries J de (2019) Reconstructing trait evolution in plant evo–devo studies. Curr Biol 29:R1110–R1118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2019.09.044
Dufayard J-F, Bettembourg M, Fischer I, Droc G, Guiderdoni E, Périn C, Chantret N, Diévart A (2017) New insights on leucine-rich repeats receptor-like kinase orthologous relationships in angiosperms. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.003812017.00381
Felix G, Duran JD, Volko S, Boller T (1999) Plants have a sensitive perception system for the most conserved domain of bacterial flagellin. Plant J 18:265–276. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00265.x
Fesenko I, Kirov I, Knyazev A, Khazigaleeva R, Lazarev V, Kharlampieva D, Grafskaia E, Zgoda V, Butenko I, Arapidi G, Mamaeva A, Ivanov V, Govorun V (2019) Distinct types of short open reading frames are translated in plant cells. Genome Res. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.253302.119
Fesenko I, Azarkina R, Kirov I, Kniazev A, Filippova A, Grafskaia E, Lazarev V, Zgoda V, Butenko I, Bukato O, Lyapina I, Nazarenko D, Elansky S, Mamaeva A, Ivanov V, Govorun V (2019) Phytohormone treatment induces generation of cryptic peptides with antimicrobial activity in the moss physcomitrella patens. BMC Plant Biol 19:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1611-z
Filippova A, Lyapina I, Kirov I, Zgoda V, Belogurov A, Kudriaeva A, Ivanov V, Fesenko I (2019) Salicylic acid influences the protease activity and posttranslation modifications of the secreted peptides in the moss physcomitrella patens. J Pept Sci 25:e3138. https://doi.org/10.1002/psc.3138
Frangedakis E, Shimamura M, Villarreal JC, Li F-W, Tomaselli M, Waller M, Sakakibara K, Renzaglia KS, Szövényi P (2021) The hornworts: morphology, evolution and development. New Phytol 229:735–754. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16874
Fürst-Jansen JMR, de Vries S, de Vries J (2020) Evo-physio: on stress responses and the earliest land plants. J Exp Bot 71:3254–3269. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eraa007
Galotto G, Abreu I, Sherman C, Liu B, Gonzalez-Guerrero M, Vidali L (2020) Chitin triggers calcium-mediated immune response in the plant model physcomitrella patens. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 33:911–920. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-03-20-0064-R
Gao Y, Wang W, Zhang T, Gong Z, Zhao H, Han G-Z (2018) Out of water: the origin and early diversification of plant R-genes. Plant Physiol 177:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.00185
Ghorbani S, Lin Y-C, Parizot B, Fernandez A, Njo MF, Van de Peer Y, Beeckman T, Hilson P (2015) Expanding the repertoire of secretory peptides controlling root development with comparative genome analysis and functional assays. J Exp Bot 66:5257–5269. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv346
Gomes A, Fernandes E, Lima JLFC (2005) Fluorescence probes used for detection of reactive oxygen species. J Biochem Biophys Methods 65:45–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbbm.2005.10.003
Halliwell B, Whiteman M (2004) Measuring reactive species and oxidative damage in vivo and in cell culture: how should you do it and what do the results mean? Br J Pharmacol 142:231–255. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0705776
Han G-Z (2019) Origin and evolution of the plant immune system. New Phytol 222:70–83. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15596
Hao G, Pitino M, Duan Y, Stover E (2016) Reduced susceptibility to xanthomonas citri in transgenic citrus expressing the FLS2 Receptor From Nicotiana benthamiana. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact MPMI 29:132–142. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-09-15-0211-R
Huang W-J, Liu H-K, McCormick S, Tang W-H (2014) Tomato pistil factor STIG1 promotes in vivo pollen tube growth by binding to phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and the extracellular domain of the pollen receptor kinase LePRK2. Plant Cell 26:2505–2523. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.123281
Huffaker A, Pearce G, Ryan CA (2006) An endogenous peptide signal in Arabidopsis activates components of the innate immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:10098–10103. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0603727103
