Abstract
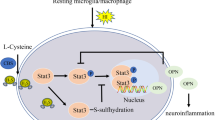
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a gasotransmitter endogenously synthesized by cystathionine-γ-lyase (CSE), cystathionine-β-synthase (CBS), and 3-mercaptopiruvate sulfurtransferase (3-MST) enzymes. H2S exogenous administration prevents the development of hemodynamic impairments after traumatic brain injury (TBI). Since the hypothalamus and the brainstem highly regulate the cardiovascular system, this study aimed to evaluate the effect of NaHS subchronic treatment on the changes of H2S-sythesizing enzymes in those brain areas after TBI and in physiological conditions. For that purpose, animals were submitted to a lateral fluid percussion injury, and the changes in CBS, CSE, and 3-MST protein expression were measured by western blot at days 1, 2, 3, 7, and 28 in the vehicle group, and 7 and 28 days after NaHS treatment. After severe TBI induction, we found a decrease in CBS and CSE protein expression in the hypothalamus and brainstem; meanwhile, 3-MST protein expression diminished only in the hypothalamus compared to the Sham group. Remarkably, i.p. daily injections of NaHS, an H2S donor, (3.1 mg/kg) during seven days: (1) restored CBS and CSE but no 3-MST protein expression in the hypothalamus at day 28 post-TBI; (2) reestablished only CSE in brainstem 7 and 28 days after TBI; and (3) did not modify H2S-sythesizing enzymes protein expression in uninjured animals. Mainly, our results show that the NaHS effect on CBS and CSE protein expression is observed in a time- and tissue-dependent manner with no effect on 3-MST expression, which may suggest a potential role of H2S synthesis in hypothalamus and brainstem impairments observed after TBI.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Agrawal N, Banerjee R (2008) Human polycomb 2 protein is a SUMO E3 ligase and alleviates substrate-induced inhibition of cystathionine β-synthase sumoylation. PLoS One 3. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0004032
Che X, Fang Y, Si X et al (2018) The role of gaseous molecules in traumatic brain injury: An updated review. Front Neurosci 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00392
Coletti R, de Lima JBM, Vechiato FMV et al (2019) Nitric oxide acutely modulates hypothalamic and neurohypophyseal carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulphide production to control vasopressin, oxytocin and atrial natriuretic peptide release in rats. J Neuroendocrinol 31. https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.12686
Corsello T, Komaravelli N, Casola A (2018) Role of hydrogen sulfide in nrf2-and sirtuin-dependent maintenance of cellular redox balance. Antioxidants 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7100129
Dawe GS, Han SP, Bian JS, Moore PK (2008) Hydrogen sulphide in the hypothalamus causes an ATP-sensitive K+ channel-dependent decrease in blood pressure in freely moving rats. Neuroscience 152:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.12.008
Duan XC, Guo R, Liu SY et al (2015) Gene transfer of cystathionine β-synthase into RVLM increases hydrogen sulfide-mediated suppression of sympathetic outflow via KATP channel in normotensive rats. Am J Physiol - Hear Circ Physiol 308:H603–H611. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00693.2014
Eric Nyam TT, Ho CH, Chio CC et al (2019) Traumatic Brain Injury Increases the Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Events: A 13-Year, Population-Based Study. World Neurosurg 122:e740–e753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.10.130
Fouda MA, El-Sayed SS, Abdel-Rahman AA (2018) Restoration of rostral ventrolateral medulla cystathionine-g lyase activity underlies moxonidine-Evoked neuroprotection and sympathoinhibition in diabetic rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 364:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.117.243865
Frieden TR, Houry D, Baldwin G (2015) Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States: Epidemiology and Rehabilitation. CDC NIH Rep to Congr 1–74. https://doi.org/10.3171/2009.10.JNS091500
Gheibi S, Aboutaleb N, Khaksari M et al (2014) Hydrogen sulfide protects the brain against ischemic reperfusion injury in a transient model of focal cerebral ischemia. J Mol Neurosci 54:264–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12031-014-0284-9
Giuliani D, Ottani A, Zaffe D et al (2013) Hydrogen sulfide slows down progression of experimental Alzheimer’s disease by targeting multiple pathophysiological mechanisms. Neurobiol Learn Mem 104:82–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2013.05.006
Goldstein B, Toweill D, Lai S et al (2017) Uncoupling of the autonomic and cardiovascular systems in acute brain injury. Am J Physiol Integr Comp Physiol 275:R1287–R1292. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1998.275.4.r1287
Guo Q, Jin S, Wang XL et al (2011) Hydrogen sulfide in the rostral ventrolateral medulla inhibits sympathetic vasomotor tone through ATP-Sensitive K+ Channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 338:458–465. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.111.180711
Guo C, Liang F, Shah Masood W, Yan X (2014) Hydrogen sulfide protected gastric epithelial cell from ischemia/reperfusion injury by Keap1 s-sulfhydration, MAPK dependent anti-apoptosis and NF-κB dependent anti-inflammation pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 725:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.01.009
