Abstract
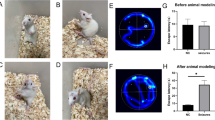
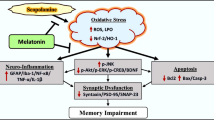
Epilepsy-associated cognitive impairment is common, and negatively impacts patients’ quality of life. However, most antiepileptic drugs focus on the suppression of seizures, and fewer emphasize treatment of cognitive dysfunction. Melatonin, an indolamine synthesized primarily in the pineal grand, is reported to be neuroprotective against several central nervous system disorders. In this study, we investigated whether melatonin could reverse cognitive dysfunction in lithium-pilocarpine treated rats. Chronic treatment with melatonin (8 mg/kg daily for 15 days) after induction of status epilepticus significantly alleviated seizure severity, reduced neuronal death in the CA1 region of the hippocampus, improved spatial learning (as measured by the Morris water maze test), and reversed LTP impairments, compared to vehicle treatment. Furthermore, we found that melatonin rescued the decreased surface levels of GluR2 in the CA1 region observed in epilepsy, which might be the underlying mechanism of the neuroprotective and synapse-modulating function of melatonin. Our study provides experimental evidence for the possible clinical utility of melatonin as an adjunctive therapy to prevent epilepsy-associated cognitive impairments.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nen AP, Lukasiuk K (2011) Mechanisms of epileptogenesis and potential treatment targets. Lancet Neurol 10:173–186
Loring DW, Meador KJ, Lee GP (2004) Determinants of quality of life in epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 5:976–980
Bell B, Lin JJ, Seidenberg M, Hermann B (2011) The neurobiology of cognitive disorders in temporal lobe epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol 7:154–164
Lenck-Santini P, Scott RC (2015) Mechanisms responsible for cognitive impairment in epilepsy. Csh Perspect Med 5:a22772
Pitk Nen A, Sutula TP (2002) Is epilepsy a progressive disorder? Prospects for new therapeutic approaches in temporal-lobe epilepsy. Lancet Neurology 1:173–181
Chapman KE, Specchio N, Shinnar S, Holmes GL (2015) Seizing control of epileptic activity can improve outcome. Epilepsia 56:1482–1485
Guardiola-Lemaitre B (1997) Toxicology of melatonin. J Biol Rhythms 12:697–706
Chen YC, Sheen JM, Tain YL, Chen CC, Tiao MM, Huang YH, Hsieh CS, Huang LT (2012) Alterations in NADPH oxidase expression and blood-brain barrier in bile duct ligation-treated young rats: effects of melatonin. Neurochem Int 60:751–758
Pandi-Perumal SR, BaHammam AS, Brown GM, Spence DW, Bharti VK, Kaur C, Hardeland R, Cardinali DP (2013) Melatonin antioxidative defense: therapeutical implications for aging and neurodegenerative processes. Neurotox Res 23:267–300
Musshoff U, Riewenherm D, Berger E, Fauteck J, Speckmann E (2002) Melatonin receptors in rat hippocampus: molecular and functional investigations. Hippocampus 12:165–173
Liu X, Yuan L, Yang D, Han W, Li Q, Yang W, Liu Q, Qi J (2013) Melatonin protects against amyloid-β-induced impairments of hippocampal LTP and spatial learning in rats. Synapse 67:626–636
Racine RJ (1972) Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 32:281–294
Saxena G, Bharti S, Kamat PK, Sharma S, Nath C (2010) Melatonin alleviates memory deficits and neuronal degeneration induced by intracerebroventricular administration of streptozotocin in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 94:397–403
Giusti P, Lipartiti M, Franceschini D, Schiavo N, Floreani M, Manev H (1996) Neuroprotection by melatonin from kainate-induced excitotoxicity in rats. FASEB J 10:891–896
