Abstract
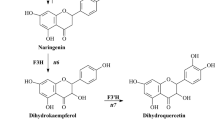
Flavonols are produced by the desaturation of dihydroflavanols, which is catalyzed by flavonol synthase (FLS). FLS belongs to the 2-oxoglutarate iron-dependent oxygenase family. The full-length cDNA and genomic DNA sequences of the FLS gene (designated as GbFLS) were isolated from Ginkgo biloba. The full-length cDNA of GbFLS contained a 1023-bp open reading frame encoding a 340-amino-acid protein. The GbFLS genomic DNA had three exons and two introns. The deduced GbFLS protein showed high identities with other plant FLSs. The conserved amino acids (H–X–D) ligating ferrous iron and residues (R–X–S) participating in 2-oxoglutarate binding were found in GbFLS at similar positions like other FLSs. GbFLS was found to be expressed in all tested tissues including roots, stems, leaves, and fruits. Expression profiling analyses revealed that GbFLS expression was induced by all of the six tested abiotic stresses, namely, UV-B, abscisic acid, cold, sucrose, salicylic acid, and ethephon, consistent with the in silico analysis results of the promoter region. The recombinant protein was successfully expressed in the E. coli strain BL21 (DE3) with a pET-28a vector. The in vitro enzyme activity assay by high performance liquid chromatography indicated that recombinant GbFLS protein could catalyze the formation of dihydrokaempferol to kaempferol and the conversion of kaempferol from naringenin, suggesting that GbFLS is a bifunctional enzyme within the flavonol biosynthetic pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ververidies F, Trantas E, Douglas C, Vollmer G, Kretzschmar G, Panopoulos N (2007) Biotechnology of flavonoids and other phenypropanoid-derived natural products. Part I: chemical diversity, impacts on plant biology and human heath. Biotechnol J 2:1214–1234
Gould KS, Lister C (2006) Flavonoid function in plants. In: Andersen M, Markham KR (eds) Flavonoids: chemistry, biochemistry and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 397–441
Kim JD, Liu L, Guo W, Meydani M (2006) Chemical structure of flavonols in relation to modulation of angiogenesis and immune-endothelial cell adhesion. J Nutr Biochem 17:165–176
Lee BH, Jeong SM, Lee JH, Kim JH, Yoon IS, Lee JH, Choi SH, Lee SM et al (2005) Quercetin inhibits the 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 receptor-mediated ion current by interacting with pretransmembrane domain I. Mol Cells 20:69–73
Schijlen E, Ric de Vos CH, Jonker H, van den Broeck H, Molthoff J, van Tunen A, Martens S, Bovy A (2006) Pathway engineering for healthy phytochemicals leading to the production of novel flavonoids in tomato fruit. Plant Biotechnol J 4:433–444
Reddy AM, Reddy VS, Scheffler BE, Wienand U, Reddy AR (2007) Novel transgenic rice overexpressing anthocyanidin synthase accumulates a mixture of flavonoids leading to an increased antioxidant potential. Metab Eng 9:95–111
Leonard E, Yan Y, Koffas MA (2006) Functional expression of a P450 flavonoid hydroxylase for the biosynthesis of plant-specific hydroxylated flavonols in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 8:172–181
Britsch L, Heller W, Grisebach H (1981) Conversion of flavanone to flavone, dihydroflavonol and flavonol with an enzyme system from cell culture of parsley. Z Naturforsch 36:742–750
Moriguchi T, Kita M, Ogawa K, Tomono Y, Endo T, Omura M (2002) Flavonol synthase gene expression during citrus fruit development. Physiol Plant 114:251–258
Preuß A, Stracke R, Weisshaar B, Hillebrecht A, Matern U, Martens S (2009) Arabidopsis thaliana expresses a second functional flavonol synthase. FEBS L 583:1981–1986
Chua CS, Biermann D, Goo KS, Sim TS (2008) Elucidation of active site residues of Arabidopsis thaliana flavonol synthase provides a molecular platform for engineering flavonols. Phytochemistry 69:66–75
Holton TA, Brugliera F, Tanaka Y (1993) Cloning and expression of flavonol synthase from Petunia hybrida. Plant J 4:1003–1010
Pelletier MK, Murrell JR, Shirley BW (1997) Characterization of flavonol synthase and leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 113:1437–1445