Hammond FM, Corrigan JD, Ketchum JM et al (2019) Prevalence of medical and psychiatric comorbidities following traumatic brain injury. J Head Trauma Rehabil 34:1. https://doi.org/10.1097/htr.0000000000000465
Hassan MI, Boosen M, Schaefer L et al (2012) Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces cystathionine Iγ-lyase expression in rat mesangial cells via a redox-dependent mechanism. Br J Pharmacol 166:2231–2242. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01949.x
Hourihan JM, Kenna JG, Hayes JD (2013) The gasotransmitter hydrogen sulfide induces Nrf2-target genes by inactivating the keap1 ubiquitin ligase substrate adaptor through formation of a disulfide bond between Cys-226 and Cys-613. Antioxidants Redox Signal 19:465–481. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.4944
Huerta de la Cruz S, Rocha L, Santiago-Castañeda C et al (2022) Hydrogen Sulfide Subchronic Treatment Improves Hypertension Induced by Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats through Vasopressor Sympathetic Outflow Inhibition. J Neurotrauma 39:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2020.7552
Jiang X, Huang Y, Lin W et al (2013) Protective effects of hydrogen sulfide in a rat model of traumatic brain injury via activation of mitochondrial adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels and reduction of oxidative stress. J Surg Res 184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2013.03.067
Karimi SA, Hosseinmardi N, Janahmadi M et al (2017) The protective effect of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) on traumatic brain injury (TBI) induced memory deficits in rats. Brain Res Bull 134:177–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.07.014
Kaur P, Sharma S (2017) Recent advances in pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury. Curr Neuropharmacol 15:1224–1238. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X15666170613083606
Kida K, Yamada M, Tokuda K et al (2011) Inhaled hydrogen sulfide prevents neurodegeneration and movement disorder in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Antioxidants Redox Signal 15:343–352. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2010.3671
Kumar M, Arora P, Sandhir R (2020) Hydrogen Sulfide Reverses LPS-Induced Behavioral Deficits by Suppressing Microglial Activation and Promoting M2 Polarization. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 162(16):483–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11481-020-09920-Z
Li M, Nie L, Hu Y et al (2013) Chronic intermittent hypoxia promotes expression of 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase in adult rat medulla oblongata. Auton Neurosci Basic Clin 179:84–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autneu.2013.08.066
Li N, Wang MJ, Jin S et al (2016) The H2S donor NaHS changes the expression pattern of H2S-producing enzymes after myocardial infarction. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6492469
Liang YF, Zhang DD, Yu XJ et al (2017) Hydrogen sulfide in paraventricular nucleus attenuates blood pressure by regulating oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in high salt-induced hypertension. Toxicol Lett 270:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.02.004
Liu H, Wang Y, Xiao Y et al (2016) Hydrogen sulfide attenuates tissue plasminogen activator-induced cerebral hemorrhage following experimental stroke. Transl Stroke Res 7:209–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-016-0459-5
Lozano D, Gonzales-Portillo GS, Acosta S et al (2015) Neuroinflammatory responses to traumatic brain injury: Etiology, Clinical consequences, And therapeutic opportunities. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 11:97–106. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S65815
McIntosh TK, Vink R, Noble L et al (1989) Traumatic brain injury in the rat: characterization of a lateral fluid-percussion model. Neuroscience 28:233–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4522(89)90247-9
Mohammed RA, Mansour SM (2021) Sodium hydrogen sulfide upregulates cystathionine β-synthase and protects striatum against 3-nitropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 73:310–321. https://doi.org/10.1093/JPP/RGAA072
Moustafa A (2021) Changes in nitric oxide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide and male reproductive hormones in response to chronic restraint stress in rats. Free Radic Biol Med 162:353–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.10.315
Mustafa AK, Gadalla MM, Sen N et al (2009) H2S Signals Through Protein S-Sulfhydration. Sci Signal 2:ra72–ra72. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2000464
National Research Council of the National Academies (2011) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals, 8th edn. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC
Ning J, Mo L, Zhao H et al (2013) Sodium hydrosulphide alleviates remote lung injury following limb traumatic injury in rats. PLoS One 8:59100. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0059100
Nogueira JE, Soriano RN, Fernandez RAR et al (2017) Effect of physical exercise on the febrigenic signaling is modulated by preoptic hydrogen sulfide production. PLoS One 12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0170468
