Abstract
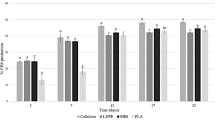
This paper presents a study on the degradation of Poly (lactic acid) (PLA), Poly (butylene abdicate—terephthalate) (PBAT) and their blends with different proportions in the environment of digested sludge. The degradation rates of PLA and PBAT were obtained through anaerobic reaction device. The samples obtained at regular intervals were measured and analyzed by differential scanning calorimeter (DSC), infrared spectrometer (FTIR) and scanning electron microscope (SEM) respectively. The results showed that the degradation rate of PLA was higher than that of PBAT under the same degradation environment and degradation time. DSC results showed that the degradation rate of PLA in the amorphous phase was slowed by the influence of PBAT. The characteristic peaks of the materials on the infrared spectrum shifted after degradation which implicit the degradation occurs. At the microscopic level, numerous protruding ribs in the material can be seen in the electron micrograph. Obviously, the samples can be degraded under the environment of digested sludge.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nampoothiri KM, Nair NR, John RP (2010) An overview of the recent developments in polylactide (PLA) research. Bioresour Technol 101(22):8493–8501
Musioł M, Sikorska W, Janeczek H, Wałach W, Hercog A, Johnston B, Rydz J (2018) (Bio)degradable polymeric materials for a sustainable future—part 1. Organic recycling of PLA/PBAT blends in the form of prototype packages with long shelf-life. Waste Manage 77:447–454
Sorrentino A, Gorrasi G, Vittoria V (2007) Potential perspectives of bio-nanocomposites for food packaging applications. Trends Food Sci Technol 18(2):84–95
Otey FH, Mark AM, Mehltretter CL, Russell CR (1974) Starch-based film for degradable agricultural mulch. Ind Eng Chem Prod Res Dev 13(1):90–92
Otey FH, Westhoff RP, Russell CR (1977) Biodegradable films from starch and ethylene-acrylic acid copolymer. Ind Eng Chem Prod Res Dev 16(4):305–308
Castro-Aguirre E, Auras R, Selke S, Rubino M, Marsh T (2018) Enhancing the biodegradation rate of poly(Lactic acid) films and PLA bio-nanocomposites in simulated composting through bioaugmentation. Polym Degrad Stab 154:46–54
Ho KLG, Pometto AL, Gadea-Rivas A, Briceño JA (1999) Augusto Rojas, degradation of polylactic acid (PLA) plastic in costa rican soil and iowa state university compost rows. J Environ Polym Degrad 7(4):173–177
Maurizio T, Miriam W, Michela S (2012) Laboratory test methods to determine the degradation of plastics in marine environmental conditions. Front Microbiol 3:225
Stoleru E, Hitruc EG, Vasile C, Oprică L (2017) Biodegradation of poly(lactic acid)/chitosan stratified composites in presence of the Phanerochaete chrysosporium fungus. Polym Degrad Stab 143:118–129
Badia JD, Strömberg E, Kittikorn T, Ek M, Karlsson S, Ribes-Greus A (2017) Relevant factors for the eco-design of polylactide/sisal biocomposites to control biodegradation in soil in an end-of-life scenario. Polym Degrad Stab 143:9–19
Karamanlioglu M, Robson GD (2013) The influence of biotic and abiotic factors on the rate of degradation of poly(lactic) acid (PLA) coupons buried in compost and soil. Polym Degrad Stab 98(10):2063–2071
Pattanasuttichonlakul W, Sombatsompop N, Prapagdee B (2018) Accelerating biodegradation of PLA using microbial consortium from dairy wastewater sludge combined with PLA-degrading bacterium. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 132:74–83
Zhu DP (2009) Development and recycling for plastics packaging waste. Shanghai Plast 147(3):25–29
Roohi K, Bano M, Kuddus MR, Zaheer Q, Zia KM, Farhan GM, Ashraf G (2017) Aliev, Microbial enzymatic degradation of biodegradable plastics. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 18(5):429
Fortunati E, Armentano I, Iannoni A, Kenny JM (2010) Development and thermal behaviour of ternary PLA matrix composites. Polymer Degrad Stab 95(11):2200–2206
Vieira AC, Marques AT, Guedes RM, Tita V (2011) Material model proposal for biodegradable materials. Proc Eng 10(7):1597–1602
Souza PMS, Corroqué NA, Morales AR, Marin-Morales MA, Mei LHI (2013) PLA and Organoclays nanocomposites: degradation process and evaluation of ecotoxicity using allium cepa as test organism. J Polym Environ 21(4):1052–1063
Rafael A, Bruce H, Susan S (2010) An overview of polylactides as packaging materials. Macromol Biosci 4(9):835–864
Weng Y, Jin L, Xu G (2010) Status of biomass and biodegradable plastics in China. China Chem Rep 2010(6):27–29
Xiang Q, Ren Y, Wang X (2017) New advances in the biodegradation of Poly(lactic) acid. Int Biodeter Biodegrad 117:215–223
Gironi F, Piemonte V (2013) Kinetics of hydrolytic degradation of PLA. J Polym Environ 21(2):313–318.