Huffaker A, Pearce G, Veyrat N, Erb M, Turlings TCJ, Sartor R, Shen Z, Briggs SP, Vaughan MM, Alborn HT, Teal PEA, Schmelz EA (2013) Plant elicitor peptides are conserved signals regulating direct and indirect antiherbivore defense. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:5707–5712. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1214668110
Kadota Y, Sklenar J, Derbyshire P, Stransfeld L, Asai S, Ntoukakis V, Jones JD, Shirasu K, Menke F, Jones A, Zipfel C (2014) Direct regulation of the NADPH oxidase RBOHD by the PRR-associated kinase BIK1 during plant immunity. Mol Cell 54:43–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.02.021
Klavina L, Springe G, Nikolajeva V, Martsinkevich I, Nakurte I, Dzabijeva D, Steinberga I (2015) Chemical composition analysis, antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity screening of moss extracts (moss phytochemistry). Molecules 20:17221–17243. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules200917221
Kovalchuk SI, Jensen ON, Rogowska-Wrzesinska A (2019) FlashPack: fast and simple preparation of ultrahigh-performance capillary columns for LC-MS. Mol Cell Proteomics: MCP 18:383–390. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.TIR118.000953
Kunze G, Zipfel C, Robatzek S, Niehaus K, Boller T, Felix G (2004) The N terminus of bacterial elongation factor Tu elicits innate immunity in arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell 16:3496–3507. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.026765
Lacombe S, Rougon-Cardoso A, Sherwood E, Peeters N, Dahlbeck D, van Esse HP, Smoker M, Rallapalli G, Thomma BPHJ, Staskawicz B, Jones JDG, Zipfel C (2010) Interfamily transfer of a plant pattern-recognition receptor confers broad-spectrum bacterial resistance. Nat Biotechnol 28:365–369. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1613
Lang D, Ullrich KK, Murat F, Fuchs J, Jenkins J, Haas FB, Piednoel M, Gundlach H, Bel MV, Meyberg R, Vives C, Morata J, Symeonidi A, Hiss M, Muchero W, Kamisugi Y, Saleh O, Blanc G, Decker EL, Gessel N van, Grimwood J, Hayes RD, Graham SW, Gunter LE, McDaniel SF, Hoernstein SNW, Larsson A, Li F-W, Perroud P-F, Phillips J, Ranjan P, Rokshar DS, Rothfels CJ, Schneider L, Shu S, Stevenson DW, Thümmler F, Tillich M, Aguilar JCV, Widiez T, Wong GK-S, Wymore A, Zhang Y, Zimmer AD, Quatrano RS, Mayer KFX, Goodstein D, Casacuberta JM, Vandepoele K, Reski R, Cuming AC, Tuskan GA, Maumus F, Salse J, Schmutz J, Rensing SA (2018) The Physcomitrella patens chromosome-scale assembly reveals moss genome structure and evolution. Plant J 93:515–533. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13801
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinforma. Oxf Engl 23:2947–2948. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Lease KA, Walker JC (2006) The arabidopsis unannotated secreted peptide database, a resource for plant peptidomics. Plant Physiol 142:831. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.086041
Lee MW, Huffaker A, Crippen D, Robbins RT, Goggin FL (2018) Plant elicitor peptides promote plant defences against nematodes in soybean. Mol Plant Pathol 19:858–869. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12570
Leebens-Mack JH, Barker MS, Carpenter EJ, Deyholos MK, Gitzendanner MA,Graham SW, Grosse I, Li Z, Melkonian M, Mirarab S, Porsch M, Quint M, Rensing SA, Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Stevenson DW, Ullrich KK, Wickett NJ, DeGironimo L, Edger PP, Jordon-Thaden IE, Joya S, Liu T, Melkonian B, Miles NW, Pokorny L, Quigley C, Thomas P, Villarreal JC, Augustin MM, Barrett MD, Baucom RS, Beerling DJ, Benstein RM, Biffin E, Brockington SF, Burge DO, Burris JN, Burris KP, Burtet-Sarramegna V, Caicedo AL, Cannon SB, Çebi Z, Chang Y, Chater C, Cheeseman JM, Chen T, Clarke ND, Clayton H, Covshoff S, Crandall-Stotler BJ, Cross H, dePamphilis CW, Der JP, Determann R, Dickson RC, Di Stilio VS, Ellis S, Fast E, Feja N, Field KJ, Filatov DA, Finnegan PM, Floyd SK, Fogliani B, García N, Gâteblé G, Godden GT, Goh F, Qi Y, Greiner S, Harkess A, Heaney JM, Helliwell KE, Heyduk K, Hibberd JM, Hodel RGJ, Hollingsworth PM, Johnson MTJ, Jost R, Joyce B, Kapralov MV, Kazamia E, Kellogg EA, Koch MA, VonKonrat M, Könyves K, Kutchan TM, Lam V, Larsson A, Leitch AR, Lentz R, Li F-W, Lowe AJ, Ludwig M, Manos PS, Mavrodiev