Abstract
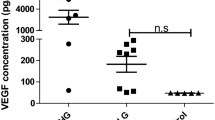
Over-expression of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) is correlated with leukemia metastasis. VEGF-A acts by binding to its membrane receptors R1 and R2 present in soluble forms (sVEGFR1, sVEGFR2) with different functions. sVEGFR could inhibit VEGF-A bioactivities, associated with favorable prognosis in solid tumors. However, its role is obscure in central nervous system leukemia (CNSL). The aim of this study was to investigate sVEGFR1, R2 as biomarkers in CNSL. Paired cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum samples were collected from 35 leukemia cases with or without CNS metastasis. Levels of sVEGFR1 and sVEGFR2 in both CSF (sVEGFR1CSF, sVEGFR2CSF) and serum (sVEGFR1Serum, sVEGFR2Serum) were detected by ELISA. Other risk factors related to CNSL prognosis were also analyzed. sVEGFRSerum levels were 2.54-fold (sVEGFR1) and 25.6-fold (sVEGFR2) higher than sVEGFRCSF in both leukemic groups. sVEGFR1CSF in CNSL were 33 % higher than in the non-CNSL, and the levels of sVEGFR2CSF and sVEGFR2Serum had the same trend. Elevated sVEGFR1CSF and sVEGFR2CSF is closely correlated with blood-brain barrier (BBB) values and WBCCSF that is an indicator of CNSL disease burden. Cox regression analysis showed that the sVEGFR2CSF had a positive effect on event-free survival. Our data suggest that sVEGFR2CSF may be more potent than sVEGFR1CSF in predicting the outcome of leukemia patients, the balance between sVEGFR2CSF and VEGF-ACSF levels might be crucial for the progression of CNSL.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J (2002) Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol 29:15–18
Ferrara N (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev 25:581–611
De Bont ES, Rosati S, Jacobs S, Kamps WA, Vellenga E (2001) Increased bone marrow vascularization in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia: a possible role for vascular endothelial growth factor. Br J Haematol 113:296–304
Aguayo A, Kantarjian HM, Estey EH, Giles FJ, Verstovsek S, Manshouri T, Gidel C, O’brien S, Keating MJ, Albitar M (2002) Plasma vascular endothelial growth factor levels have prognostic significance in patients with acute myeloid leukemia but not in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer 95:1923–1930
Masood R, Cai J, Zheng T, Smith DL, Hinton DR, Gill PS (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is an autocrine growth factor for VEGF receptor-positive human tumors. Blood 98:1904–1913
Price DJ, Miralem T, Jiang S, Steinberg R, Avraham H (2001) Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the stimulation of cellular invasion and signaling of breast cancer cells. Cell Growth Differ 12:129–135
Jackson MW, Roberts JS, Heckford SE, Ricciardelli C, Stahl J, Choong C, Horsfall DJ, Tilley WD (2002) A potential autocrine role for vascular endothelial growth factor in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 62:854–859
Mylona E, Alexandrou P, Giannopoulou I, Liapis G, Sofia M, Keramopoulos A, Nakopoulou L (2007) The prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs)-A and -B and their receptor, VEGFR-1, in invasive breast carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 104:557–563
Seto T, Higashiyama M, Funai H, Imamura F, Uematsu K, Seki N, Eguchi K, Yamanaka T, Ichinose Y (2006) Prognostic value of expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its flt-1 and KDR receptors in stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 53:91–96
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, Lecouter J (2003) The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9:669–676
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J, Claesson-Welsh L (2006) VEGF receptor signalling—in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:359–371
Rahimi N, Dayanir V, Lashkari K (2000) Receptor chimeras indicate that the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (VEGFR-1) modulates mitogenic activity of VEGFR-2 in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 275:16986–16992
Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM (2005) Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol 23:1011–1027
Torsney C, Macdermott AB (2005) Neuroscience: a painful factor. Nature 438:923–925
Hu Q, Dey AL, Yang Y, Shen Y, Jilani IB, Estey EH, Kantarjian HM, Giles FJ, Albitar M (2004) Soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1, and not receptor 2, is an independent prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer 100:1884–1891
Wu FT, Stefanini MO, Mac Gabhann F, Popel AS (2009) A compartment model of VEGF distribution in humans in the presence of soluble VEGF receptor-1 acting as a ligand trap. PLoS ONE 4:e5108
Kou B, Li Y, Zhang L, Zhu G, Wang X, Xia J, Shi Y (2004) In vivo inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by a soluble VEGFR-2 fragment. Exp Mol Pathol 76:129–137
Kuhnert F, Tam BY, Sennino B, Gray JT, Yuan J, Jocson A, Nayak NR, Mulligan RC, Mcdonald DM, Kuo CJ (2008) Soluble receptor-mediated selective inhibition of VEGFR and PDGFRbeta signaling during physiologic and tumor angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:10185–10190
Scheufler KM, Drevs J, Van Velthoven V, Reusch P, Klisch J, Augustin HG, Zentner J, Marme D (2003) Implications of vascular endothelial growth factor, sFlt-1, and sTie-2 in plasma, serum and cerebrospinal fluid during cerebral ischemia in man. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:99–110
Toi M, Bando H, Ogawa T, Muta M, Hornig C, Weich HA (2002) Significance of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/soluble VEGF receptor-1 relationship in breast cancer. Int J Cancer 98:14–18
