ABSTRACT
Purpose
To incorporate phospho-ibuprofen (P-I), a lipophilic, water insoluble novel anti-cancer agent, into pegylated liposomes and upon formulation optimization to evaluate its antitumor activity in vitro and in vivo.
Methods
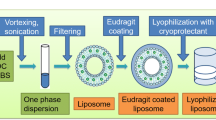
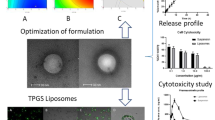
P-I loaded liposomes were prepared using the thin-film hydration method, and characterized for size, zeta potential, drug content and drug release. We examined their physical stability by particle size changes; their lyophilization ability in the presence of cryoprotectants; and their antitumor activity in vitro in human cancer cell lines and in vivo in a xenograft murine model.
Results
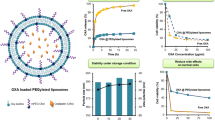
P-I was successfully loaded into liposomes consisting of soy-PC and PEG2000-PE. These liposomes were <150 nm in diameter; exhibited prolonged stability in suspension and can be lyophilized using sucrose as cryoprotectant. P-I liposomes inhibited the growth of human cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo of xenograft in nude mice to a greater extent than free P-I.
Conclusions
High levels of P-I can be incorporated into liposomes which can be lyophilized in the presence of sucrose and showed good stability upon storage. Moreover, these drug-incorporating liposomes were capable of inhibiting the growth of xenografted tumors in mice more effectively than free P-I. These results justify further development of the P-I liposomes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EE:
-
entrapment efficiency
- egg-PC:
-
egg-phosphatidylcholine
- P-I:
-
phospho-ibuprofen
- RES:
-
recticuloendothelial system
- soy-PC:
-
soy-phosphatidylcholine
- soy-PE:
-
soy-phosphatidylethanolamine
- soy-PS:
-
soy-phosphatidylserine
REFERENCES
Coussensand LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 2002;420:860–7.
Harris RE, Namboodiri KK, Farrar WB. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and breast cancer. Epidemiology. 1996;7:203–5.
Marnett LJ. Aspirin and related nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as chemopreventive agents against colon cancer. Prev Med. 1995;24:103–6.
Meier CR, Schmitz S, Jick H. Association between acetaminophen or nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and risk of developing ovarian, breast, or colon cancer. Pharmacotherapy. 2002;22:303–9.
Harris RE, Beebe-Donk J, Doss H, Burr Doss D. Aspirin, ibuprofen, and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in cancer prevention: a critical review of non-selective COX-2 blockade (review). Oncol Rep. 2005;13:559–83.
Huang L, Zhu C, Sun Y, Xie G, Mackenzie GG, Qiao G, et al. Phospho-sulindac (OXT-922) inhibits the growth of human colon cancer cell lines: a redox/polyamine-dependent effect. Carcinogenesis. 2010;31:1982–90.
Mackenzie GG, Sun Y, Huang L, Xie G, Ouyang N, Gupta RC, et al. Phospho-sulindac (OXT-328), a novel sulindac derivative, is safe and effective in colon cancer prevention in mice. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:1320–32.
Xie G, Sun Y, Nie T, Mackenzie GG, Huang L, Kopelovich L, et al. Phospho-ibuprofen (MDC-917) is a novel agent against colon cancer: efficacy, metabolism, and pharmacokinetics in mouse models. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011;337:876–86.
Immordino ML, Dosio F, Cattel L. Stealth liposomes: review of the basic science, rationale, and clinical applications, existing and potential. Int J Nanomedicine. 2006;1:297–315.
Crosasso P, Ceruti M, Brusa P, Arpicco S, Dosio F, Cattel L. Preparation, characterization and properties of sterically stabilized paclitaxel-containing liposomes. J Control Release. 2000;63:19–30.
Markman M. Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin: appraisal of its current role in the management of epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2011;3:219–25.
Torchilin VP. Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4:145–60.
Gabizon A, Goren D, Horowitz AT, Tzemach D, Lossos A, Siegal T. Long-circulating liposomes for drug delivery in cancer therapy: a review of biodistribution studies in tumor-bearing animals. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 1997;24:337–44.
Yuan F, Dellian M, Fukumura D, Leunig M, Berk DA, Torchilin VP, et al. Vascular permeability in a human tumor xenograft: molecular size dependence and cutoff size. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3752–6.
Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983;65:55–63.
Hwang TL, Lee WR, Hua SC, Fang JY. Cisplatin encapsulated in phosphatidylethanolamine liposomes enhances the in vitro cytotoxicity and in vivo intratumor drug accumulation against melanomas. J Dermatol Sci. 2007;46:11–20.
Roy MT, Gallardo M, Estelrich J. Influence of size on electrokinetic behavior of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine lipid vesicles. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1998;206:512–7.
Bittmanand R, Blau L. The phospholipid-cholesterol interaction. Kinetics of water permeability in liposomes. Biochemistry. 1972;11:4831–9.
Papahadjopoulos D, Cowden M, Kimelberg H. Role of cholesterol in membranes. Effects on phospholipid-protein interactions, membrane permeability and enzymatic activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973;330:8–26.
Sharmaand A, Sharma US. Liposomes in drug delivery: progress and limitations. Int J Pharm. 1997;154:123–40.
Yoshiharaand E, Nakae T. Cytolytic activity of liposomes containing stearylamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986;854:93–101.
Crowe LM, Crowe JH, Rudolph A, Womersley C, Appel L. Preservation of freeze-dried liposomes by trehalose. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985;242:240–7.
Huang L, Mackenzie G, Ouyang N, Sun Y, Xie G, Johnson F, et al. The novel phospho-non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, OXT-328, MDC-22 and MDC-917, inhibit adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;162:1521–33.
Matsumuraand Y, Maeda H. A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs. Cancer Res. 1986;46:6387–92.
Sarisuta N, Benjakul R, Panyarachun B. Preparation of dry reconstituted liposomal powder by freeze-drying at room temperature. J Liposome Res. 2011;21:28–37.
Fahr A, van Hoogevest P, May S, Bergstrand N, Leigh MLS. Transfer of lipophilic drugs between liposomal membranes and biological interfaces: consequences for drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2005;26:251–65.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS & DISCLOSURES
Financial support was from NIH grant HHSN261201000109C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattheolabakis, G., Nie, T., Constantinides, P.P. et al. Sterically Stabilized Liposomes Incorporating the Novel Anticancer Agent Phospho-Ibuprofen (MDC-917): Preparation, Characterization, and In Vitro/In Vivo Evaluation. Pharm Res 29, 1435–1443 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-011-0619-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-011-0619-y