E, McCormick MK, McKain M, McLellan T, McNeal JR, Miller RE, Nelson MN, Peng Y, Ralph P, Real D, Riggins CW, Ruhsam M, Sage RF, Sakai AK, Scascitella M, Schilling EE, Schlösser E-M, Sederoff H, Servick S, Sessa EB, Shaw AJ, Shaw SW, Sigel EM, Skema C, Smith AG, Smithson A, Stewart CN, Stinchcombe JR, Szövényi P, Tate JA, Tiebel H, Trapnell D, Villegente M, Wang C-N, Weller SG, Wenzel M, Weststrand S, Westwood JH, Whigham DF, Wu S, Wulff AS, Yang Y, Zhu D, Zhuang C, Zuidof J, Chase MW, Pires JC, Rothfels CJ, Yu J, Chen C, Chen L, Cheng S, Li J, Li R, Li X, Lu H, Ou Y, Sun X, Tan X, Tang J, Tian Z, Wang F, Wang J, Wei X, Xu X, Yan Z, Yang F, Zhong X, Zhou F, Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Ayyampalayam S, Barkman TJ, Nguyen N, Matasci N, Nelson DR, Sayyari E, Wafula EK, Walls RL, Warnow T, An H, Arrigo N, Baniaga AE, Galuska S, Jorgensen SA, Kidder TI, Kong H, Lu-Irving P, Marx HE, Qi X, Reardon CR, Sutherland BL, Tiley GP, Welles SR, Yu R, Zhan S, Gramzow L, Theißen G, Wong GK-S. (2019) One thousand plant transcriptomes initiative. One thousand plant transcriptomes and the phylogenomics of green plants. Nature 574:679–685. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1693-2
Lehtonen MT, Akita M, Frank W, Reski R, Valkonen JPT (2012) Involvement of a class III peroxidase and the mitochondrial protein TSPO in oxidative burst upon treatment of moss plants with a fungal elicitor. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact MPMI 25:363–371. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-10-11-0265
Lehtonen MT, Akita M, Kalkkinen N, Ahola-Iivarinen E, Rönnholm G, Somervuo P, Thelander M, Valkonen JPT (2009) Quickly-released peroxidase of moss in defense against fungal invaders. N Phytologist 183:432–443. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02864.x
Li YL, Dai XR, Yue X, Gao X-Q, Zhang XS (2014) Identification of small secreted peptides (SSPs) in maize and expression analysis of partial SSP genes in reproductive tissues. Planta 240:713–728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-014-2123-1
Liu F, Zhang X, Lu C, Zeng X, Li Y, Fu D, Wu G (2015) Non-specific lipid transfer proteins in plants: presenting new advances and an integrated functional analysis. J Exp Bot 66:5663–5681. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv313
Lori M, van Verk MC, Hander T, Schatowitz H, Klauser D, Flury P, Gehring CA, Boller T, Bartels S (2015) Evolutionary divergence of the plant elicitor peptides (Peps) and their receptors: interfamily incompatibility of perception but compatibility of downstream signalling. J Exp Bot 66:5315–5325. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv236
Luo W, Xiao Y, Liang Q, Su Y, Xiao L (2019) Identification of potential auxin-responsive small signaling peptides through a peptidomics approach in Arabidopsis thaliana. Molecules 24:3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24173146
Luu DD, Joe A, Chen Y, Parys K, Bahar O, Pruitt R, Chan LJG, Petzold CJ, Long K, Adamchak C, Stewart V, Belkhadir Y, Ronald PC (2019) Biosynthesis and secretion of the microbial sulfated peptide RaxX and binding to the rice XA21 immune receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:8525–8534. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1818275116
Ma Y, Zhao Y, Walker RK, Berkowitz GA (2013) Molecular steps in the immune signaling pathway evoked by plant elicitor peptides: Ca2+-dependent protein kinases, nitric oxide, and reactive oxygen species are downstream from the early Ca2 + signal1[OPEN]. Plant Physiol 163:1459–1471. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.226068
Matsui H, Iwakawa H, Hyon G-S, Yotsui I, Katou S, Monte I, Nishihama R, Franzen R, Solano R, Nakagami H (2020) Isolation of natural fungal pathogens from marchantia polymorpha reveals antagonism between salicylic acid and jasmonate during liverwort–fungus interactions. Plant Cell Physiol 61:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcz187
Mergaert P, Nikovics K, Kelemen Z, Maunoury N, Vaubert D, Kondorosi A, Kondorosi E (2003) A novel family in Medicago truncatula consisting of more than 300 nodule-specific genes coding for small, secreted polypeptides with conserved cysteine motifs. Plant Physiol 132:161–173. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.102.018192