Wellmann F, Lukačin R, Moriguchi T, Britsch L, Schiltz E, Matern U (2002) Functional expression and mutational analysis of flavonol synthase from Citrus unshiu. Eur J Biochem 269:4134–4142
Fujita A, Goto-Yamamoto N, Aramaki I, Hashizume K (2006) Organ-specific transcription of putative flavonol synthase genes of grapevine and effects of plant hormones and shading on flavonol biosynthesis in grape berry skins. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:632–638
Lin G, Lian Y, Ryu J, Sung M, Park J, Park H, Park B, Shin J, Lee M, Cheon C (2007) Expression and purification of His-tagged flavonol synthase of Camellia sinensis from Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 55:287–292
van Beek TA, Montoro P (2009) Chemical analysis and quality control of Ginkgo biloba leaves, extracts, and phytopharmaceuticals. J Chromatogr A 1216:2002–2032
Granado-Serrano AB, Martín MA, Bravo L, Goya L, Ramos S (2006) Quercetin induces apoptosis via caspase activation, regulation of Bcl-2, and inhibition of PI-3-Kinase/Akt and ERK pathways in a human hepatoma cell line (HepG2). J Nutr 136:2715–2721
Noda N, Kanno Y, Kato N, Kazuma K, Suzuki M (2004) Regulation of gene expression involved in flavonol and anthocyanin biosynthesis during petal development in lisianthus (Eustoma grandiflorum). Physiol Plant 122:305–313
Xu F, Cai R, Cheng S, Du H, Wang Y, Cheng S (2008) Molecular cloning, characterization and expression of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene from Ginkgo biloba. Afr J Biotechnol 7:721–729
Pang Y, Shen G, Wu W, Liu X, Lin J, Tan F, Sun X, Tang K (2005) Characterization and expression of chalcone synthase gene from Ginkgo biloba. Plant Sci 168:1525–1531
Xu F, Cheng SY, Cheng SH, Wang Y, Du HW (2007) Time course of expression of chalcone synthase gene in Ginkgo biloba. J Plant Physiol Mol Biol 33:309–317
Shen G, Pang Y, Wu W, Deng Z, Zhao L, Cao Y, Sun X, Tang K (2006) Cloning and characterization of a flavanone 3-hydroxylase gene from Ginkgo biloba. Biosci Rep 26:19–29
Cheng H, Li L, Cheng S, Cao F, Wang F, Yuan H (2011) Molecular cloning and function assay of a chalcone isomerase gene (GbCHI) from Ginkgo biloba. Plant Cell Rep 30:49–62
Pang YZ (2005) Molecular cloning and characterization of important genes involved in the biosynthetic pathways of flavonoids and terpenoids from Ginkgo biloba L., PhD Thesis. Fudan University, China, pp 69–81
Liao ZH, Chen M, Guo L, Gong Y, Tan F, Sun X, Tang K (2004) Rapid isolation of high-quality total RNA from Taxus and Ginkgo. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 34:209–214
Prescott AG, Stamford NPJ, Wheeler G, Firmin JL (2002) In vitro properties of a recombinant flavonol synthase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytochemistry 60:589–593
Abe H, Urao T, Ito T, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) Arabidopsis AtMYC2 (bHLH) and AtMYB2 (MYB) function as transcriptional activators in abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 15:63–78
Finkelstein RR, Lynch TJ (2000) The Arabidopsis abscisic acid response gene ABI5 encodes a basic leucine zipper transcription factor. Plant Cell 12:599–609
Buchel AS, Brederode FT, Bol JF, Linthorst HJM (1999) Mutation of GT-1 binding sites in the Pr-1A promoter influences the level of inducible gene expression in vivo. Plant Mol Biol 40:387–396
Redman J, Whitcraft J, Johnson C, Arias J (2002) Abiotic and biotic stress differentially stimulate as-1 element activity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 21:180–185
Reyes JC, Muro-Pastor MI, Florencio F (2004) The GATA family of transcription factors in Arabidopsis and rice. J Plant Physiol 134:1718–1732
Kropat J, Tottey S, Birkenbihl RP, Depege N, Huijser P, Merchant S (2005) A regulator of nutritional copper signaling in Chlamydomonas is an SBP domain protein that recognize the GTAC core of copper response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:18730–18735