Andrade MFCD, Souza PMS, Cavalett O, Morales AR (2016) Life cycle assessment of poly(lactic acid) (PLA): comparison between chemical recycling, mechanical recycling and composting. J Polym Environ 24(4):372–384
Shogren RL, Doane WM, Garlotta D, Lawton JW, Willett JL (2003) Biodegradation of starch/polylactic acid/poly(hydroxyester-ether) composite bars in soil. Polym Degrad Stab 79(3):405–411
Iñiguezfranco F, Auras R, Rubino M, Dolan K, Sotovaldez H, Selke S (2017) Effect of nanoparticles on the hydrolytic degradation of PLA-nanocomposites by water-ethanol solution. Polym Degrad Stab 146:287–297
Weber CJ, Haugaard V, Festersen R, Bertelsen G (2002) Production and applications of biobased packaging materials for the food industry. Food Addit Contam 19:172–177
Fupeng YE (2016) LCA on CO2 from PLA. Energy and Energy Conservation 132(9):80–81
Arrieta MP, Samper MD, Aldas M, López J (2017) On the Use of PLA-PHB Blends for sustainable food packaging applications. Materials 10(9):1008
Fukushima K, Tabuanib D, Arena M, Rizzarelli P (2011) Preparation, characterization and biodegradation of biopolymer nanocomposites based on fumed silica. Eur Polym J 47(2):139–152
Velde KVD, Kiekens P (2002) Biopolymers: overview of several properties and consequences on their applications. Polym Test 21(4):433–442
Okamoto K, Ichikawa T, Yokohara T, Yamaguchi M (2009) miscibility, mechanical and thermal properties of poly(lactic acid)/polyester-diol blends. Eur Polym J 45(8):2304–2312
Liu GC, He YS, Zeng JB, Li QT, Wang YZ (2014) Fully biobased and supertough polylactide-based thermoplastic vulcanizates fabricated by peroxide-induced dynamic vulcanization and interfacial compatibilization. Biomacromol 15(11):4260–4271
Wang M, Wu Y, Li YD, Zeng JB (2017) Progress in toughening poly(lactic acid) with renewable polymers. Polym Rev 57(4):557–593
Si WJ, Yang L, Zhu J, Li YD, Zeng JB (2019) Highly toughened and heat-resistant poly(L-lactide) materials through interfacial interaction control via chemical structure of biodegradable elastomer. Appl Surf Sci 483:1090–1100
Han JJ, Huang HX (2015) Preparation and characterization of biodegradable polylactide/thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer blends. J Appl Polym Sci 120(6):3217–3223
Yun H, Zhang C, Pan Y, Zhou Y, Long J, Yi D (2013) Effect of NR on the hydrolytic degradation of PLA. Polym Degrad Stab 98(5):943–950
Oyama HT (2009) Super-tough poly(lactic acid) materials: reactive blending with ethylene copolymer. Polymer 50(3):747–751
Zhang W, Chen L, Zhang Y (2009) Surprising shape-memory effect of polylactide resulted from toughening by polyamide elastomer. Polymer 50(5):1311–1315
Liu GC, He YS, Zeng JB, Xu Y, Wang YZ (2014) In situ formed crosslinked polyurethane toughened polylactide. Polym Chem 5(7):2530–2539
Zhao TH, He Y, Li YD, Wang M, Zeng JB (2016) Dynamic vulcanization of castor oil in polylactide matrix for toughening. RSC Adv 6(83):79542–79553
Zhao TH, Yuan WQ, Li YD, Weng YX, Zeng JB (2018) Relating chemical structure to toughness via morphology control in fully sustainable sebacic acid cured epoxidized soybean oil toughened polylactide blends. Macromolecules 51(5):2027–2037