Miya A, Albert P, Shinya T, Desaki Y, Ichimura K, Shirasu K, Narusaka Y, Kawakami N, Kaku H, Shibuya N (2007) CERK1, a LysM receptor kinase, is essential for chitin elicitor signaling in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19613–19618. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0705147104
Monte I, Franco-Zorrilla JM, García-Casado G, Zamarreño AM, García-Mina JM, Nishihama R, Kohchi T, Solano R, (2019) A single JAZ repressor controls the Jasmonate pathway in Marchantia polymorpha. Mol. Plant 12:185–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2018.12.0172018.12.017
Monte I, Ishida S, Zamarreño AM, Hamberg M, Franco-Zorrilla JM, García-Casado G, Gouhier-Darimont C, Reymond P, Takahashi K, García-Mina JM, Nishihama R, Kohchi T, Solano R (2018) Ligand-receptor co-evolution shaped the jasmonate pathway in land plants. Nat Chem Biol 14:480–488. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-018-0033-4
Murphy E, Smith S, Smet ID (2012) Small signaling peptides in arabidopsis development: how cells communicate over a short distance. Plant Cell 24:3198. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.099010
Nallu S, Silverstein KAT, Samac DA, Bucciarelli B, Vance CP, VandenBosch KA (2013) Regulatory patterns of a large family of defensin-like genes expressed in nodules of Medicago truncatula. PLoS ONE 8:e60355. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060355
Oelkers K, Goffard N, Weiller GF, Gresshoff PM, Mathesius U, Frickey T (2008) Bioinformatic analysis of the CLE signaling peptide family. BMC Plant Biol 8:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-8-1
Oh E, Seo PJ, Kim J (2018) Signaling peptides and receptors coordinating plant root development. Trends Plant Sci 23:337–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2017.12.007
Ohyama K, Ogawa M, Matsubayashi Y (2008) Identification of a biologically active, small, secreted peptide in Arabidopsis by in silico gene screening, followed by LC-MS-based structure analysis. Plant J 55:152–160. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03464.x
Oliver JP, Castro A, Gaggero C, Cascón T, Schmelz EA, Castresana C, Ponce de León I (2009) Pythium infection activates conserved plant defense responses in mosses. Planta 230:569–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-009-0969-4
Onrubia M, Pollier J, Bossche RV, Goethals M, Gevaert K, Moyano E, Vidal-Limon H, Cusidó RM, Palazón J, Goossens A (2014) Taximin, a conserved plant-specific peptide is involved in the modulation of plant-specialized metabolism. Plant Biotechnol J 12:971–983. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12205
Overdijk EJR, Keijzer JD, Groot DD, Schoina C, Bouwmeester K, Ketelaar T, Govers F (2016) Interaction between the moss Physcomitrella patens and Phytophthora: a novel pathosystem for live-cell imaging of subcellular defence. J Microsc 263:171–180. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmi.12395
Pan B, Sheng J, Sun W, Zhao Y, Hao P, Li X (2013) OrysPSSP: a comparative platform for small secreted proteins from rice and other plants. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D1192–D1198. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1090
Pastor-Fernández J, Gamir J, Pastor V, Sanchez-Bel P, Sanmartín N, Cerezo M, Flors V (2020) Arabidopsis plants sense non-self peptides to promote resistance against Plectosphaerella cucumerina. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.005292020.00529
Pavelescu L (2015) On reactive oxygen species measurement in living systems. J Med Life 8:38–42
Peñuelas M, Monte I, Schweizer F, Vallat A, Reymond P, García-Casado G, Franco-Zorrilla JM, Solano R (2019) Jasmonate-related MYC transcription factors are functionally conserved in Marchantia polymorpha. Plant Cell 31:2491–2509. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00974
Perez-Riverol Y, Csordas A, Bai J, Bernal-Llinares M, Hewapathirana S, Kundu DJ, Inuganti A, Griss J, Mayer G, Eisenacher M, Pérez E, Uszkoreit J, Pfeuffer J, Sachsenberg T, Yilmaz S, Tiwary S, Cox J, Audain E, Walzer M, Jarnuczak AF, Ternent T, Brazma A, Vizcaíno JA (2019) The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D442–D450. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1106
