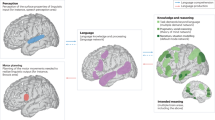
Abstract
The role of corticostriatal circuits in language functions is unclear. In this review, we consider evidence from language learning, syntax, and controlled language production and comprehension tasks that implicate various corticostriatal circuits. Converging evidence from neuroimaging in healthy individuals, studies in populations with subcortical dysfunction, pharmacological studies, and brain stimulation suggests a domain-general regulatory role of corticostriatal systems in language operations. The role of corticostriatal systems in language operations identified in this review is likely to reflect a broader function of the striatum in responding to uncertainty and conflict which demands selection, sequencing, and cognitive control. We argue that this role is dynamic and varies depending on the degree and form of cognitive control required, which in turn will recruit particular corticostriatal circuits and components organised in a cognitive hierarchy.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Recently, Seeley (2019) suggested that there is a further distinction between the cingulo-opercular task-control network and a separate, but anatomically close, saliency network. The cingulo-opercular network described by Dosenbach and colleagues (2007), he suggests, incorporates the dorsal aI and frontal operculum and is involved in task-set initiation and maintenance. In contrast, he suggests that the saliency network, as described by Seeley and colleagues (2007), incorporates the more ventral aI and functions to engage, maintain or switch the task-control network in response to changes in salient stimuli.
References
Abdullaev, Y. G., Bechtereva, N. P., & Melnichuk, K. V. (1998). Neuronal activity of human caudate nucleus and prefrontal cortex in cognitive tasks. Behavioral Brain Research, 97, 159–177.
Abutalebi, J., & Green, D. (2007). Bilingual language production: The neurocognition of language representation and control. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 20(3), 242–275.
Abutalebi, J., & Green, D. W. (2008). Control mechanisms in bilingual language production: Neural evidence from language switching studies. Language and Cognitive Processes, 23, 557–582.
Abutalebi, J., Rosa, P. A. D., Castro Gonzaga, A. K., et al. (2013). The role of the left putamen in multilingual language production. Brain and Language, 125, 307–315.
Alegre, M., Lopez-Azcarate, J., Obeso, I., Wilkinson, L., Rodriguez-Oroz, M. C., Valencia, M., Garcia-Garcia, D., Guridi, J., Artieda, J., Jahanshahi, M., & Obeso, J. A. (2013). The subthalamic nucleus is involved in successful inhibition in the stop-signal task: a local field potential study in Parkinson's disease. Experimental Neurology, 239, 1–12.
Alexander, C. E., DeLong, M. R., & Strick, P. L. (1986). Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking the basal ganglia and cortex. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 9, 357–381.
Ardila, A., Bernal, B., & Rosselli, M. (2016). How localized are language brain areas? A review of Brodmann areas involvement in oral language. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 31, 112–122.
Argyropoulos, G., Tremblay, P., & Small, S. (2013). The neostriatum and response selection in overt sentence production: An fMRI study. NeuroImage, 82, 53–60.
Ali, N., Green, D. W., Kherif, F., Devlin, J. T., & Price, C. J. (2010). The role of the left head of caudate in suppressing irrelevant words. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 22(10), 2369–2386.
Angwin, A. J., Chenery, H. J., Copland, D. A., Murdoch, B. E., & Silburn, P. A. (2005). Summation of semantic priming and complex sentence comprehension in Parkinson’s disease. Cognitive Brain Research, 25(1), 78–89.
Angwin, A. J., Chenery, H. J., Copland, D. A., Murdoch, B. E., & Silburn, P. A. (2006). Self-paced reading and sentence comprehension in Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 19, 239–252.
Anzak A, Gaynor L, Beigi M, Limousin P, Hariz M, Zrinzo L, Foltynie T, Brown P, Jahanshahi M. (2011). A gamma band specific role of the subthalamic nucleus in switching during verbal fluency tasks in Parkinson's disease. Experimental Neurology, 232, 136–142.
Aron, A.R, Poldrack, R.A., & Wise, S.P. (2009): Cognition: basal ganglia role; in Squire LR (ed.): Encyclopedia of Neuroscience, vol 2, pp 1069–1077.
Aron, A. R., Shohamy, D., Clark, J., Myers, C., Gluck, M. A., & Poldrack, R. A. (2004). Human midbrain sensitivity to cognitive feedback and uncertainty during classification learning. Journal of Neurophysiology, 92(2), 1144–1152.
Arnott, W. L., Copland, D. A., Chenery, H. J., Murdoch, B. E., Silburn, P. A., & Angwin, A. J. (2011). The influence of dopamine on automatic and controlled semantic activation in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinson’s Disease, 2011, 157072.
Ashby, F. G., & Maddox, W. T. (2005). Human category learning. Annual Review of Psychology, 56, 149–178.
Averbeck, B.B., Lehman, J., Jacobson, M., & Haber, S.N. (2014). Estimates of projection overlap and zones of convergence within frontal-striatal circuits. Journal of Neuroscience, 34 (29), 9497–9505.
Badre, D., Lebrecht, S., Pagliaccio, D., Long, N. M., & Scimeca, J. M. (2014). Ventral striatum and the evaluation of memory retrieval strategies. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 26(9), 1928–1948.
