Abstract
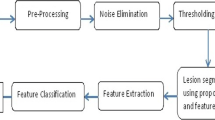
Melanoma is a life threading disease when it grows outside the corium layer of the skin. Mortality rates of the Melanoma cases are maximum among the skin cancer patients. The cost required for the treatment of advanced melanoma cases is very high and the survival rate is low. Numerous computerized dermoscopy systems are developed based on the combination of shape, texture and color features to facilitate early diagnosis of melanoma. The availability and cost of the dermoscopic imaging system is still an issue. To mitigate this issue, this paper presented an integrated segmentation and Third Dimensional (3D) feature extraction approach for the accurate diagnosis of melanoma. A multi-atlas method is applied for the image segmentation. The patch-based label fusion model is expressed in a Bayesian framework to improve the segmentation accuracy. A depth map is obtained from the Two-dimensional (2D) dermoscopic image for reconstructing the 3D skin lesion represented as structure tensors. The 3D shape features including the relative depth features are obtained. Streaks are the significant morphological terms of the melanoma in the radial growth phase. The proposed method yields maximum segmentation accuracy, sensibility, specificity and minimum cost function than the existing segmentation technique and classifier.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Menzies, S. W., Ingvar, C., Crotty, K. A., and McCarthy, W. H., Frequency and morphologic characteristics of invasive melanomas lacking specific surface microscopic features. Arch. Dermatol. 132:1178–1182, 1996.
Argenziano, G., Fabbrocini, G., Carli, P., De Giorgi, V., Sammarco, E., and Delfino, M., Epiluminescence microscopy for the diagnosis of doubtful melanocytic skin lesions: Comparison of the ABCD rule of dermatoscopy and a new 7-point checklist based on pattern analysis. Arch. Dermatol. 134:1563–1570, 1998.
Stolz, W., ABCD rule of dermatoscopy: A new practical method for early recognition of malignant melanoma. Eur. J. Dermatol. 4:521–527, 1994.
Blum, A., Rassner, G., and Garbe, C., Modified ABC-point list of dermoscopy: A simplified and highly accurate dermoscopic algorithm for the diagnosis of cutaneous melanocytic lesions. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 48:672–678, 2003.
Barata, C., Ruela, M., Francisco, M., Mendonça, T., and Marques, J. S., Two systems for the detection of melanomas in dermoscopy images using texture and color features. IEEE Syst. J. 8:965–979, 2014.
Pereyra, M. A., Dobigeon, N., Batatia, H., and Tourneret, J.-Y., Segmentation of skin lesions in 2D and 3D ultrasound images using a spatially coherent generalized Rayleigh mixture model. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 31:1509–1520, 2012.
Steiner, A., Binder, M., Schemper, M., Wolff, K., and Pehamberger, H., Statistical evaluation of epiluminescence microscopy criteria for melanocytic pigmented skin lesions. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 29:581–588, 1993.
Sadeghi, M., Lee, T. K., McLean, D., Lui, H., and Atkins, M. S., Detection and analysis of irregular streaks in dermoscopic images of skin lesions. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 32:849–861, 2013.
Heckemann, R. A., Hajnal, J. V., Aljabar, P., Rueckert, D., and Hammers, A., Automatic anatomical brain MRI segmentation combining label propagation and decision fusion. NeuroImage 33:115–126, 2006.
Rohlfing, T., Russakoff, D. B., and Maurer, C. R., Performance-based classifier combination in atlas-based image segmentation using expectation-maximization parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 23:983–994, 2004.
Rohlfing, T., Brandt, R., Menzel, R., and Maurer, Jr., C. R., Evaluation of atlas selection strategies for atlas-based image segmentation with application to confocal microscopy images of bee brains. NeuroImage 21:1428–1442, 2004.
Svarer, C., Madsen, K., Hasselbalch, S. G., Pinborg, L. H., Haugbøl, S., Frøkjær, V. G. et al., MR-based automatic delineation of volumes of interest in human brain PET images using probability maps. Neuroimage 24:969–979, 2005.
Abuzaghleh, O., Barkana, B. D., and Faezipour, M., Noninvasive real-time automated skin lesion analysis system for melanoma early detection and prevention. IEEE J. Trans. Eng. Health Med. 3:1–12, 2015.
Glaister, J., Wong, A., and Clausi, D. A., Segmentation of skin lesions from digital images using joint statistical texture distinctiveness. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61:1220–1230, 2014.
M. H. Jafari, N. Karimi, E. Nasr-Esfahani, S. Samavi, S. M. R. Soroushmehr, K. Ward, et al., "Skin lesion segmentation in clinical images using deep learning," in Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 2016 23rd International Conference on, 2016, pp. 337-342.