Plattner S, Gruber C, Stadlmann J, Widmann S, Gruber CW, Altmann F, Bohlmann H (2015) Isolation and characterization of a thionin proprotein-processing enzyme from barley. J Biol Chem 290:18056–18067. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.647859
Ponce de León I, Montesano M (2013) Activation of defense mechanisms against pathogens in mosses and flowering plants. Int J Mol Sci 14:3178–3200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14023178
Ponce de León I, Oliver JP, Castro A, Gaggero C, Bentancor M, Vidal S (2007) Erwinia carotovora elicitors and Botrytis cinerea activate defense responses in Physcomitrella patens. BMC Plant Biol 7:52. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-7-52
Ponce de León I, Schmelz EA, Gaggero C, Castro A, Alvarez A, Montesano M (2012) Physcomitrella patens activates reinforcement of the cell wall, programmed cell death and accumulation of evolutionary conserved defence signals, such as salicylic acid and 12-oxo‐phytodienoic acid, but not jasmonic acid, upon Botrytis cinerea infection. Mol Plant Pathol 13:960–974. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2012.00806.x
Ponce de León I (2011) The moss physcomitrella patens as a model system to study interactions between plants and phytopathogenic fungi and oomycetes. J. Pathog. 2011:719873. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/7198732011/719873
Puttick MN, Morris JL, Williams TA, Cox CJ, Edwards D, Kenrick P, Pressel S, Wellman CH, Schneider H, Pisani D, Donoghue PCJ (2018) The interrelationships of land plants and the nature of the ancestral embryophyte. Curr Biol 28:733-745.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.01.063
Qi J, Wang J, Gong Z, Zhou J-M (2017) Apoplastic ROS signaling in plant immunity. Curr. Opin Plant Biol Biotic interactions 38:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2017.04.0222017.04.022
Qiu Y-L, Li L, Wang B, Chen Z, Knoop V, Groth-Malonek M, Dombrovska O, Lee J, Kent L, Rest J, Estabrook GF, Hendry TA, Taylor DW, Testa CM, Ambros M, Crandall-Stotler B, Duff RJ, Stech M, Frey W, Quandt D, Davis CC (2006) The deepest divergences in land plants inferred from phylogenomic evidence. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:15511–15516. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0603335103
Reboledo G, del Campo R, Alvarez A, Montesano M, Mara H, Ponce de León I (2015) Physcomitrella patens activates defense responses against the pathogen Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Int J Mol Sci 16:22280–22298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160922280
Rocco M, Corrado G, Arena S, D’Ambrosio C, Tortiglione C, Sellaroli S, Marra M, Rao R, Scaloni A (2008) The expression of tomato prosystemin gene in tobacco plants highly affects host proteomic repertoire. J Proteom 71:176–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2008.04.003
Roux M, Schwessinger B, Albrecht C, Chinchilla D, Jones A, Holton N, Malinovsky FG, Tör M, de Vries S, Zipfel C (2011) The Arabidopsis leucine-rich repeat receptor–like kinases BAK1/SERK3 and BKK1/SERK4 are required for innate immunity to hemibiotrophic and biotrophic pathogens[W]. Plant Cell 23:2440–2455. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.084301
Ruiz C, Nadal A, Foix L, Montesinos L, Montesinos E, Pla M (2018) Diversity of plant defense elicitor peptides within the Rosaceae. BMC Genet 19:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-017-0593-4
Saur IML, Kadota Y, Sklenar J, Holton NJ, Smakowska E, Belkhadir Y, Zipfel C, Rathjen JP (2016) NbCSPR underlies age-dependent immune responses to bacterial cold shock protein in Nicotiana benthamiana. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113:3389–3394. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1511847113
Schoonbeek H, Wang H-H, Stefanato FL, Craze M, Bowden S, Wallington E, Zipfel C, Ridout CJ (2015) Arabidopsis EF-Tu receptor enhances bacterial disease resistance in transgenic wheat. New Phytol 206:606–613. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13356
Schwessinger B, Bahar O, Thomas N, Holton N, Nekrasov V, Ruan D, Canlas PE, Daudi A, Petzold CJ, Singan VR, Kuo R, Chovatia M, Daum C, Heazlewood JL, Zipfel C, Ronald PC (2015) Transgenic expression of the dicotyledonous pattern recognition receptor EFR in rice leads to ligand-dependent activation of defense responses. PLoS Pathog. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004809