Badre, D., & Frank, M. J. (2012). Mechanisms of hierarchical reinforcement learning in cortico-striatal circuits 2: evidence from fMRI. Cerebral Cortex, 22(3), 527–536.
Bahlmann, J., Schubotz, R. I., & Friederici, A. D. (2008). Hierarchical artificial grammar processing engages Broca's area. NeuroImage, 42(2), 525–534.
Bell, P. T., & Shine, J. M. (2016). Subcortical contributions to large-scale network communication. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Review, 71, 313–322.
Berens, S. C., Horst, J. S., & Bird, C. M. (2018). Cross-Situational Learning Is Supported by Propose-but-Verify Hypothesis Testing. Current Biology, 28(7), 1132–1136.
Berg, E., Bjornram, C., Hartelius, L., Laakso, K., & Johnels, B. (2003). High-level language difficulties in Parkinson’s disease. Clinical Linguistics and Phonetics, 17(1), 63–80.
Bhattasali, S., Fabre, M., Luh, W., Saied, H., Constant, M., Pallier, C., et al. (2019). Localising memory retrieval and syntactic composition: an fMRI study of naturalistic language comprehension. Language, Cognition and Neuroscience, 34, 491–510.
Bohsali, A., & Crosson, B. (2016). The basal ganglia and language: A tale of two loops. In J.J. Soghomonian (ed.), The Basal Ganglia, Innovations in Cognitive Neuroscience, 217–242.
Binder, J. R., McKiernan, K. A., Parsons, M. E., Westbury, C. F., Possing, E. T., Kaufman, J. N., & Buchanan, L. (2003). Neural correlates of lexical access during visual word recognition. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 15, 372–393.
Booth, J. R., Wood, L., Lu, D., Houk, J. C., & Bitan, T. (2007). The role of the basal ganglia and cerebellum in language processing. Brain Research, 1133, 136–144.
Bouquet, C. A., Bonnaud, V., & Gil, R. (2003). Investigation of supervisory attentional system functions in patients with Parkinson’s disease using the Hayling task. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 25(6), 751–760.
Bradley, K. A., King, K. E., & Hernandez, A. E. (2013). Language experience differentiates prefrontal and subcortical activation of the cognitive control network in novel word learning. NeuroImage, 67, 101–110.
Brittain, J. S., Watkins, K. E., Joundi, R. A., Ray, N. J., Holland, P., Green, A. L., Aziz, T. Z., & Jenkinson, N. (2012). A role for the subthalamic nucleus in response inhibition during conflict. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 32(39), 13396–13401.
Bromberg-Martin, E. S., Matsumoto, M., & Hikosaka, O. (2010). Dopamine in motivational control: rewarding, aversive, and alerting. Neuron, 68(5), 815–834.
Brownsett, S. L. E., Warren, J., Geranmayeh, F., Woodhead, Z., Leech, R., & Wise, R. (2014). Cognitive control and its impact on recovery from aphasic stroke. Brain, 137, 242–254.
Cabeza, R., & Nyberg, L. (2000). Imaging cognition II: An empirical review of 275 PET and fMRI studies. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 12(1), 1–47.
Calabresi, P., Picconi, B., Tozzi, A., & Di Filippo, M. (2007). Dopamine-mediated regulation of corticostriatal synaptic plasticity. Trends in Neurosciences, 30, 211-219.
Calabria, M., Costa, A., Green, D. W., & Abutalebi, J. (2018). Neural basis of bilingual language control. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.13879.
Canini, M., Della Rosa, P. A., Catricalà, E., Strijkers, K., Branzi, F. M., Costa, A., & Abutalebi, J. (2016). Semantic interference and its control: A functional neuroimaging and connectivity study. Human Brain Mapping, 37(11), 4179–4196.
Cappa, S. F., & Vallar, G. (1992). Neuropsychological disorders after subcortical lesions: implications for neural models of language and spatial attention. In G. Vallar, S. F. Cappa, & C.-W. Wallesch (Eds.), Neuropsychological Disorders Associated with Subcortical Lesions (pp. 7–41). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Cardona, J. F., Gershanik, O., Gelormini-Lezama, C., Houck, A. L., Cardona, S., Kargieman, L., Trujillo, N., Arévalo, A., Amoruso, L., Manes, F., & Ibáñez, A. (2013). Action-verb processing in Parkinson's disease: new pathways for motor-language coupling. Brain Structure & Function, 218(6), 1355–1373.
Castner, J. E., Chenery, H. J., Copland, D. A., Coyne, T. J., Sinclair, F., & Silburn, P. A. (2007). Semantic and affective priming as a function of stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease. Brain, 130, 1395–1407.
Castner, J. E., Copland, D. A., Silburn, P. A., Coyne, T. J., Sinclair, F., & Chenery, H. J. (2007). Lexical-semantic inhibitory mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease as a function of subthalamic stimulation. Neuropsychologia, 45(14), 3167–3177.
Castner, J. E., Chenery, H. J., Silburn, P. A., Coyne, T. J., Sinclair, F., Smith, E. R., & Copland, D. A. (2008). Effects of subthalamic deep brain stimulation on noun/verb generation and selection from competing alternatives in Parkinson's disease. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 79(6), 700–705.
Chan, S., Ryan, L., & Bever, T. G. (2013). Role of the striatum in language: Syntactic and conceptual sequencing. Brain and Language, 125, 283–294.