Peruch, F., Bogo, F., Bonazza, M., Cappelleri, V.-M., and Peserico, E., Simpler, faster, more accurate melanocytic lesion segmentation through meds. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61:557–565, 2014.
Ma, Z., and Tavares, J. M. R., A review of the quantification and classification of pigmented skin lesions: From dedicated to hand-held devices. J. Med. Syst. 39:177, 2015.
Navarro, F., Escudero-Vinolo, M., and Bescos, J., Accurate segmentation and registration of skin lesion images to evaluate lesion change. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform., 2018.
Dhawan, A. P., Gordon, R., and Rangayyan, R. M., Nevoscopy: Three-dimensional computed tomography of nevi and melanomas in situ by transillumination. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 3:54–61, 1984.
Tittmann, B. R., Miyasaka, C., Maeva, E., and Shum, D., Fine mapping of tissue properties on excised samples of melanoma and skin without the need for histological staining. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 60:320–331, 2013.
Vogt, M., and Ermert, H., In vivo ultrasound biomicroscopy of skin: Spectral system characteristics and inverse filtering optimization. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 54, 2007.
Kaur, G., and Joshi, K., Automatic detection and segmentation of skin melanoma images-an introduction. Int. J. Emerg. Res. Manag. Technol. ISSN:2278–9359, 2015.
Esteva, A., Kuprel, B., Novoa, R. A., Ko, J., Swetter, S. M., Blau, H. M. et al., Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 542:115, 2017.
Menzies, S., Ingvar, C., and McCarthy, W., A sensitivity and specificity analysis of the surface microscopy features of invasive melanoma. Melanoma Res. 6:55–62, 1996.
Kasmi, R., Mokrani, K., Rader, R., Cole, J., and Stoecker, W., Biologically inspired skin lesion segmentation using a geodesic active contour technique. Skin Res. Technol. 22:208–222, 2016.
Pennisi, A., Bloisi, D. D., Nardi, D., Giampetruzzi, A. R., Mondino, C., and Facchiano, A., Skin lesion image segmentation using Delaunay triangulation for melanoma detection. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 52:89–103, 2016.
N. Mittal, S. Tanwar, and S. K. Khatri, "Identification & enhancement of different skin lesion images by segmentation techniques," in Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions)(ICRITO), 2017 6th International Conference on, 2017, pp. 609-614.
B. Patel, K. Dhayal, S. Roy, and R. Shah, "Computerized skin cancer lesion identification using the combination of clustering and entropy," in Big Data Analytics and Computational Intelligence (ICBDAC), 2017 International Conference on, 2017, pp. 46–51.
Ma, Z., and Tavares, J. M. R., A novel approach to segment skin lesions in dermoscopic images based on a deformable model. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 20:615–623, 2016.
L. Bi, J. Kim, E. Ahn, D. Feng, and M. Fulham, "Automated skin lesion segmentation via image-wise supervised learning and multi-scale superpixel based cellular automata," in Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), 2016 IEEE 13th International Symposium on, 2016, pp. 1059-1062.
A. A. A. Al-abayechi, H. A. Jalab, R. W. Ibrahim, and A. M. Hasan, "Image Enhancement Based on Fractional Poisson for Segmentation of Skin Lesions Using the Watershed Transform," in International Visual Informatics Conference, 2017, pp. 249-259.
S. Ross-Howe and H. R. Tizhoosh, "The Effects of Image Pre-and Post-Processing, Wavelet Decomposition, and Local Binary Patterns on U-Nets for Skin Lesion Segmentation," in 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), 2018, pp. 1-8.
Li, Y., and Shen, L., Skin lesion analysis towards melanoma detection using deep learning network. Sensors 18:556, 2018.
N. C. Codella, D. Gutman, M. E. Celebi, B. Helba, M. A. Marchetti, S. W. Dusza, et al., "Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: A challenge at the 2017 international symposium on biomedical imaging (isbi), hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (isic)," in 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), 2018, pp. 168-172.
A. R. Jadhav, A. G. Ghontale, and V. K. Shrivastava, "Segmentation and Border Detection of Melanoma Lesions Using Convolutional Neural Network and SVM," in Computational Intelligence: Theories, Applications and Future Directions-Volume I, ed: Springer, 2019, pp. 97-108.
Nida, N., Irtaza, A., Javed, A., Yousaf, M. H., and Mahmood, M. T., Melanoma lesion detection and segmentation using deep region based convolutional neural network and fuzzy C-means clustering. Int. J. Med. Inform., 2019.
Nasir, M., Attique Khan, M., Sharif, M., Lali, I. U., Saba, T., and Iqbal, T., An improved strategy for skin lesion detection and classification using uniform segmentation and feature selection based approach. Microsc. Res. Tech. 81:528–543, 2018.