Shapiguzov A, Vainonen J, Wrzaczek M, Kangasjärvi J (2012) ROS-talk – how the apoplast, the chloroplast, and the nucleus get the message through. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2012.002922012.00292
Shaw AJ, Schmutz J, Devos N, Shu S, Carrell AA, Weston DJ (2016) Chapter five---the sphagnum genome project: a new model for ecological and evolutionary genomics. In: Rensing SA (Ed) Advances in botanical research, genomes and evolution of charophytes, bryophytes, lycophytes and ferns. Academic Press, London, pp 167–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.abr.2016.01.0032016.01.003
Shiu SH, Bleecker AB (2003) Expansion of the receptor-like kinase/Pelle gene family and receptor-like proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 132:530–543. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.021964
Shiu S-H, Karlowski WM, Pan R, Tzeng Y-H, Mayer KFX, Li W-H (2004) Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell 16:1220–1234. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.020834
Slavokhotova AA, Shelenkov AA, Andreev YaA, Odintsova TI (2017) Hevein-like antimicrobial peptides of plants. Biochem Mosc 82:1659–1674. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917130065
Smakowska-Luzan E, Mott GA, Parys K, Stegmann M, Howton TC, Layeghifard M, Neuhold J, Lehner A, Kong J, Grünwald K, Weinberger N, Satbhai SB, Mayer D, Busch W, Madalinski M, Stolt-Bergner P, Provart NJ, Mukhtar MS, Zipfel C, Desveaux D, Guttman DS, Belkhadir Y (2018) An extracellular network of Arabidopsis leucine-rich repeat receptor kinases. Nature 553:342–346. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25184
Smirnova AV, Matveyeva NP, Polesskaya OG, Yermakov IP (2009) Generation of reactive oxygen species during pollen grain germination. Russ J Dev Biol 40:345. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360409060034
Song WY, Wang GL, Chen LL, Kim HS, Pi LY, Holsten T, Gardner J, Wang B, Zhai WX, Zhu LH, Fauquet C, Ronald P (1995) A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene, Xa21. Science 270: 1804–1806. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.270.5243.18041804
Sugita S, Yamada Y, Horie S, Nakamura O, Ishidoh K, Yamamoto Y, Yamagami S, Mochizuki M (2011) Induction of T regulatory cells by cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-2α on corneal endothelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:2598–2605. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.10-6322
Vellosillo T, Vicente J, Kulasekaran S, Hamberg M, Castresana C (2010) Emerging complexity in reactive oxygen species production and signaling during the response of plants to pathogens. Plant Physiol 154:444–448. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.161273
Virtanen P, Gommers R, Oliphant TE, Haberland M, Reddy T, Cournapeau D, Burovski E, Peterson P, Weckesser W, Bright J, van der Walt SJ, Brett M, Wilson J, Millman KJ, Mayorov N, Nelson ARJ, Jones E, Kern R, Larson E, Carey CJ, Polat İ, Feng Y, Moore EW, VanderPlas J, Laxalde D, Perktold J, Cimrman R, Henriksen I, Quintero EA, Harris CR, Archibald AM, Ribeiro AH, Pedregosa F, van Mulbregt P (2020) SciPy 1.0: fundamental algorithms for scientific computing in Python. Nat Methods 17:261–272. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-019-0686-2
Vries S de, Vries J de, Dahlen JK von, Gould SB, Archibald JM, Rose LE, Slamovits CH (2018) On plant defense signaling networks and early land plant evolution. Commun Integr Biol 11:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/19420889.2018.1486168
Wan J, Zhang X-C, Neece D, Ramonell KM, Clough S, Kim S-Y, Stacey MG, Stacey G (2008) A LysM receptor-like kinase plays a critical role in chitin signaling and fungal resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20:471–481. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.056754
Wang P, Yao S, Kosami K, Guo T, Li J, Zhang Y, Fukao Y, Kaneko-Kawano T, Zhang H, She Y-M, Wang P, Xing W, Hanada K, Liu R, Kawano Y (2020) Identification of endogenous small peptides involved in rice immunity through transcriptomics- and proteomics-based screening. Plant Biotechnol J 18:415–428. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13208
Waterhouse AM, Procter JB, Martin DMA, Clamp M, Barton GJ (2009) Jalview Version 2—a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 25:1189–1191. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp033
