Abstract
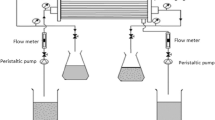
Low level radioactive liquid waste (LLW) obtained after treatment of Intermediate level radioactive waste (ILW) is highly alkaline and rich in 99Tc as the pertechnetate ion. It is considered as a long-term hazard in nuclear waste disposal. Solvent extraction of Pertechnetate species was performed using crown ether impregnated hollow fibre membrane using nitrobenzene and TBP solvents in different membrane modules. Better D values were obtained with Nitrobenzene however in view of toxicity of nitrobenzene study was also conducted with TBP and TBP nitrobenzene mix solvent. With nitrobenzene solvent almost 95% of 99Tc was separated in four contacts. However with increase in TBP content the percentage extraction is decreasing due to decrease in D value. The results are presented and discussed in the paper.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Atomic Energy Agency (1985) Chemical Durability and related properties of solidified high level waste forms, Technical Reports Series no. 257, IAEA, Vienna
Yeotikar RG, Sonavane MS, Shah JG, Raj Kanwar (1993) Development of Vitrified Matrix for High Level Waste and its Characterisation – Experience at WIP, Tarapur. National Symposium on management of Radioactive and Toxic Waste (SMART-93) Kalpakkam, p 257 – 260
Samanta SK, Ramanswamy M, Sen P, Varadarajan N, Singh RK (1993) Removal of radiocesium from alkaline IL waste, National Symposium on management of Radioactive and Toxic waste (SMART-93) Kalpakkam, p 56 – 58
Yeotikar RG, Kaushik CP, Gabriel Johnson, Kanwar Raj (1995) Treatment of Alkaline Intermediate Level Radioactive waste” NUCAR 95 – IGCAR, Kalpakkam, p 429 – 430
Kulkarni Y, Samanta SK, Bakre SY, Raj K, Kumra MS (1996) Process for treatment of Intermediate level radioactive waste based on radionuclide separation. Waste Management 96, Proc. Int. Symp. Tucson, Arizona
Valsala TP, Sonavane MS, Kore SG, Sonar NL, De Vaishali, Raghvendra Y,Chattopadhyay S, Dani D, Kulkarni Y, Changrani RD (2011) Treatment of Low Level Radioactive liquid waste containing appreciable concentration of TBP degraded products”, J. Hazardous Materials, 196: 22–28
Kotegov KV, Pavlov ON, Shvedov VP (1968) Technetium. In Advances in organic chemistry and radiochemistry, Vol 11, Edited by: Emélius, H J and Sharpe, A G. 1–90. New York: Academic Press
Hu QH, Weng JQ, Wang J-S (2010) Sources of anthropogenic radionuclides in the environment – a review. J Environ Radioact 101(6):426
Wildung KE, Garland TR, Cataldo DA (1977) Accumulation of technetium by plants. Health Phys 32:314–317
Lieser KH, Bauscher Ch (1987) Technetium in the hydrosphere and in the geosphere. I. Chemistry of technetium and iron in natural waters and influence of the redox potential on the sorption of technetium. Radiochim. Acta 42, 205
Wildung RE, Garland TR, McFadden KM, Cowan CE (1986) Technetium sorption m surface soil. In: Desmet,G. and Myttenaere. C. (eds), Technetium in the Environment. Elsevier Applied Science Publishers, p 115-129
Lee SY, Bondietti EA (1983) Technetium behavior insulfide and ferrous iron solutions. Mat. Res. Sot. Symp. Pro. 15. Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc
Walton FB, Paquette J, Ross JPM, Lawrence WE (1986) TdIV) and Tc<VII) interactions with iron oxyhydroxides. Nucl Chem Waste Manage 6:121–126
Wooyong Um, Steven A. Luksic, Guohui Wang, Sarah Saslow, Dong-Sang kim, Michal J. Schweiger, /chuck Z. Soderquist, Mark E. Bowden, Wayne W. Lukens, Albert A. Kruger (2017) Enhanced 99Tc retention in glass waste form using Tc(IV) incorporated Fe minerals”, J. Nuclear Materials, 495: 455–462
Wooyong Um,Hyun-Shik Chang, Jonathan P. Icenhower, Wayne W. Lukens, R. Jeffrey Serne, Nikolla P. Qafoku, Joseph H. Westsik, Jr., Edgar C. Buck and Steven C. Smith (2017) Immobilisation of 99Tc(VII) by Fe(II)- Goethite and Limited Reoxidation” Environmental Science and Technology, 45: 4904–4913
