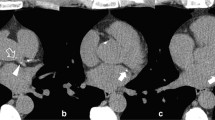
Abstract
Coronary calcium detection in medicine image processing is a hot research topic. According to the low resolution and complex background in medicine image, an improved coronary calcium detection algorithm based on the Single Shot MultiBox Detector (SSD) in Mimics is proposed in this paper. The algorithm firstly uses the aggregate channel feature model to preprocess the image to obtain the suspected calcium area, which greatly reduces the time of single-frame image detection. The basic network VGG-16 is replaced by Resnet-50, which introduces the identity mapping to solve the problem of reducing the detection accuracy when the number of network layers are increased. Finally, the powerful and flexible two-parameter loss function is used to optimize the training deep network and improve the network model generalization ability. Qualitative and quantitative experiments show that the performance of the proposed detection algorithm exceeds the existing calcium detection algorithms, and the detection efficiency is improved while ensuring the accuracy of calcium detection.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mcclelland, R. L., Jorgensen, N. W., Budoff, M. J. et al., 10-year coronary heart disease risk prediction using coronary artery calcium and traditional risk factors: Derivation in the MESA (multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis) with validation in the HNR (Heinz Nixdorf Recall) study and the DHS (Dallas Heart Study).[J]. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 66(15):1643–1653, 2015.
Hecht, H. S., Coronary artery calcium scanning: Past, present, and future[J]. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 8(5):579–596, 2015.
Rahhal, M. M., Bazi, Y., Alhichri, H. S. et al., Deep learning approach for active classification of electrocardiogram signals[J]. Inf. Sci. 345(345):340–354, 2016.
Moeskops P, Moeskops P, Wolterink J M, et al. Deep learning for multi-task medical image segmentation in multiple modalities[C]. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention: 478–486, 2016.
Wolterink, J. M., Leiner, T., Takx, R. A. et al., Automatic coronary calcium scoring in non-contrast-enhanced ECG-triggered cardiac CT with ambiguity detection[J]. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 34(9):1867–1878, 2015.
Lloydjones, D. M., Coronary artery calcium scoring: Are we there yet?[J]. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 66(15):1654–1656, 2015.
Araki, T., Ikeda, N., Dey, N. et al., Shape-based approach for coronary calcium lesion volume measurement on intravascular ultrasound imaging and its association with carotid intima-media thickness[J]. J. Ultrasound Med. 34(3):469–482, 2015.
Chaikriangkrai, K., Valderrabano, M., Bala, S. K. et al., Abstract 491: Detection of subclinical coronary artery disease by calcium score in patients with atrial fibrillation: Potential clinical implications[J]. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 2015.
Vonder, M., Pelgrim, G. J., Huijsse, S. E. et al., Feasibility of spectral shaping for detection and quantification of coronary calcifications in ultra-low dose CT[J]. Eur. Radiol. 27(5):2047–2054, 2017.
Qanadli, S. D., Qanadli, S. D., Jouannic, A. et al., CT attenuation values of blood and myocardium: Rationale for accurate coronary artery calcifications detection with multi-detector CT.[J]. PLoS ONE 10(4), 2015.
Antonopoulos, A. S., Sanna, F., Sabharwal, N. et al., Detecting human coronary inflammation by imaging perivascular fat[J]. Sci. Transl. Med. 9(398), 2017.
Greenland, P., Blaha, M. J., Budoff, M. J. et al., Coronary calcium score and cardiovascular risk[J]. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 72(4):434–447, 2018.
Chang, H., Lin, F. Y., Lee, S. et al., Coronary atherosclerotic precursors of acute coronary syndromes[J]. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 71(22):2511–2522, 2018.
Suzuki, K., Overview of deep learning in medical imaging[J]. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 10(3):257–273, 2017.
Mahabadi, A. A., and Rassaf, T., Imaging of coronary inflammation for cardiovascular risk prediction[J]. Lancet 392(10151):894–896, 2018.
Sun, J., Cerebral micro-bleeding identification based on nine-layer convolutional neural network with stochastic pooling, Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 2019. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.5130.
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., and Hinton, G., Deep learning[J]. nature 521(7553):436, 2015.
Erhan, D., Bengio, Y., Courville, A. et al., Why does unsupervised pre-training help deep learning?[J]. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 11(Feb):625–660, 2010.
Liu, W., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., et al. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector[C]//European conference on computer vision. Springer, Cham: 21–37, 2016.
Han, S., Mao, H., and Dally, W. J., Deep compression: Compressing deep neural networks with pruning, trained quantization and huffman coding[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1510.00149, 2015.
Yang, B., Yan, J., Lei, Z., et al., Aggregate channel features for multi-view face detection[C]//Biometrics (IJCB), 2014 IEEE International Joint Conference on. IEEE, 1–8, 2014.
He, K., Gkioxari, G., Dollár, P., et al., Mask r-cnn[C]//Computer Vision (ICCV), 2017 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2980–2988, 2017.
Szegedy, C., Ioffe, S., Vanhoucke, V., et al., Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]//AAAI, 4:12, 2017.
Targ, S., Almeida, D., and Lyman, K., Resnet in Resnet: generalizing residual architectures[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.08029, 2016.
Sünderhauf, N., Shirazi, S., Dayoub, F., et al., On the performance of convnet features for place recognition[C]//Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on. IEEE, 4297–4304, 2015.
Redmon, J., Divvala, S., Girshick, R., et al., You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 779–788, 2016.
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., et al., Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]//Advances in neural information processing systems. 91–99, 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Image & Signal Processing
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Datong, C., Minghui, L., Cheng, J. et al. Coronary Calcium Detection Based on Improved Deep Residual Network in Mimics. J Med Syst 43, 119 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1218-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1218-4