Whitewoods CD, Cammarata J, Nemec Venza Z, Sang S, Crook AD, Aoyama T, Wang XY, Waller M, Kamisugi Y, Cuming AC, Szövényi P, Nimchuk ZL, Roeder AHK, Scanlon MJ, Harrison CJ (2018) CLAVATA was a genetic novelty for the morphological innovation of 3d growth in land plants. Curr Biol 28:2365-2376.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.05.068
Wickett NJ, Mirarab S, Nguyen N, Warnow T, Carpenter E, Matasci N, Ayyampalayam S, Barker MS, Burleigh JG, Gitzendanner MA, Ruhfel BR, Wafula E, Der JP, Graham SW, Mathews S, Melkonian M, Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Miles NW, Rothfels CJ, Pokorny L, Shaw AJ, DeGironimo L, Stevenson DW, Surek B, Villarreal JC, Roure B, Philippe H, dePamphilis CW, Chen T, Deyholos MK, Baucom RS, Kutchan TM, Augustin MM, Wang J, Zhang Y, Tian Z, Yan Z, Wu X, Sun X, Wong GK-S, Leebens-Mack J (2014) Phylotranscriptomic analysis of the origin and early diversification of land plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:E4859–E4868. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1323926111
Yamaguchi Y, Huffaker A (2011) Endogenous peptide elicitors in higher plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:351–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2011.05.001
Yamaguchi Y, Huffaker A, Bryan AC, Tax FE, Ryan CA (2010) PEPR2 Is a second receptor for the Pep1 and Pep2 peptides and contributes to defense responses in arabidopsis. Plant Cell 22:508–522. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.068874
Zhang H, Hu Y (2017) Long-distance transport of prosystemin messenger RNA in tomato. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.018942017.01894
Zhang H, Yu P, Zhao J, Jiang H, Wang H, Zhu Y, Botella MA, Šamaj J, Li C, Lin J (2018) Expression of tomato prosystemin gene in Arabidopsis reveals systemic translocation of its mRNA and confers necrotrophic fungal resistance. New Phytol 217:799–812. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14858
Zhang J, Fu X-X, Li R-Q, Zhao X, Liu Y, Li M-H, Zwaenepoel A, Ma H, Goffinet B, Guan Y-L, Xue J-Y, Liao Y-Y, Wang Q-F, Wang Q-H, Wang J-Y, Zhang G-Q, Wang Z-W, Jia Y, Wang M-Z, Dong S-S, Yang J-F, Jiao Y-N, Guo Y-L, Kong H-Z, Lu A-M, Yang H-M, Zhang S-Z, Van de Peer Y, Liu Z-J, Chen Z-D (2020a) The hornwort genome and early land plant evolution. Nature Plants 6:107–118. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-019-0588-4
Zhang Z, Liu L, Kucukoglu M, Tian D, Larkin RM, Shi X, Zheng B (2020) Predicting and clustering plant CLE genes with a new method developed specifically for short amino acid sequences. BMC Genom. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.2.21530/v2
Zhou B, Benbow HR, Brennan CJ, Arunachalam C, Karki SJ, Mullins E, Feechan A, Burke JI, Doohan FM (2020) Wheat encodes small, secreted proteins that contribute to resistance to septoria tritici blotch. Front Genet. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.004692020.00469
Zhou P, Silverstein KA, Gao L, Walton JD, Nallu S, Guhlin J, Young ND (2013) Detecting small plant peptides using SPADA (small peptide alignment discovery application). BMC Bioinform 14:335. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-335
Funding
This work was funded by the Russian Science Foundation (Project No. 17-14-01189).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
IL, AF, IF wrote the manuscript. IL, AF conducted all experiments, performed bioinformatic search for SSP candidates and contributed to data analysis. AM, EM and OP contributed to ROS accumulation analysis. OI performed bioinformatic search for homologes of receptor-like kinases. SK, RZ conducted mass-spectrometry analysis. VL and IL conducted peptide synthesis. IF performed data analysis. IF and VI designed and supervised the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Consent for publication
All authors have approved the manuscript and agreed with its submission.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyapina, I., Filippova, A., Kovalchuk, S. et al. Possible role of small secreted peptides (SSPs) in immune signaling in bryophytes. Plant Mol Biol 106, 123–143 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-021-01133-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-021-01133-z