Chenery, H. J., Angwin, A. J., & Copland, D. A. (2008). The basal ganglia circuits, dopamine, and ambiguous word processing: a neurobiological account of priming studies in Parkinson’s disease. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 14(3), 351–364.
Chenery, H. J., Copland, D. A., & Murdoch, B. E. (2002). Complex language functions and subcortical mechanisms: evidence from Huntington's disease and patients with non-thalamic subcortical lesions. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders, 37(4), 459–474.
Cilia, R., Siri, C., Marotta, G., De Gaspari, D., Landi, A., Mariani, C. B., Benti, R., Isaias, I. U., Vergani, F., Pezzoli, G., & Antonini, A. (2007). Brain networks underlining verbal fluency decline during STN-DBS in Parkinson's disease: an ECD-SPECT study. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 13(5), 290–294.
Cohen, M. X., & Frank, M. J. (2009). Neurocomputational models of basal ganglia function in learning, memory and choice. Behavioural Brain Research, 199(1), 141–156.
Cohen, J. D., & Servan-Schreiber, D. (1992). Context, cortex, and dopamine: a connectionist approach to behavior and biology in schizophrenia. Psychological Review, 99(1), 45–77.
Cools, R., Gibbs, S. E., Miyakawa, A., Jagust, W., & D’esposito, M. (2008). Working memory capacity predicts dopamine synthesis capacity in the human striatum. Journal of Neuroscience, 28, 1208–1212.
Copland, D. (2003). The basal ganglia and semantic engagement: Potential insights from semantic priming in individuals with subcortical vascular lesions, Parkinson’s disease, and cortical lesions. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 9(7), 1041–1052.
Copland, D. A., Chenery, H. J., & Murdoch, B. E. (2000a). Persistent deficits in complex language function following dominant nonthalamic subcortical lesions. Journal of Medical Speech Language Pathology, 8, 1–15.
Copland, D. A., Chenery, H. J., & Murdoch, B. E. (2000b). Processing lexical ambiguities in word triplets: Evidence of lexical-semantic deficits following dominant nonthalamic sub-cortical lesions. Neuropsychology, 14(3), 379–390.
Copland, D. A., Chenery, H. J., & Murdoch, B. E. (2000c). Understanding ambiguous words in biased sentences: Evidence of transient contextual effects in individuals with nonthalamic subcortical lesions and Parkinson’s disease. Cortex, 36(5), 601–622.
Copland, D. A., Chenery, H. J., & Murdoch, B. E. (2001). Discourse priming of homophones in individuals with dominant nonthalamic subcortical lesions, cortical lesions and Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 23, 538–556.
Copland, D. A., de Zubicaray, G. I., McMahon, K., & Eastburn, M. (2007). Neural correlates of semantic priming for ambiguous words: an event-related fMRI study. Brain Research, 1131(1), 163–172.
Crinion, J., Turner, R., Grogan, A., Hanakawa, T., Noppeney, U., Devlin, J. T., Price, C. J. (2006). Language control in the bilingual brain. Science, 312(5779), 1537–1540.
Crossley, N. A., Mechelli, A., Scott, J., Carletti, F., Fox, P. T., McGuire, P., & Bullmore, E. T. (2014). The hubs of the human connectome are generally implicated in the anatomy of brain disorders. Brain: a Journal of Neurology, 137(Pt 8), 2382–2395.
Crosson, B. (1985). Subcortical functions in language: a working model. Brain and Language, 25, 257–292.
Crosson, B. (1992). Subcortical functions in language and memory. New York: Guilford Press.
Crosson, B., Bejamin, M., & Levy, I. (2007). Role of the basal ganglia in language and semantics: Supporting cast. In J. Hart, Jr. & M. A. Kraut (Eds.), Neural basis of semantic memory (p. 219–243). Cambridge University Press.
Crosson, B., Benefield, H., Cato, M. A., Sadek, J. R., Moore, A. B., Wierenga, C. E., et al. (2003). Left and right basal ganglia and frontal activity during language generation: contributions to lexical, semantic, and phonological processes. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 9(7), 1061–1077.
Cummings, J. L. (1993). Frontal-subcortical circuits and human behavior. Archives of Neurology, 50(8), 873–880.
Divac, I., Oberg, G., & Rosenkilde, C. (1987). Patterned neural activity: implications for neurology and neuropharmacology. In J. S. Schneider & T. I. Lidsky (Eds.), Basal Ganglia and Behavior: Sensory Aspects of Motor Functioning . Huber, NY: Lewistown.
Davis, M. H., & Gaskell, M. G. (2009). A complementary systems account of word learning: Neural and behavioural evidence. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences, 364(1536), 3773–3800.
De Diego-Balaguer, R., Couette, M., Dolbeau, G., Dürr, A., Youssov, K., & Bachoud-Lévi, A. C. (2008). Striatal degeneration impairs language learning: evidence from Huntington’s disease. Brain, 131(11), 2870–2881.
De Letter, M., Bruggeman, A., Keyser, K. D., Van Mierlo, P., Buysse, H., Van Roost, D., & Santens, P. (2020). Subthalamic nucleus activity in the processing of body and mental action verbs in people with Parkinson’s disease. Brain and Language, 202, 104738.