Han J, Kesner P, Metna-Laurent M, Duan T, Xu L, Georges F, Koehl M, Abrous DN, Mendizabal-Zubiaga J, Grandes P, Liu Q, Bai G, Wang W, Xiong L, Ren W, Marsicano G, Zhang X (2012) Acute cannabinoids impair working memory through astroglial CB1 receptor modulation of hippocampal LTD. Cell 148:1039–1050
Ou-Yang TP, Zhu GM, Ding YX, Yang F, Sun XL, Jiang W (2016) The effects of amiloride on seizure activity, cognitive deficits and seizure-induced neurogenesis in a novel rat model of febrile seizures. Neurochem Res 41:933–942
André V, Dubé C, François J, Leroy C, Rigoulot M, Roch C, Namer IJ, Nehlig A (2007) Pathogenesis and pharmacology of epilepsy in the lithium-pilocarpine model. Epilepsia 48:41–47
Cull-Candy S, Kelly L, Farrant M (2006) Regulation of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors: synaptic plasticity and beyond. Curr Opin Neurobiol 16:288–297
Lenck-Santini PP, Holmes GL (2008) Altered phase precession and compression of temporal sequences by place cells in epileptic rats. J Neurosci 28:5053–5062
Liu X, Muller RU, Huang LT, Kubie JL, Rotenberg A, Rivard B, Cilio MR, Holmes GL (2003) Seizure-induced changes in place cell physiology: relationship to spatial memory. J Neurosci 23:11505–11515
Olney JW, Fuller T, de Gubareff T (1979) Acute dendrotoxic changes in the hippocampus of kainate treated rats. Brain Res 176:91–100
Ben-Ari Y (2001) Cell death and synaptic reorganizations produced by seizures. Epilepsia 42(Suppl 3):5–7
Reddy D, Kuruba R (2013) Experimental models of status epilepticus and neuronal injury for evaluation of therapeutic interventions. Int J Mol Sci 14:18284–18318
Steve TA, Jirsch JD, Gross DW (2014) Quantification of subfield pathology in hippocampal sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsy Res 108:1279–1285
Barry JM, Rivard B, Fox SE, Fenton AA, Sacktor TC, Muller RU (2012) Inhibition of protein kinase Mzeta disrupts the stable spatial discharge of hippocampal place cells in a familiar environment. J Neurosci 32:13753–13762
Zhou JL, Shatskikh TN, Liu X, Holmes GL (2007) Impaired single cell firing and long-term potentiation parallels memory impairment following recurrent seizures. Eur J Neurosci 25:3667–3677
Nicoll RA, Roche KW (2013) Long-term potentiation: peeling the onion. Neuropharmacology 74:18–22
Isaac JT, Ashby MC, McBain CJ (2007) The role of the GluR2 subunit in AMPA receptor function and synaptic plasticity. Neuron 54:859–871
Boehm J, Kang M, Johnson RC, Esteban J, Huganir RL, Malinow R (2006) Synaptic incorporation of AMPA receptors during LTP Is controlled by a PKC phosphorylation site on GluR1. Neuron 51:213–225
Jiang J, Parameshwaran K, Seibenhener ML, Kang M, Suppiramaniam V, Huganir RL, Diaz-Meco MT, Wooten MW (2009) AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity require SQSTM1/p62. Hippocampus 19:392–406
Burnashev N, Monyer H, Seeburg PH, Sakmann B (1992) Divalent ion permeability of AMPA receptor channels is dominated by the edited form of a single subunit. Neuron 8:189–198
Swanson GT, Kamboj SK, Cull-Candy SG (1997) Single-channel properties of recombinant AMPA receptors depend on RNA editing, splice variation, and subunit composition. J Neurosci 17:58–69
Tanaka H, Grooms SY, Bennett MV, Zukin RS (2000) The AMPAR subunit GluR2: still front and center-stage. Brain Res 886:190–207
Soundarapandian MM, Tu WH, Peng PL, Zervos AS, Lu Y (2005) AMPA receptor subunit GluR2 gates injurious signals in ischemic stroke. Mol Neurobiol 32:145–155
Liu S, Lau L, Wei J, Zhu D, Zou S, Sun HS, Fu Y, Liu F, Lu Y (2004) Expression of Ca(2+)-permeable AMPA receptor channels primes cell death in transient forebrain ischemia. Neuron 43:43–55
Grooms SY, Opitz T, Bennett MV, Zukin RS (2000) Status epilepticus decreases glutamate receptor 2 mRNA and protein expression in hippocampal pyramidal cells before neuronal death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3631–3636