Kumar M, Mohanty S, Nayak SK, Parvaiz MR (2010) Effect of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) on the thermal, mechanical and morphological property of biodegradable PLA/PBAT blend and its nanocomposites. Bioresour Technol 101(21):8406–8415
Yue D, Bo L, Wang P, Wang G, Ji J (2018) PLA-PBAT-PLA tri-block copolymers: effective compatibilizers for promotion of the mechanical and rheological properties of PLA/PBAT blends. Polym Degrad Stab 147:41–48
Liu H, Zhang J (2011) Research progress in toughening modification of poly(lactic acid). J Polym Sci B 49(15):1051–1083
Alitry R, Lamnawar K, Maazouz A (2012) Improvement of thermal stability, rheological and mechanical properties of PLA, PBAT and their blends by reactive extrusion with functionalized epoxy. Polym Degrad Stab 97(10):1898–1914
Long J, Wolcott MP, Jinwen Z (2006) Study of biodegradable polylactide/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blends. Biomacromol 7(1):199–207
Si Peng HN, Yang L, Yihui Z, Jifei Y, Fangfang W, Yingzhe Q (2016) Preparation and degradation properties of PLA/PBAT film. Plast Sci Technol 43(10):68–72.
Palsikowski PA, Kuchnier CN, Pinheiro IF, Morales AR (2018) Biodegradation in soil of PLA/PBAT blends compatibilized with chain extender. J Polym Environ 26:330–341
Oyama HT, Tanaka Y, Hirai S, Shida S, Kadosaka A (2011) Water-disintegrative and biodegradable blends containing poly(L-lactic acid) and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate). J Polym Sci B 49(5):342–354
Kale G, Auras R, Singh SP, Narayan R (2007) Biodegradability of polylactide bottles in real and simulated composting conditions. Polym Test 26(8):1049–1061
Hao W, Wei D, Zheng A, Xiao H (2015) Soil burial biodegradation of antimicrobial biodegradable PBAT films. Polym Degrad Stab 116(2):14–22
Weng YX, Jin YJ, Meng QY, Wang L, Zhang M, Wang YZ (2013) Biodegradation behavior of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT), poly(lactic acid) (PLA), and their blend under soil conditions. Polym Test 32(5):918–926
T.C. /Sc, ISO/DIS 13975 - Plastics—Determination of the ultimate anaerobic biodegradation of plastic materials in controlled slurry digestion systems—Method by measurement of biogas production.
Zhang M, Meng QY, Diao XQ, Weng YX (2016) Biodegradation behavior of PLA/PBAT blends. China Plast 30(8):79–86
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) with the Grant No. 51601002 and The Science and Technology Development Project of Beijing Municipal Commission of Education (Grant No. SQKM201710011003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, Y., Hu, J., Yang, M. et al. Biodegradation Behavior of Poly (Lactic Acid) (PLA), Poly (Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate) (PBAT), and Their Blends Under Digested Sludge Conditions. J Polym Environ 27, 2784–2792 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01563-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01563-3