Dockès, J., Poldrack, R. A., Primet, R., Gözükan, H., Yarkoni, T., Suchanek, F., Thirion, B., & Varoquaux, G. (2020). NeuroQuery, comprehensive meta-analysis of human brain mapping. eLife, 9, e53385.
Dominey, P.F., Inui, T., & Hoen, M. (2009). Neural network processing of natural language: II. Towards a unified model of corticostriatal function in learning sentence comprehension and non-linguistic sequencing. Brain and Language, 109(2–3), 80–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandl.2008.08.00
Dosenbach, N. U., Fair, D. A., Miezin, F. M., Cohen, A. L., Wenger, K. K., Dosenbach, R. A., et al. (2007). Distinct brain networks for adaptive and stable task control in humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 104, 11073–11078.
Dosenbach, N. U., Fair, D. A., Cohen, A. L., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2008). A dual networks architecture of top-down control. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 12, 99–105.
Duncan, J., & Owen, A. M. (2000). Common regions of the human frontal lobe recruited by diverse cognitive demands. Trends in Neurosciences, 23, 475–483.
Duncan, J. (2010). The multiple-demand (MD) system of the primate brain: mental programs for intelligent behaviour. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 14, 172–179.
Fasano, A., Daniele, A., & Albanese, A. (2012). Treatment of motor and non-motor features of Parkinson’s disease with deep brain stimulation. The Lancet. Neurology, 11(5), 429–442.
Fedorenko, E., & Thompson-Schill, S. L. (2014). Reworking the language network. Trends in cognitive sciences, 18(3), 120–126.
Ford, A., Triplett, W., Sudhyadhom, A., Gullett, J., McGregor, K., FitzGerald, D. B., et al. (2013). Broca’s area and its striatal and thalamic connections: a diffusion-MRI tractography study. Frontiers in Neuroanatomy, 7(8), 1–12.
Frank, M. J. (2005). Dynamic dopamine modulation in the basal ganglia: a neurocomputational account of cognitive deficits in medicated and nonmedicated Parkinsonism. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 17(1), 51–72.
Frank, M. J. (2006). Hold your horses: a dynamic computational role for the subthalamic nucleus in decision making. Neural Networks, 19(8), 1120–1136.
Frank, M. J., & Badre, D. (2012). Mechanisms of hierarchical reinforcement learning in corticostriatal circuits 1: computational analysis. Cerebral Cortex, 22(3), 509–526.
Friederici, A. D., & Gierhan, S. M. (2013). The language network. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 23(2), 250–254.
Friederici, A. D., & Kotz, S. A. (2003). The brain basis of syntactic processes: functional imaging and lesion studies. NeuroImage, 20, S8–S17.
García, A. M., Carrillo, F., Orozco-Arroyave, J. R., Trujillo, N., Bonilla, J. F. V., Fittipaldi, S., et al. (2016). How language flows when movements don’t: an automated analysis of spontaneous discourse in Parkinson’s disease. Brain and Language, 162, 19–28.
García, A. M., Sedeño, L., Trujillo, N., Bocanegra, Y., Gomez, D., Pineda, D., et al. (2017). Language deficits as a preclinical window into Parkinson’s disease: evidence from asymptomatic parkin and dardarin mutation carriers. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 23, 150–158.
Geranmayeh, F., Brownsett, S. L. E., & Wise, R. (2014). Task-induced brain activity in aphasic stroke patients: what is driving recovery? Brain, 137(10), 2632–2648.
Geranmayeh, F., Chau, T. W., Wise, R. J. S., Leech, R., & Hampshire, A. (2017). Domain-general subregions of the medial prefrontal cortex contribute to recovery of language after stroke. Brain, 140, 1947–1958.
Ghio, M., Haegert, K., Vaghi, M. M., & Tettamanti, M. (2018). Sentential negation of abstract and concrete conceptual categories: a brain decoding multivariate pattern analysis study. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 373, 20170124.
Giavazzi, M., Daland, R., & Palminteri, S. (2018). The role of the striatum in linguistic selection: Evidence from Huntington’s disease and computational modelling. Cortex, 109, 189–204.
Grossman, M., Carvell, S., Stern, M. B., Gollomp, S., & Hurtig, H. I. (1992). Sentence comprehension in Parkinson’s disease: The role of attention and memory. Brain and Language, 42, 347–384.
Grossman, M., Cooke, A., DeVita, C., Lee, C., Alsop, D., Detre, J., et al. (2003). Grammatical and resource components of sentence processing in Parkinson’s disease: An fMRI study. Neurology, 60, 775–781.
Grossman, M., Lee, C., Morris, J., Stern, M. B., & Hurtig, H. I. (2002a). Assessing resource demands during sentence processing in Parkinson’s disease. Brain and Language, 80(3), 603–616.
Grossman, M., Zurif, E., Lee, C., Prather, P., Kalmanson, J., Stern, M. B., et al. (2002b). Information processing speed and sentence comprehension in Parkinson’s disease. Neuropsychology, 16(2), 174–181.
Haber, S. N. (2003). The primate basal ganglia: parallel and integrative networks. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy, 26, 317–330.
Haber, S. N., Kim, K. S., Mailly, P., & Calzavara, R. (2006). Reward-related cortical inputs define a large striatal region in primates that interface with associative cortical connections, providing a substrate for incentive-based learning. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26(32), 8368–8376
Hagoort, P. (2005). On Broca, brain, and binding: a new framework. Trends in Cognitive Science, 9, 416–423.