Olson KR, DeLeon ER, Gao Y et al (2013) Thiosulfate: A readily accessible source of hydrogen sulfide in oxygen sensing. Am J Physiol - Regul Integr Comp Physiol 305:592–603. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00421.2012
Renga B, Cipriani S, Carino A et al (2015) Reversal of endothelial dysfunction by gpbar1 agonism in portal hypertension involves a AKT/FOXOA1 dependent regulation of H2S generation and endothelin-1. PLoS One 10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141082
Roa-Coria JE, Pineda-Farias JB, Barragán-Iglesias P et al (2019) Possible involvement of peripheral TRP channels in the hydrogen sulfide-induced hyperalgesia in diabetic rats. BMC Neurosci 20:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-018-0483-3
Santiago-Castañeda C, Segovia-Oropeza M, Concha L et al (2020) Propylparaben Reduces the Long-Term Consequences in Hippocampus Induced by Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats: Its Implications as Therapeutic Strategy to Prevent Neurodegenerative Diseases. J Alzheimer’s Dis 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-200914
Searcy D, Lee S (1998) Sulfur reduction by human erythrocytes. J Exp Zool 282:310–322. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-010x(19981015)282:3%3c310::aid-jez4%3e3.0.co;2-p
Segovia-Oropeza M, Santiago-Castañeda C, Orozco-Suárez SA et al (2020) Sodium cromoglycate decreases sensorimotor impairment and hippocampal alterations induced by severe traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurotrauma 37:2595–2603. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2019.6975
Shan H, Qiu J, Chang P et al (2019) Exogenous Hydrogen sulfide offers neuroprotection on intracerebral hemorrhage injury through modulating endogenous H2S metabolism in mice. Front Cell Neurosci 13:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00349
D’Emmanuele di Villa Bianca R, Mitidieri E, Fusco F et al (2016) Urothelium muscarinic activation phosphorylates CBS Ser227 via cGMP/PKG pathway causing human bladder relaxation through H 2 S production. Sci Rep 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31491
Wang R (2002) Two’s company, three’s a crowd: can H2S be the third endogenous gaseous transmitter? FASEB J 16:1792–1798. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.02-0211hyp
Wang R (2012) Physiological implications of hydrogen sulfide: a whiff exploration that blossomed. Physiol Rev 92:791–896. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00017.2011
Xiao L, Dong J-H, Jin S et al (2016) Hydrogen sulfide improves endothelial dysfunction via downregulating BMP4/COX-2 pathway in rats with hypertension. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:8128957. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8128957
Xu K, Wu F, Xu K et al (2018) NaHS restores mitochondrial function and inhibits autophagy by activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway to improve functional recovery after traumatic brain injury. Chem Biol Interact 286:96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.028
Yang G, Pei Y, Teng H et al (2011) Specificity protein-1 as a critical regulator of human cystathionine ??-lyase in smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 286:26450–26460. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.266643
Yang J, Minkler P, Grove D et al (2019) Non-enzymatic hydrogen sulfide production from cysteine in blood is catalyzed by iron and vitamin B 6. Commun Biol 2. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-019-0431-5
Yu H, Xu H, Liu X et al (2015) Superoxide mediates depressive effects induced by hydrogen sulfide in rostral ventrolateral medulla of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/927686
Zhang M, Shan H, Wang T et al (2013) Dynamic change of hydrogen sulfide after traumatic brain injury and its effect in mice. Neurochem Res 38:714–725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-0969-4
Zhang M, Shan H, Chang P et al (2016) Upregulation of 3-MST relates to neuronal autophagy after traumatic brain injury in mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37:291–302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0369-9
Zhang J, Shi C, Wang H et al (2019) Hydrogen sulfide protects against cell damage through modulation of PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 signaling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 117:105636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2019.105636
Funding
The National Council for Science and Technology (CONACyT) supported this work [Grant No. 252702].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huerta de la Cruz S, Rocha L and Centurion D conceived the original idea. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Huerta de la Cruz S, Rodríguez-Palma EJ, Santiago-Castañeda CL, Beltrán-Ornelas JH and Sánchez-López A. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Huerta de la Cruz S and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huerta de la Cruz, S., Rodríguez-Palma, E.J., Santiago-Castañeda, C.L. et al. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide restores CSE and CBS but no 3-MST protein expression in the hypothalamus and brainstem after severe traumatic brain injury. Metab Brain Dis 37, 1863–1874 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01033-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01033-1