Sanchez RM, Koh S, Rio C, Wang C, Lamperti ED, Sharma D, Corfas G, Jensen FE (2001) Decreased glutamate receptor 2 expression and enhanced epileptogenesis in immature rat hippocampus after perinatal hypoxia-induced seizures. J Neurosci 21:8154–8163
Koh S, Tibayan FD, Simpson JN, Jensen FE (2004) NBQX or topiramate treatment after perinatal hypoxia-induced seizures prevents later increases in seizure-induced neuronal Injury. Epilepsia 45:569–575
Ijff DM, Aldenkamp AP (2013) Chap. 73—Cognitive side-effects of antiepileptic drugs in children. In: handbook of clinical neurology. Edited by Olivier Dulac MLAH, vol. Volume 111: Elsevier, pp 707–718
Wang LM, Suthana NA, Chaudhury D, Weaver DR, Colwell CS (2005) Melatonin inhibits hippocampal long-term potentiation. Eur J Neurosci 22:2231–2237
Ozcan M, Yilmaz B, Carpenter DO (2006) Effects of melatonin on synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation in two areas of mouse hippocampus. Brain Res 1111:90–94
Esposito E, Cuzzocrea S (2010) Antiinflammatory activity of melatonin in central nervous system. Curr Neuropharmacol 8:228–242
Mahlberg R, Walther S, Kalus P, Bohner G, Haedel S, Reischies FM, Kuhl KP, Hellweg R, Kunz D (2008) Pineal calcification in alzheimer’s disease: an in vivo study using computed tomography. Neurobiol Aging 29:203–209
Peled N, Shorer Z, Peled E, Pillar G (2001) Melatonin effect on seizures in children with severe neurologic deficit disorders. Epilepsia 42:1208–1210
Tchekalarova J, Petkova Z, Pechlivanova D, Moyanova S, Kortenska L, Mitreva R, Lozanov V, Atanasova D, Lazarov N, Stoynev A (2013) Prophylactic treatment with melatonin after status epilepticus: effects on epileptogenesis, neuronal damage, and behavioral changes in a kainate model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 27:174–187
Banach M, Gurdziel E, Drych MJ, Borowicz KK (2011) Melatonin in experimental seizures and epilepsy. Pharmacol Rep 63: 1–11
Yeleswaram K, McLaughlin LG, Knipe JO, Schabdach D (1997) Pharmacokinetics and oral bioavailability of exogenous melatonin in preclinical animal models and clinical implications. J Pineal Res 22:45–51
Munoz-Hoyos A, Molina-Carballo A, Macias M, Rodriguez-Cabezas T, Martin-Medina E, Narbona-Lopez E, Valenzuela-Ruiz A, Acuna-Castroviejo D (1998) Comparison between tryptophan methoxyindole and kynurenine metabolic pathways in normal and preterm neonates and in neonates with acute fetal distress. Eur J Endocrinol 139:89–95
Costa-Lotufo LV, Fonteles MM, Lima IS, de Oliveira AA, Nascimento VS, de Bruin VM, Viana GS (2002) Attenuating effects of melatonin on pilocarpine-induced seizures in rats. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 131:521–529
Yahyavi-Firouz-Abadi N, Tahsili-Fahadan P, Riazi K, Ghahremani MH, Dehpour AR (2007) Melatonin enhances the anticonvulsant and proconvulsant effects of morphine in mice: role for nitric oxide signaling pathway. Epilepsy Res 75:138–144
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants from the National Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers 81271432 and 81571262). The funders played no role in study design, data collection and analysis, the decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Yue Ma and Xiaolong Sun have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Sun, X., Li, J. et al. Melatonin Alleviates the Epilepsy-Associated Impairments in Hippocampal LTP and Spatial Learning Through Rescue of Surface GluR2 Expression at Hippocampal CA1 Synapses. Neurochem Res 42, 1438–1448 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2200-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2200-5