Hazy, T. E., Frank, M. J., & O’Reilly, R. C. (2006). Banishing the homunculus: making working memory work. Neuroscience, 139(1), 105–118.
Henry, J. D., & Crawford, J. R. (2004). Verbal fluency deficits in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 10(4), 608–622.
Houk, J. C., Bastianen, C., Fansler, D., Fishbach, A., Fraser, D., Reber, P. J., Roy, S. A., & Simo, L. S. (2007). Action selection and refinement in subcortical loops through basal ganglia and cerebellum. Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological sciences, 362(1485), 1573–1583.
Houk, J. C., & Wise, S. P. (1995). Distributed modular architectures linking basal ganglia, cerebellum, and cerebral cortex: their role in planning and controlling action. Cerebral Cortex, 5(2), 95–110.
Hillis, A. E., Wityk, R. J., Barker, P. B., Beauchamp, N. J., Gailoud, P., Murphy, K., et al. (2002). Subcortical aphasia and neglect in acute stroke: The role of cortical hypoperfusion. Brain, 125, 1094–1104.
Inase, M., Tokuno, H., & Nambu, A. (1999). Corticostriatal and corticosubthalamic input zones from the presupplementary motor area in the macaque monkey: comparison with the input zones from the supplementary motor area. Brain Research, 833, 191–201.
Isaacs, M. L., McMahon, K. L., Angwin, A. J., Crosson, B., & Copland, D. A. (2019). Functional correlates of strategy formation and verbal suppression in Parkinson’s disease. NeuroImage. Clinical, 22, 101683.
Jeon, H. A., Anwander, A., & Friederici, A. D. (2014). Functional network mirrored in the prefrontal cortex, caudate nucleus, and thalamus: High-resolution functional imaging and structural connectivity. Journal of Neuroscience, 34, 9202–9212.
Joel, D., & Weiner, I. (2000). The connections of the dopaminergic system with the striatum in rats and primates: an analysis with respect to the functional and compartmental organization of the striatum. Neuroscience, 96, 451–474.
Johari, K., Walenski, M., Reifegerste, J., Ashrafi, F., Behroozmand, R., Daemi, M., & Ullman, M. T. (2019). A dissociation between syntactic and lexical processing in Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 51, 221–235.
Johari, K., Walenski, M., Reifegerste, J., Ashrafi, F., & Ullman, M. T. (2019). Sex, dopamine, and hypokinesia: a study of inflectional morphology in Parkinson’s disease. Neuropsychology, 33, 508–522.
Ketteler, D., Kastrau, F., Vohn, R., Huber, W. (2008). The subcortical role of language pro cessing. High level linguistic features such as ambiguity-resolution and the human brain; an fMRI study. NeuroImage, 39(4), 2002–2009.
Ketteler, S., Ketteler, D., Vohn, R., Kastrau, F., Schulz, J. B., Reetz, K., & Huber, W. (2014). The processing of lexical ambiguity in healthy ageing and Parkinsons disease: Role of cortico-subcortical networks. Brain Research, 1581, 51–63.
Kemmerer, D. (1999). Impaired comprehension of raising- to- subject constructions in Parkinson’s disease. Brain and Language, 66, 311–328.
Korb, F. M., Jiang, J., King, J. A., & Egner, T. (2017). Hierarchically Organized Medial Frontal Cortex-Basal Ganglia Loops Selectively Control Task- and Response-Selection. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 37(33), 7893–7905.
Kotz, S. A., Cappa, S. F., von Cramon, D. Y., & Friederici, A. D. (2002). Modulation of the lexical-semantic network by auditory semantic priming: An event-related functional MRI study. NeuroImage, 17, 1761–1772.
Kotz, S. A., & Schwartze, M. (2010). Cortical speech processing unplugged: a timely subcortico-cortical framework. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 14(9), 392–399.
Kotz, S. A., Schwartze, M., & Schmidt-Kassow, M. (2009). Non-motor basal ganglia functions: a review and proposal for a model of sensory predictability in auditory language perception. Cortex, 45(8), 982–990.
Krishnan, S., Watkins, K.E., & Bishop, D.V. (2016). Neurobiological basis of language learning difficulties. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 20(9), 701–714.
Lawrence, A. D., Sahakian, B. J., & Robbins, T. W. (1998). Cognitive functions and corticostriatal circuits: insights from Huntington’s disease. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2(10), 379–388.
Lee, C., Grossman, M., Morris, J., Stern, M.B., & Hurtig, H.I. (2003). Attentional resource and processing speed limitations during sentence processing in Parkinson’s disease. Brain and Language, 85, 347–356.
Lehericy, S., Ducros, M., Krainik, A., Francois, C., Van de Moortele, P., Ugurbil, K., & Kim, D. (2004). 3-D diffusion tensor axonal tracking shows distinct SMA and Pre-SMA projections to the human striatum. Cerebral Cortex, 14, 1302–1309.
Lehricy, S., Ducros, M., Van de Moortele, P., Francois, C., Thivard, L., Poupon, C., et al. (2004). Diffusion tensor fiber tracking shows distinct corticostriatal circuits in humans. Annals of Neurology, 55, 522–529.