Tapia G, Verdugo I, Yañez M, Ahumada I, Theoduloz C, Cordero C, Poblete F, González E, Ru Ruiz-Lara S (2005) Involvement of ethylene in stress-Induced expression of the TLC1.1 retrotransposon from Lycopersicon chilense Dun. Plant Physiol 138:2075–2086
Sun C, Palmqvist S, Olsson H, Borén M, Ahlandsberg S, Jansson C (2003) A novel WRKY transcription factor, SUSIBA2, participates in sugar signaling in barley by binding to the sugar-responsive elements of the iso1 promoter. Plant Cell 15:2076–2092
Lukacin R, Britsch L (1997) Identification of strictly conserved histidine and arginine residues as part of the active site in Petunia hybrida flavanone 3b-hydroxylase. Eur J Biochem 249:748–757
Roach PL, Clifton IJ, Fulop V, Harlos K, Barton GJ, Hajdu J, Andersson I, Schofield CJ, Baldwin JE (1995) Crystal structure of isopenicillin N synthase is the first from a new structural family of enzymes. Nature 375:700–704
Prescott AG, John P (1996) Dioxygenases: molecular structure and role in plant metabolism. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47:245–271
Owens DK, Alerding AB, Crosby KC, Bandara AB, Westwood JH, Winkel BSJ (2008) Functional analysis of a predicted flavonol synthase gene family in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 147:1046–1061
Lukačin R, Wellmann F, Britsch L, Martens S, Matern U (2003) Flavonol synthase from Citrus unshiu is a bifunctional dioxygenase. Phytochemistry 62:287–292
El-Kereamya A, Chervin C, Roustan J, Cheynier V, Souquet J, Moutounet M, Raynal J, Ford C, Latché A, Pech J, Bouzayen M (2003) Exogenous ethylene stimulates the long-term expression of genes related to anthocyanin biosynthesis in grape berries. Physiol Plant 119:175–182
Gaffney T, Friedrich L, Vernooij B, Negrotto D, Nye D, Uknes S, Ward E, Kessmann H, Ryals J (1993) Requirement of salicylic acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science 261:754–756
Kush A, Goyvaerts E, Chye ML, Chua NH (1990) Laticifer-specific gene expression in Hevea brasiliensis (rubber tree). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1787–1790
Ardi R, Kobiler I, Jacoby B, Keen NT, Prusky D (1998) Involvement of epicatechin biosynthesis in the activation of the mechanism of resistance of avocado fruits to Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 53:269–285
Ferreyra MLF, Rius S, Emiliani J, Pourcel L, Feller A, Morohashi K, Casati P, Grotewold E (2010) Cloning and characterization of a UV-B-inducible maize flavonol synthase. Plant J 62:77–91
Weiss D (2000) Regulation of flower pigmentation and growth: multiple signaling pathways control anthocyanin synthesis in expanding petals. Physiol Plant 110:152–157
Gollop R, Even S, Colova-Tsolova V, Peri A (2002) Expression of the grape dihydroflavonol reductase gene and analysis of its promoter region. J Exp Bot 53:1397–1409
Cheng S, Wang Y, Li J, Gu M, Shu H (2001) The relationships between flavonoids and other related compositions in Ginkgo biloba leaf during its anabolism. J Huazhong Agric Univ 20:474–477
Xu F, Cheng H, Cai R, Li LL, Chang J, Zhu J, Zhang FX, Chen LJ, Wang Y, Cheng SH, Cheng SY (2008) Molecular cloning and function analysis of an anthocyanidin synthase gene from Ginkgo biloba, and its expression in abiotic stress responses. Mol Cells 26:536–547
Tsukaya H, Ohshima T, Naito S, Chino M, Komeda Y (1991) Sugar-dependent expression of the CHS-A gene for chalcone synthase from Petunia in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 97:1414–1421
Cheng SY, Xu F, Wang Y (2009) Advances in the study of flavonoids in Ginkgo biloba leaves. J Med Plants Res 3:1248–1252
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30971974), Natural Science Fund of Hubei Province (2008CDA061), and University-Industry Cooperation Fund of Hubei Educational Office (CXY2009B009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, F., Li, L., Zhang, W. et al. Isolation, characterization, and function analysis of a flavonol synthase gene from Ginkgo biloba . Mol Biol Rep 39, 2285–2296 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-0978-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-0978-9