Kikuchi S, Obata Y, Yagyu K, Lin Y, Nakajima T, Kobayashi O, Kikuichi M, Ushijima R, Kurosawa M, Ueda J (2011) Reduced serum vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (sVEGFR-2) and sVEGFR-1 levels in gastric cancer patients. Cancer Sci 102:866–869
Shantha Kumara HM, Cabot JC, Hoffman A, Luchtefeld M, Kalady MF, Hyman N, Feingold D, Baxter R, Whelan RL (2010) Minimally invasive colon resection for malignant colonic conditions is associated with a transient early increase in plasma sVEGFR1 and a decrease in sVEGFR2 levels after surgery. Surg Endosc 24:283–289
Wierzbowska A, Robak T, Wrzesien-Kus A, Krawczynska A, Lech-Maranda E, Urbanska-Rys H (2003) Circulating VEGF and its soluble receptors sVEGFR-1 and sVEGFR-2 in patients with acute leukemia. Eur Cytokine Netw 14:149–153
Tang YT, Jiang F, Guo L, Si MY, Jiao XY (2012) Expression and significance of vascular endothelial growth factor A and C in leukemia central nervous system metastasis. Leuk Res. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2012.10.008
Bosc LV, Resta T, Walker B, Kanagy NL (2010) Mechanisms of intermittent hypoxia induced hypertension. J Cell Mol Med 14:3–17
Kumai Y, Ooboshi H, Ibayashi S, Ishikawa E, Sugimori H, Kamouchi M, Kitazono T, Egashira K, Iida M (2007) Postischemic gene transfer of soluble Flt-1 protects against brain ischemia with marked attenuation of blood-brain barrier permeability. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1152–1160
Bailey AP, Shparago M, Gu JW (2006) Exercise increases soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (sFlt-1) in circulation of healthy volunteers. Med Sci Monit 12:CR45–CR50
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, Sultan C (1985) Proposed revised criteria for the classification of acute myeloid leukemia. A report of the French–American–British Cooperative Group. Ann Intern Med 103:620–625
Mastrangelo R, Poplack D, Bleyer A, Riccardi R, Sather H, D’angio G (1986) Report and recommendations of the Rome workshop concerning poor-prognosis acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children: biologic bases for staging, stratification, and treatment. Med Pediatr Oncol 14:191–194
Hirohata S, Isshi K, Oguchi H, Ohse T, Haraoka H, Takeuchi A, Hashimoto T (1997) Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-6 in progressive Neuro-Behcet’s syndrome. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 82:12–17
Andersson LM, Hagberg L, Fuchs D, Svennerholm B, Gisslen M (2001) Increased blood-brain barrier permeability in neuro-asymptomatic HIV-1-infected individuals–correlation with cerebrospinal fluid HIV-1 RNA and neopterin levels. J Neurovirol 7:542–547
Feng S, Cen J, Huang Y, Shen H, Yao L, Wang Y, Chen Z (2011) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 secreted by leukemic cells increase the permeability of blood-brain barrier by disrupting tight junction proteins. PLoS ONE 6:e20599
Rahimi N, Golde TE, Meyer RD (2009) Identification of ligand-induced proteolytic cleavage and ectodomain shedding of VEGFR-1/FLT1 in leukemic cancer cells. Cancer Res 69:2607–2614
Barleon B, Siemeister G, Martiny-Baron G, Weindel K, Herzog C, Marme D (1997) Vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulates its receptor fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (FLT-1) and a soluble variant of FLT-1 in human vascular endothelial cells. Cancer Res 57:5421–5425
Dikov MM, Ohm JE, Ray N, Tchekneva EE, Burlison J, Moghanaki D, Nadaf S, Carbone DP (2005) Differential roles of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors 1 and 2 in dendritic cell differentiation. J Immunol 174:215–222
De Bont ES, Fidler V, Meeuwsen T, Scherpen F, Hahlen K, Kamps WA (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor secretion is an independent prognostic factor for relapse-free survival in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients. Clin Cancer Res 8:2856–2861
Ruffini F, Failla CM, Orecchia A, Bani MR, Dorio AS, Fortes C, Zambruno G, Graziani G, Giavazzi R, D’atri S, Lacal PM (2011) Expression of the soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 in cutaneous melanoma: role in tumour progression. Br J Dermatol 164:1061–1070
Hornig C, Behn T, Bartsch W, Yayon A, Weich HA (1999) Detection and quantification of complexed and free soluble human vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (sVEGFR-1) by ELISA. J Immunol Methods 226:169–177
Arshad F, Wang L, Sy C, Avraham S, Avraham HK (2010) Blood-brain barrier integrity and breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Patholog Res Int 2011:920509
Yang F, Jin C, Jiang YJ, Li J, Di Y, Fu DL (2011) Potential role of soluble VEGFR-1 in antiangiogenesis therapy for cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 11:541–549
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr.Frieda Law and Dr. Stanley Lin for the manuscript review and literature support. This study was funded by Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (NO9151008901000043), Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Province, China (No.2010B031600321, and No.2012B031800217), and Medical Research Foundation of Guangdong Province (B2011220).
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, YT., Jiang, F., Guo, L. et al. The soluble VEGF receptor 1 and 2 expression in cerebral spinal fluid as an indicator for leukemia central nervous system metastasis. J Neurooncol 112, 329–338 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1066-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1066-x