Lewis, F. M., Lapointe, L. L., Murdoch, B. E., & Chenery, H. J. (1998). Language impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Aphasiology, 12(3), 193–206.
Longworth, C. E., Keenan, S. E., Barker, R. A., Marslen-Wilson, W. D., & Tyler, L. K. (2005). The basal ganglia and rule-governed language use: Evidence from vascular and degenerative conditions. Brain, 128(3), 584–596.
López-Barroso, D., Ripollés, P., Marco-Pallarés, J., Mohammadi, B., Münte, T. F., Bachoud-Lévi, A. C., et al. (2015). Multiple brain networks underpinning word learning from fluent speech revealed by independent component analysis. NeuroImage, 110, 182–193.
Mason, R. A., & Just, M. A. (2007). Lexical ambiguity in sentence comprehension. Brain Research, 1146, 115–127.
McNab, F., & Klingberg, T. (2008). Prefrontal cortex and basal ganglia control access to working memory. Nature Neuroscience, 11(1), 103–107.
Mega, M. S., & Alexander, M. P. (1994). Subcortical aphasia: the core profile of capsulostriatal infarction. Neurology, 44(10), 1824–1829.
Menon, V., & Uddin, L. Q. (2010). Saliency, switching, attention and control: a network model of insula function. Brain Structure and Function, 214, 655–667.
Menon, V. (2011). Large-scale brain networks and psychopathology: A unifying triple network model. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15, 483–506.
Mestres-Missé, A., Bazin, P. L., Trampel, R., Turner, R., & Kotz, S. A. (2014). Dorsomedial striatum involvement in regulating conflict between current and presumed outcomes. NeuroImage, 98, 159–167.
Mestres-Missé, A., Trampel, R., Turner, R., & Kotz, S. A. (2017). Uncertainty and expectancy deviations require cortico-subcortical cooperation. NeuroImage, 144(Pt A), 23–34.
Mestres-Misse, A., Turner, R., & Friederici, A. D. (2012). An anterior–posterior gradient of cognitive control within the dorsomedial striatum. NeuroImage, 62, 41–47.
Middleton, F. A., & Strick, P. L. (2000). Basal ganglia and cerebellar loops: motor and cognitive circuits. Brain Research Review, 31, 236–250.
Miller, E. K., & Cohen, J. D. (2001). An integrative theory of prefrontal cortex function. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 24, 167–202.
Mink, J. W. (1996). The basal ganglia: Focused selection and inhibition of competing motor programs. Progress in Neurobiology, 50, 381–425.
Monchi, O., Petrides, M., Petre, V., Worsley, K., & Dagher, A. (2001). Wisconsin card sorting revisited: Distinct neural circuits participating in different stages of the task identified by event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of Neuroscience, 21(19), 7733–7741.
Monetta, L., & Pell, M. D. (2007). Effects of verbal working memory deficits on metaphor comprehension in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Brain and Language, 101(1), 80–89.
Moretti, R., Bava, A., Torre, P., Antonello, R. M., Zorzon, M., Zivadinov, R., & Cazzato, G. (2001). Bilingual aphasia and subcortical-cortical lesions. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 92(3 Pt 1), 803–814.
Moro, A., Tettamanti, M., Perani, D., Donati, C., Cappa, S. F., & Fazio, F. (2001). Syntax and the brain: disentangling grammar by selective anomalies. NeuroImage, 13, 110–118.
Nadeau, S. E., & Crosson, B. (1997). Subcortical aphasia. Brain and Language, 58, 355–402.
Nambu, A. (2008). Seven problems on the basal ganglia. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 18(6), 595–604.
Nimchinsky, E., Vogt, B., Morrison, J., & Hof, P. (1995). Spindle neurons of the human anterior cingulate cortex. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 355, 27–37.
Obeso, I., Wilkinson, L., Casabona, E., Bringas, M. L., Alvarez, M., Alvarez, L., & Jahanshahi, M. (2011). Deficits in inhibitory control and conflict resolution on cognitive and motor tasks in Parkinson’s disease. Experimental Brain Research, 212(3), 371–384.
O’Reilly, R. C. (2006). Biologically based computational models of high-level cognition. Science, 314(5796), 91–94.
O’Reilly, R. C., & Frank, M. J. (2006). Making working memory work: a computational model of learning in the prefrontal cortex and basal ganglia. Neural Computation, 18(2), 283–328.
Pauli, W. M., O’Reilly, R. C., Yarkoni, T., & Wager, T. D. (2016). Regional specialization within the human striatum for diverse psychological functions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113(7), 1907–1912.
Packard, M.G., & Knowlton, B.J. (2002). Learning and memory functions of the basal ganglia. Annual Reviews in Neuroscience, 25, 563–593.
Parsons, T. D., Rogers, S. A., Braaten, A. J., Woods, S. P., & Troster, A. I. (2006). Cognitive sequelae of subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation in Parkinson's disease: A meta-analysis. Lancet Neurology, 5, 578-588.
Phillips, L., Litcofsky, K.A., Pelster, M., Gelfand, M., Ullman, M.T., & Charles, P.D. (2012). Subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation impacts language in early Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One, 7, e42829.
Postuma, R. B., & Dagher, A. (2006). Basal ganglia functional connectivity based on a meta-analysis of 126 positron emission tomography and functional magnetic resonance imaging publications. Cerebral Cortex, 16(10), 1508–1521.
