Abstract
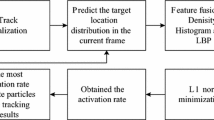
In order to solve the problem of complex environmental impact like illumination variation, appearance change and partial occlusion during the object tracking in the sequence images, a hybrid particle filter tracking method based on the global and local information was proposed. The Local Binary Patterns (LBP) textual feature was imported into the particle filter algorithm which uses local information of the target via sparse coding on local patches and combines the global information to determine the tracking object. In the procedure, the robustness of the tracking algorithm was improved since the template is updated on the time. Experimental results show that the proposed tracking algorithm exhibited good result in the presence of complex background and partial occlusion.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baum M, Hanebeck UD (2014) Extended object tracking with random hypersurface models. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst 50(1):149–159
Bousetouane F, Dib L, Snoussi H (2013) Improved mean shift integrating texture and color features for robust real time object tracking. Vis Comput 29(3):155–170
Chen F, Wang Q, Wang S, et al. (2011) Object tracking via appearance modeling and sparse representation. Image Vis Comput 29(11):787–796
Dawei Y, Yang C, Yandong T (2013) Object tracking method based on particle filter and sparse representation. PRAI 26(7):680–687
Ho MC, Chiang CC, Su YY (2012) Object tracking by exploiting adaptive region-wise linear subspace representations and adaptive templates in an iterative particle filter. Pattern Recogn Lett 33(5):500–512
Hsia KH, Lien SF, Su JP (2013) Moving target tracking based on CamShift approach and Kalman filter. International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Information Sciences 7(1):193–200
Jia X, Lu H, Yang MH (2012) Visual tracking via adaptive structural local sparse appearance model. In: 2012 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp 1882–1829
Karavasilis V, Nikou C, Likas A (2010) Visual tracking by adaptive kalman filtering and mean shift, Artificial intelligence: theories, models and applications, pp 153–162
Kim DY, Jeon M (2014) Data fusion of radar and image measurements for multi-object tracking via Kalman filtering. Inf Sci 278:641–652
Kumar A, Chan TST (2006) Robust ear identification using sparse representation of local texture descriptors. Pattern Recogn:1279–1284
Li J, Lu X, Ding L, et al. (2010) Moving target tracking via particle filter based on color and contour features. In: 2010 2nd International Conference on Information Engineering and Computer Science (ICIECS). IEEE, pp 1–4
Lu X, Yuan Y, Yan P (2013) Robust visual tracking with discriminative sparse learning. Pattern Recogn 46(7):1762–1771
Mei X, Ling HB (2009) Robust visual tracking using l 1 minimization. In: Proceedings of the 12th IEEE international conference on computer vision. Los Alamitos: IEEE Computer Society Press, pp 1436–1443
Ristic B, Arulampalam S, Gordon N (2004) Beyond the Kalman filter: particle filters for tracking applications. USA: Artech house Boston, pp 1–318
Rui T, Zhang Q, Zhou Y, et al. (2013) Object tracking using particle filter in the wavelet subspace. Neurocomputing 119:125–130
Su Y, Zhao Q, Zhao L, et al. (2014) Abrupt motion tracking using a visual saliency embedded particle filter. Pattern Recogn 47(5):1826–1834
Tsagkatakis G Savakis A (2011) Online distance metric learning for object tracking, Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 21. NO 12:1810–1821
Vijay AA, Johnson AK (2014) An integrated system for tracking and recognition using Kalman filter. In: 2014 International Conference on Control, Instrumentation Communication and Computational Technologies (ICCICCT), pp 1065–1069
Wang Q, Chen F, Xu W, et al. (2012) Object tracking via partial least squares analysis. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(10):4454–4465
Xie C, Tan J, Chen P, et al. (2014) Collaborative object tracking model with local sparse representation. J Vis Commun Image Represent 25(2):423–434
Yang Y, Cao Q (2013) A fast feature points- based object tracking method for robot grasp. Int J Adv Robot Syst 10(170):1–6
Zhong W, Yang M (2014) Robust object tracking via sparse collaborative appearance model, image processing. IEEE Transactions on Biometrics Compendium 23(5):2356–2368
Zhu J, Lao Y, Zheng YF (2010) Object tracking in structured environments for video surveillance applications. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 20(2):223–235
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Z., Zhou, M. & Li, J. Object tracking method based on hybrid particle filter and sparse representation. Multimed Tools Appl 76, 2979–2993 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3211-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3211-3