J. P. Ebenezer and J. C. Rajapakse, "Automatic segmentation of skin lesions using deep learning," arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.04893, 2018.
Chambolle, A., An algorithm for total variation minimization and applications. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 20:89–97, 2004.
Rajchl, M., Yuan, J., White, J. A., Ukwatta, E., Stirrat, J., Nambakhsh, C. M. et al., Interactive hierarchical-flow segmentation of scar tissue from late-enhancement cardiac MR images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33:159–172, 2014.
Rousseau, F., Habas, P. A., and Studholme, C., A supervised patch-based approach for human brain labeling. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 30:1852–1862, 2011.
Zhuo, S., and Sim, T., Defocus map estimation from a single image. Pattern Recogn. 44:1852–1858, 2011.
A. Levin, D. Lischinski, Y. Weiss, "A closed form solution to natural image matting," in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on, 2006, pp. 61-68.
P. Risholm, E. Samset, and W. Wells, "Bayesian estimation of deformation and elastic parameters in non-rigid registration," in International Workshop on Biomedical Image Registration, 2010, pp. 104-115.
P. Risholm, S. Pieper, E. Samset, and W. M. Wells, "Summarizing and visualizing uncertainty in non-rigid registration," in International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, 2010, pp. 554-561.
Simpson, I. J., Schnabel, J. A., Groves, A. R., Andersson, J. L., and Woolrich, M. W., Probabilistic inference of regularisation in non-rigid registration. NeuroImage 59:2438–2451, 2012.
Simpson, I. J., Woolrich, M. W., Andersson, J. R., Groves, A. R., and Schnabel, J., Ensemble learning incorporating uncertain registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 32:748–756, 2013.
W. Bai, W. Shi, D. P. O'Regan, T. Tong, H. Wang, S. Jamil-Copley, et al., "A probabilistic patch-based label fusion model for multi-atlas segmentation with registration refinement: Application to cardiac MR images," IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, vol. 32, pp. 1302-1315, 2013.
Coupé, P., Manjón, J. V., Fonov, V., Pruessner, J., Robles, M., and Collins, D. L., Patch-based segmentation using expert priors: Application to hippocampus and ventricle segmentation. NeuroImage 54:940–954, 2011.
Senthilselvi, A., and Sukumar, R., Removal of salt and pepper noise from images using hybrid filter (HF) and fuzzy logic noise detector (FLND). J. Concur. Comput. Pract. Exp., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.4501.
Senthilselvi, A., and Sukumar, R., A survey on image restoration technique. Int. J. Emerg. Eng. Res. Technol. 2(8):123–128, 2014.
Flusser, J., and Suk, T., Pattern recognition by affine moment invariants. Pattern Recogn. 26:167–174, 1993.
Hu, M.-K., Visual pattern recognition by moment invariants. IRE Trans. Inform. Theory 8:179–187, 1962.
Sadeghi, M., Razmara, M., Lee, T. K., and Atkins, M. S., A novel method for detection of pigment network in dermoscopic images using graphs. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 35:137–143, 2011.
C. Szegedy, V. Vanhoucke, S. Ioffe, J. Shlens, and Z. Wojna, "Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision," in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2016, pp. 2818-2826.
Satheesha, T., Satyanarayana, D., Prasad, M. G., and Dhruve, K. D., Melanoma is skin deep: A 3D reconstruction technique for computerized dermoscopic skin lesion classification. IEEE J Trans. Eng. Health Med. 5:1–17, 2017.
T. Mendonça, P. M. Ferreira, J. S. Marques, A. R. Marcal, and J. Rozeira, "PH 2-A dermoscopic image database for research and benchmarking," in Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE, 2013, pp. 5437-5440.
A. A. Marghoob, R. P. Braun, and A. W. Kopf, Interactive CD-ROM of Dermoscopy: Informa Healthcare, 2007.
G. Argenziano, H. Soyer, V. De Giorgi, D. Piccolo, P. Carli, and M. Delfino, "Interactive atlas of dermoscopy (Book and CD-ROM)," 2000.
H. Soyer, G. Argenziano, S. Chimenti, S. Menzies, H. Pehamberger, H. Rabinovitz, et al., "Dermoscopy of pigmented skins lesions. An Atlas based on the Consensus Net Meeting on Dermoscopy 2000," 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interests and the paper has not been submitted to any other Journals.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
It is not required as the dataset is taken online databases.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Image & Signal Processing
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roja Ramani, D., Ranjani, S.S. An Efficient Melanoma Diagnosis Approach Using Integrated HMF Multi-Atlas Map Based Segmentation. J Med Syst 43, 225 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1315-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1315-4