Price, A. L. (2006). Explicit category learning in Parkinson’s disease: deficits related to impaired rule generation and selection processes. Neuropsychology, 20(2), 249–257.
Progovac, L., Rakhlin, N., Angell, W., Liddane, R., Tang, L., & Ofen, N. (2018a). Neural correlates of syntax and proto-syntax: Evolutionary dimension. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 2415.
Progovac, L., Rakhlin, N., Angell, W., Liddane, R., Tang, L., & Ofen, N. (2018b). Diversity of grammars and their diverging evolutionary and processing paths: evidence from functional MRI study of Serbian. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 278.
Provost, J. S., Hanganu, A., & Monchi, O. (2015). Neuroimaging studies of the striatum in cognition Part I: healthy individuals. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 9, 140.
Ripolles, P., Marco-Pallares, J., Hielscher, U., Mestres-Misse, A., Tempelmann, C., Heinze, H., et al. (2014). The role of reward in word learning and its implications for language acquisition. Current Biology, 24, 2606–2611.
Ripollés, P., Marco-Pallarés, J., Alicart, H., Tempelmann, C., Rodríguez-Fornells, A., & Noesselt, T. (2016). Intrinsic monitoring of learning success facilitates memory encoding via the activation of the SN/VTA-Hippocampal loop. eLife, 5, e17441.
Ripollés, P., Ferreri, L., Mas-Herrero, E., Alicart, H., Gómez-Andrés, A., Marco-Pallares, J., Antonijoan, R.M., Noesselt, T., Valle, M., Riba, J., & Rodriguez-Fornells, A. (2018). Intrinsically regulated learning is modulated by synaptic dopamine signaling. eLife, 7, e38113
Rodd, J. M., Davis, M. H., & Johnsrude, I. S. (2005). The neural mechanisms of speech comprehension: fMRI studies of semantic ambiguity. Cerebral Cortex, 15(8), 1261–1269.
Rodriguez-Fornells, A., Cunillera, T., Mestres-Misse, A., & de Diego-Balaguer, R. (2009). Neurophysiological mechanisms involved in language learning in adults. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences, 364, 3711–3735.
Sambin, S., Teichmann, M., de Diego Balaguer, R., Giavazzi, M., Sportiche, D., Schlenker, P., & Bachoud-Levi, A. (2012). The role of the striatum in sentence processing: Disentangling syntax from working memory in Huntington’s disease. Neuropsychologia, 50, 2625–2635.
Schroeder, U., Kuehler, A., Haslinger, B., Erhard, P., Fogel, W., Tronnier, V. M., Lange, K. W., Boecker, H., & Ceballos-Baumann, A. O. (2002). Subthalamic nucleus stimulation affects striato-anterior cingulate cortex circuit in a response conflict task: a PET study. Brain, 125, 1995–2004.
Schroeder, U., Kuehler, A., Lange, K. W., Haslinger, B., Tronnier, V. M., Krause, M., Pfister, R., Boecker, H., & Ceballos-Baumann, A. O. (2003). Subthalamic nucleus stimulation affects a frontotemporal network: a PET study. Annals of Neurology, 54(4), 445–450.
Scimeca, J. M., & Badre, D. (2012). Striatal contributions to declarative memory retrieval. Neuron, 75(3), 380–392.
Seeley W. W. (2019). The Salience Network: A Neural System for Perceiving and Responding to Homeostatic Demands. The Journal of Neuroscience, 39(50), 9878–9882.
Seeley, W. W., Menon, V., Schatzberg, A. F., Keller, J., Glover, G. H., Kenna, H., et al. (2007). Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. The Journal of Neuroscience, 27, 2349–2356.
Seger, C. A., & Cincotta, C. M. (2005). The roles of the caudate nucleus in human classification learning. The Journal of Neuroscience, 25(11), 2941–2951.
Shellshear, L., MacDonald, A. D., Mahoney, J., Finch, E., McMahon, K., Silburn, P., et al. (2015). Levodopa enhances explicit new-word learning in healthy adults: a preliminary study. Human Psychopharmacology, 30(5), 341–349.
Simard, F., Monetta, L., Nagano-Saito, A., & Monchi, O. (2013). A new lexical card-sorting task for studying fronto-striatal contribution to processing language rules. Brain and Language, 125(3), 295–306.
Simonyan, K., Herscovitch, P., & Horwitz, B. (2013). Speech-induced striatal dopamine release is left lateralized and coupled to functional striatal circuits in healthy humans: a combined PET, fMRI and DTI study. NeuroImage, 70, 21–32.
Sliwinska, M. W., Violante, I. R., Wise, R. J. S., Leech, R., Devlin, J. T., Geranmayeh, F., & Hampshire, A. (2017). Stimulating Multiple-Demand Cortex Enhances Vocabulary Learning. The Journal of Neuroscience, 37(32), 7606–7618.
Snijders, T. M., Petersson, K. M., & Hagoort, P. (2010). Effective connectivity of cortical and subcortical regions during unification of sentence structure. NeuroImage, 52, 1633–1644.
Stocco, A. (2018). A Biologically Plausible Action Selection System for Cognitive Architectures: Implications of Basal Ganglia Anatomy for Learning and Decision-Making Models. Cognitive Science, 42(2), 457–490.