W. Um G. Wang, H.B.Jung, R.A. Peterson (2013) Technetium removal using Tc- Goethite Coprecipitation” PNNL – 22967
King WD, McCabe DJ, Hassan NM, Walker DD (2000) Intermediate Scale Ion Exchange Removal of Technetium from Savannah River Site Tank 44 F Supernate Solution”, BNF-00398–0230
Vaishali De, Sonar NL, Y. Raghvendra, T.P. Valsala, M.S. Sonavane, Savital jain (2012) Removal of 99Tc from Low level radioactive liquid waste using commercial anion exchanger resin.” Desalination and Water Treatment, 38, 1–3 p 22–28
Alexander A.A, MagomedS. Dzhigirkhanov, Yurii I Matyunin and Boris A. Iofa (2012) Extraction of oxoanions by tetraalkyl ammonium salts”Mendeleev Communications, 11/3 p 121–122
Baohua Gu a, Kathryn E, Dowlena, Liyuan Liang (1996) Jay L Clausenb (1996) Efficient separation and recovery of technetium-99 fromcontaminated groundwater” Separations Technology 6: 123–132
Lee and Bondietti (1983) J. AWWA, 75(10) : 536 , 1983; Lukens et al. 2002, Environ. Sc. Techn, 36, 5, 1124–1129
Turcotte MDS (1982) Environmental Behavior of Technetium: Report DE83 010 342, Aiken, SC (USA): Savannah River Lab
Shkrob IA, Martin TW, Stepinski DC, Vandegrift GF et.al (2011) Extraction and Reductive Stripping of Pertechnetate from Spent Nuclear Fuel Waste Stream, Separation Science and Technology, p-357–368
Sonar NL, Vaishali De, Pardeshi V, Raghavendra Y, Valsala TP, Sonavane MS, Kulkarni Y, Raj Kanwar (2012) Analysis of 99Tc in the radioactive liquid waste after extraction into suitable solvent”, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 294: 185–189
Peter V. Bonnesen, Bruce A. Moyer, Derek J. Presley, Virginia S. Armstrong, TamaraJ. Haverlock, Robert M. Counce, Richard A. Sachleben, Alkaline-Side Extraction of Technetium from Tank Waste Using Crown Ethers and Other Extractants, ORNL/TM-13241 Chemical and Analytical Sciences Division, 1996 (June).
J.N. Sharma, Prithwish Sinharoy, B. Kharwandikar, Vidya S. Thorata, V. Tessy, C.P. Kaushik (2018) Process for separation of technetium from alkaline low level waste using ditert-butyldibenzo-18-crown-6+isodecyl alcohol/n-dodecane solvent, Separation and Purification Technology 207: 416–419
Patricia Paviet – Hartmann (2002) Solvent Extraction of 99Tc from Radioactive Intermediate Liquid Waste by Dibenzo-18C6”, LA – UR -01–4974, WM-02 Tucson, Arizona.
Tiziana Marino and Alberto Figoli (2015) Arsenic Removal by Liquid Membranes. Memb, 5: 150-167
Li NN (1969) Permeation through liquid surfactant membranes. AIChE J 17:459–463
Parhi PK (2013) Supported liquid membrane principle and Its practices: A short review. J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/618236
Simulation of non-linear flow density in transition state from the mathematical model of the diffusion of metal anions through a flat sheet supported liquid membrane, G. Benzal a, A. Kumar b, A.M. Sastre c and A. Delshams d Journal of Mathematical Chemistry Vol. 34, Nos. 1–2, July 2003 (© 2003)
Smita Gupta, Mousumi Chakraborty, Z.V.P. Murthy (2014) Performance study of hollow fiber supported liquid membrane system for the separation of bisphenol a from aqueous solutions, J Ind Eng Chem. 20: 2138–2145
Clàudia Fontàs , Enriqueta Anticó and Victòria Salvadó (2018) Design of a Hollow Fiber Supported Liquid Membrane System for Zn Speciation in Natural Waters, Memb. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040088
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Prof. (Dr.) A.K.Tyagi, Associate Director, Chemistry Group, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, Mumbai, for his guidance and support in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thakur, D.A., Sonar, N.L., Pabby, A. et al. Separation of 99Tc from low level radioactive liquid waste using hollow fiber supported liquid membrane: optimisation and performance evaluation. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 330, 811–820 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07983-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07983-7