Abstract
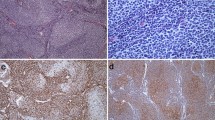
Medulloblastoma (MB) is the most common malignant primary brain tumour in childhood. Metastatic disease (M+) at diagnosis is the most important negative prognostic clinical marker and, despite craniospinal irradiation and intensive chemotherapy, it remains one of the leading causes of treatment failure. To date, few clinical and biological data have been evaluated to obtain an additional prognostic profile for these high-risk patients. In this study, 169 patients with metastatic MB registered in the multicentre HIT2000 trial of the German Society of Pediatric Oncology and Haematology (GPOH) have been investigated to determine the importance of p53 protein expression in predicting survival. At a median follow-up of 4.1 years, 159 patients with p53-negative tumours had significantly better four-year event-free survival (EFS) and progression-free survival (PFS) (56 ± 11, 59 ± 4%) than 10 patients with p53-positive tumours (40 ± 16, 40 ± 16%; P = 0.018 for EFS, P = 0.007 for PFS, respectively). Furthermore, four-year overall survival (OS) of children with p53-negative tumours was higher than for children with p53-positive tumours (72 ± 4 vs. 35 ± 18%, P = 0.05). Three of the p53-positive MBs harbored a point mutation in the TP53 gene. p53 protein assessment by immunohistochemistry may be a useful tool for sub-stratification of metastatic high-risk MB patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giangaspero F, Eberhart CG, Haapasalo HH, Pietsch T, Wiestler OD, Ellison DW (2007) Medulloblastoma. In: Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD (eds) WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System, 4th edn. IARC press, Lyon, pp 132–140
Ellison DW (2010) Childhood medulloblastoma: novel approaches to the classification of a heterogeneous disease. Acta Neuropathol 120:305–316
Packer RJ, Rood BR, MacDonald TJ (2003) Medulloblastoma: present concepts of stratification into risk groups. Pediatr Neurosurg 39:60–67
Rutkowski S, von Hoff K, Emser A et al (2010) Survival and prognostic factors of early childhood medulloblastoma: an international meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol 28:4961–4968
Zeltzer PM, Boyett JM, Finlay JL et al (1999) Metastasis stage, adjuvant treatment, and residual tumor are prognostic factors for medulloblastoma in children: conclusions from the Children’s Cancer Group 921 randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol 17:832–845
Royds JA, Iacopetta B (2006) p53 and disease: when the guardian angel fails. Cell Death Differ 6:1017–1026
Machado-Silva A, Perrier S, Bourdon JC (2010) p53 family members in cancer diagnosis and treatment. Semin Cancer Biol 20:57–62
Eberhart CG, Chaudhry A, Daniel RW, Khaki L, Shah KV, Gravitt PE (2005) Increased p53 immunopositivity in anaplastic medulloblastoma and supratentorial PNET is not caused by JC virus. BMC Cancer 5:19
Miralbell R, Tolnay M, Bieri S et al (1999) Pediatric medulloblastoma: prognostic value of p53, bcl-2, Mib-1, and microvessel density. J Neurooncol 45:103–110
Nam DH, Wang KC, Kim YM et al (2000) The effect of isochromosome 17q presence, proliferative and apoptotic indices, expression of C-erbB-2, bcl-2 and p53 proteins on the prognosis of medulloblastoma. J Korean Med Sci 15:452–456
Wooburn RT, Azzarelli B, Montebello JF, Goss IE (2001) Intense p53 staining is a valuable prognostic indicator for poor prognosis in medulloblastoma/central nervous system primitive neuroectodermal tumors. J Neuro-oncol 52:57–62
Ray A, Ho M, Ma J et al (2004) A clinicobiological model predicting survival in medulloblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 10:7613–7620
Jaros E, Lunec J, Perry RH et al (1993) p53 protein overexpression identifies a group of central primitive neuroectodermal tumours with poor prognosis. Br J Cancer 68:801–807