Stockert, A., Wawrzyniak, M., Klingbeil, J., Wrede, K., Kümmerer, D., Hartwigsen, G., et al. (2020). Dynamics of language reorganization after left temporo-parietal and frontal stroke. Brain, 143(3), 844–861. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awaa023.
Szalisznyo, K., Silverstein, D., Teichmann, M., Duffau, H., & Smits, A. (2017). Cortico-striatal language pathways dynamically adjust for syntactic complexity: A computational study. Brain and Language, 164, 53–62.
Takashima, A., Bakker, I., van Hell, J. G., Janzen, G., & McQueen, J. M. (2014). Richness of information about novel words influences how episodic and semantic memory networks interact during lexicalization. NeuroImage, 84, 265–278.
Tagarelli, K. M., Shattuck, K. F., Turkeltaub, P. E., & Ullman, M. T. (2019). Language learning in the adult brain: A neuro-anatomical meta-analysis of lexical and grammatical learning. NeuroImage, 193, 178–200.
Teichmann, M., Rosso, C., Martini, J., Bloch, I., Brugieres, P., Duffau, H., et al. (2015). A cortical-subcortical syntax pathway linking Broca’s area and the striatum. Human Brain Mapping, 36(6), 2270–2283. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22769.
Teichmann, M., Gaura, V., Demonet, J., Supiot, F., Delliaux, M., Verny, C., et al. (2008). Language processing within the striatum: Evidence from a PET correlation study in Huntington’s disease. Brain, 131, 1046–1056.
Tettamanti, M., Moro, A., Messa, C., Moresco, R. M., Rizzo, G., Carpinelli, A., et al. (2005). Basal ganglia and language: phonology modulates dopaminergic release. NeuroReport, 16, 397–401.
Tomasi, D., & Volkow, N. D. (2012). Language network: segregation, laterality and connectivity. Molecular Psychiatry, 17(8), 759.
Thompson, H. E., Almaghyuli, A., Noonan, K. A., Barak, O., Lambon Ralph, M. A., & Jefferies, E. (2018). The contribution of executive control to semantic cognition: Convergent evidence from semantic aphasia and executive dysfunction. Journal of Neuropsychology, 12(2), 312–340.
Tinaz, S., Schendan, H. E., & Stern, C. E. (2008). Fronto-striatal deficit in Parkinson’s disease during semantic event sequencing. Neurobiology of Aging, 29(3), 397–407.
Ullman, M.T. (2001). The declarative/procedural model of lexicon and grammar. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 30, 37–69.
Ullman, M. T., Pancheva, R., Love, T., Yee, E., Swinney, D., & Hickok, C. (2005). Neural correlates of lexicon and grammar: Evidence from the production, reading, and judgment of inflection in aphasia. Brain and Language, 93, 185–238.
van Holstein, M., Froböse, M. I., O’Shea, J., Aarts, E., & Cools, R. (2018). Controlling striatal function via anterior frontal cortex stimulation. Scientific reports, 8(1), 3312.
van den Heuvel, M. P., Bullmore, E. T., & Sporns, O. (2016). Comparative Connectomics. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 20(5), 345–361.
van den Heuvel, M. P., & Sporns, O. (2011). Rich-club organization of the human connectome. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(44), 15775–15786.
van Heuven, W. J., Schriefers, H., Dijkstra, T., & Hagoort, P. (2008). Language conflict in the bilingual brain. Cerebral Cortex, 18(11), 2706–2716.
Verstynen, T. D., Badre, D., Jarbo, K., & Schneider, W. (2012). Microstructural organizational patterns in the human corticostriatal system. Journal of Neurophysiology, 107(11), 2984–2995.
Wallesch, C. W. (1997). Symptomatology of subcortical aphasia. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 10(4), 267–275.
Wallesch, C.W., & Pagagno, C. (1988). Subcortical aphasia. In: Rose FC, Whurr R, Wyke MA (eds) Aphasia. Whurr Publishers, London, pp 256–287.
Wiesendanger, R., & Wiesendanger, M. (1985). The thalamic connections with medial area 6 (supplementary motor cortex) in the monkey (Macaca fascicularis). Experimental Brain Research, 59(1), 91–104.
Ye, Z., Kutas, M., St George, M., Sereno, M. I., Ling, F., & Munte, T. F. (2012). Rearranging the world: Neural network supporting the processing of temporal connectives. NeuroImage, 59, 3662–3667.
Ye, Z., Mestres-Missé, A., Rodriguez-Fornells, A., & Münte, T. F. (2011). Two distinct neural networks support the mapping of meaning to a novel word. Human Brain Mapping, 32(7), 1081–1090.
Zempleni, M. Z., Renken, R., Hoeks, J. C., Hoogduin, J. M., & Stowe, L. A. (2007). Semantic ambiguity processing in sentence context: Evidence from event-related fMRI. Neuroimage, 34(3), 1270-1279.
Zou, L., Ding, G., Abutalebi, J., et al. (2012). Structural plasticity of the left caudate in bimodal bilinguals. Cortex, 48, 1197–1206.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Copland, D.A., Brownsett, S., Iyer, K. et al. Corticostriatal Regulation of Language Functions. Neuropsychol Rev 31, 472–494 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-021-09481-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-021-09481-9