Abstract
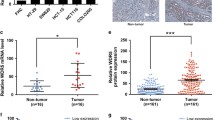
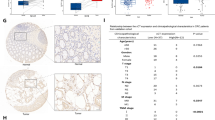
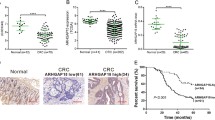
GATA1, a member of the GATA transcription factor family, was reported to play a role in development and progression of erythroid cells and breast cancer cells. However, the role of GATA1 in colorectal cancer (CRC) is unknown. Here, we demonstrate that GATA1 was upregulated in CRC tissues compared with normal tissues, and predicted poor clinical outcome in CRC. Biological functional analyses showed that GATA1 knockdown decreased CRC cells proliferation, migration and invasion, and regulated the process of epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT). Moreover, silencing of GATA1 suppressed colorectal tumor growth in nude mice. Mechanistically, GATA1 overexpression significantly increased the activity of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in CRC cells. These data provide insight into the important role of GATA1 in CRC progression and suggest that GATA1 is a potential therapeutic target for CRC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jernal A (2017) Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 67:7–30
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, Ahnen DJ, Meester RGS, Barzi A, Jemal A (2017) Colorectal cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 67:177–193
Lansdorp-Vogelaar I, Kuntz KM, Knudsen AB, Ballegooijen MV, Zauber AG, Jemal A (2012) Contribution of screening and survival differences to racial disparities in colorectal cancer rates. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 21:728–736
Imperiale TF, Juluri R, Sherer EA, Glowinski EA, Johnson CS, Morelli MS (2014) A risk index for advanced neoplasia on the second surveillance colonoscopy in patients with previous adenomatous polyps. Gastrointest Endosc 80:471–478
Laukoetter MG, Mennigen R, Hannig CM, Osada N, Rijcken E, Vowinkel T, Krieglstein CF, Senninger N, Anthoni C, Bruewer M (2011) Intestinal cancer risk in Crohn’s disease: a meta-analysis. J Gastrointest Surg 15:576–583
Cunningham D, Atkin W, Lenz H-J, Lynch HT, Minsky B, Nordlinger B, Starling N (2010) Colorectal cancer. Lancet 375:1030–1047
Bockelman C, Engelmann BE, Kaprio T, Hansen TF, Glimelius B (2015) Risk of recurrence in patients with colon cancer stage II and III: a systematic review and meta-analysis of recent literature. Acta Oncol 54:5–16
Boland PM, Ma WW (2017) Immunotherapy for colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel) 9:50
Syn NL, Teng MWL, Mok TSK, Soo RA (2017) De-novo and acquired resistance to immune checkpoint targeting. Lancet Oncol 18:e731–e741
Zheng R, Blobel GA (2010) GATA transcription factors and cancer. Genes Cancer 1:1178–1188
Shimizu R, Engel JD, Yamamoto M (2008) GATA1-related leukaemias. Nat Rev Cancer 8:279–287
Boidot R, Vegran F, Jacob D, Chevrier S, Cadouot M, Feron O, Solary E, Lizard-Nacol S (2010) The transcription factor GATA-1 is overexpressed in breast carcinomas and contributes to survivin upregulation via a promoter polymorphism. Oncogene 29:2577–2584
Zhang Y, Liu J, Lin J, Zhou L, Song Y, Wei B, Luo X, Chen Z, Chen Y, Xiong J, Xu X, Ding L, Ye Q (2016) The transcription factor GATA1 and the histone methyltransferase SET7 interact to promote VEGF-mediated angiogenesis and tumor growth and predict clinical outcome of breast cancer. Oncotarget 7:9859–9875
Li Y, Ke Q, Shao Y, Zhu G, Li Y, Geng N, Jin F, Li F (2015) GATA1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells through PAK5 oncogenic signaling. Oncotarget 6:4345–4356
Feng Y, Xu X, Zhang Y, Ding J, Wang Y, Zhang X, Wu Z, Kang L, Liang Y, Zhou L, Song S, Zhao K, Ye Q (2015) HPIP is upregulated in colorectal cancer and regulates colorectal cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis and invasion. Sci Rep 5:9429
evans T, Reitman M, Felsenfeld G (1988) An erythrocyte-specific DNA-binding factor recognizes a regulatory sequence common to all chicken globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:5976–5980
Krepischi ACV, Maschietto M, Ferreira EN, Silva AG, Costa SS, Cunha IWD, Barros BDF, Grundy PE, Rosenberg C, Carraro DM (2016) Genomic imbalances pinpoint potential oncogenes and tumor suppressors in Wilms tumors. Mol Cytogenet 9:20
Altom DA, Testa JR (2005) Perturbations of the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene 24:7455–7464
Nicholson KM, Anderson NG (2002) The protein kinase B/Akt signalling pathway in human malignancy. Cell Signal 14:381–395
Xue G, Hemmings BA (2013) PKB/Akt-dependent regulation of cell motility. J Natl Cancer Inst 105:393–404
Grille SJ, Bellacosa A, Upson J, Klein-Szanto AJ, Roy FV, Lee-Kwon W, Donowitz M, Tsichlis PN, Larue L (2003) The protein kinase Akt induces epithelial mesenchymal transition and promotes enhanced motility and invasiveness of squamous cell carcinoma lines. Cancer Res 63:2172–2178
Lamouille S, Derynck R (2007) Cell size and invasion in TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition is regulated by activation of the mTOR pathway. J Cell Biol 178:437–451
Pon YL, Zhou HY, Cheung ANY, Ngan HYS, Wong AST (2008) p70 S6 kinase promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition through snail induction in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res 68:6524–6532
Smith AP, Verrecchia A, Faga G, Doni M, Perna D, Martinato F, Guccione E, Amati B (2009) A positive role for Myc in TGFbeta-induced Snail transcription and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 28:422–430
Scaltriti M, Baselga J (2006) The epidermal growth factor receptor pathway: a model for targeted therapy. Clin Cancer Res 12:5268–5272
Danielsen SA, Eide PW, Nesbakken A, Guren T, Leithe E, Lothe RA (2015) Portrait of the PI3K/AKT pathway in colorectal cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1855:104–121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Liu, M., Liu, H. et al. GATA1 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via activating AKT signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 457, 191–199 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03523-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03523-w