MacDonald TJ, Brown KM, LaFleur B et al (2001) Expression profiling of medulloblastoma: PDGFRA and the RAS/MAPK pathway as therapeutic targets for metastatic disease. Nat Genet 2:143–152
Pfaff E, Remke M, Sturm D et al (2010) TP3 mutation is frequently associated with CTNNB1 mutation or MYCN amplification and is compatible with long-term survival in medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol 28:5188–5196
Tabori U, Baskin B, Shago M et al (2010) Universal poor survival in children with medulloblastoma harboring somatic TP53 mutations. J Clin Oncol 28:1345–1350
Lindsey JC, Hill RM, Megahed H et al (2011) TP53 mutations in favorable-risk Wnt/Wingless-subtype medulloblastomas. J Clin Oncol 29:344–346
Chang CH, Housepian EM, Herbert C Jr (1969) An operative staging system and a megavoltage radiotherapeutic technique for cerebellar medulloblastomas. Radiology 93:1351–1359
Rutkowski S, Bode U, Deinlein F et al (2005) Treatment of early childhood medulloblastoma by postoperative chemotherapy alone. N Engl J Med 352:978–979
Kraus JA, Bolln C, Wolf HK et al (1994) TP53 alterations and clinical outcome in low grade astrocytomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 10:143–149
Kraus JA, Felsberg J, Tonn JC, Reifenberger G, Pietsch T (2002) Molecular genetic analysis of the TP53, PTEN, CDKN2A, EGFR, CDK4 and MDM2 tumour-associated genes in supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumours and glioblastomas of childhood. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 28:325–333
Koch A, Waha A, Tonn JC et al (2001) Somatic mutations of WNT/wingless signaling pathway components in primitive neuroectodermal tumors. Int J Cancer 93:445–449
Rutkowski S, von Bueren A, von Hoff K et al (2007) Prognostic relevance of clinical and biological risk factors in childhood medulloblastoma: results of patients treated in the prospective multicenter trial HIT’91. Clin Cancer Res 13:2651–2657
Waha A, Watzka M, Koch A et al (1998) A rapid and sensitive protocol for competitive reverse transcriptase (cRT) PCR analysis of cellular genes. Brain Pathol 8:13–18
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Robles AI, Harris CC (2010) Clinical outcomes and correlates of TP53 mutations and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2:1–15
Min HS, Lee YJ, Park K, Cho BK, Park SH (2006) Medulloblastoma: histopathologic and molecular markers of anaplasia and biologic behavior. Acta Neuropathol 112:13–20
Frank AJ, Hernan R, Hollander A et al (2004) The TP53-ARF tumor suppressor pathway is frequently disrupted in large/cell anaplastic medulloblastoma. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 121:137–140
Lowe SW, Bodis S, McClatchey A et al (1994) p53 status and the efficacy of cancer therapy in vivo. Science 266:807–810
Huse JT, Holland EC (2009) Genetically engineered mouse models of brain cancer and the promise of preclinical testing. Brain Pathol 19:132–143
Adesina AM, Nalbantoglu J, Cavenee WK (1994) p53 gene mutation and mdm2 gene amplification are uncommon in medulloblastoma. Cancer Res 54:5649–5651
Castellino RC, De Bortoli M, Lu X et al (2008) Medulloblastomas overexpress the p53-inactivating oncogene WIP1/PPM1D. J Neurooncol 86:245–256
Acknowledgments
We thank Wiebke Treulieb and Christine Lindow for excellent data management and the contributing pathologists for the submission of tumour samples. Financially supported by German Childhood Cancer Foundation-Deutsche Kinderkrebsstiftung.
Conflicts of interests
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Marco Gessi and André O. von Bueren contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gessi, M., von Bueren, A.O., Rutkowski, S. et al. p53 expression predicts dismal outcome for medulloblastoma patients with metastatic disease. J Neurooncol 106, 135–141 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0648-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0648-8