Abstract
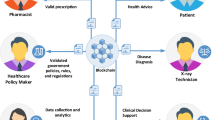
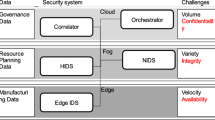
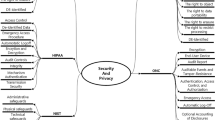
This paper presents a case study of a hospital operating room that evaluated a Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID)-enabled traceability system for the management of consignment and high value products requiring item level traceability. Results indicate that the traceability system in conjunction with the redesign of replenishment processes facilitates item level traceability, improves financial controls and case costing, upgrades service levels and reduces inventory shrinkage. Other benefits include time saved from non-value-added activities that can be transferred to patient care activities. The solution can be considered (i) as an alternative to RFID-enabled cabinets used in the replenishment of consignment and high value supplies in certain operating rooms, cardiac catheterization laboratories and interventional radiology departments, or (ii) as a complementary solution facilitating the tracking of medical devices removed from RFID-enabled cabinets. In short, the end-to-end traceability of medical products in the healthcare supply chain can be significantly enhanced.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABC:
-
Activity-based costing
- AHRMM:
-
Association for healthcare resource & materials management
- AIDC:
-
Automatic identification and data capture
- ANSI:
-
American national standards institute
- BPR:
-
Business process reengineering
- CHUM:
-
Centre hospitalier de l'Université de Montréal
- CMS:
-
Clinical management software
- EDI:
-
Electronic data interchange
- EMI:
-
Electromagnetic interference
- EPC:
-
Electronic product code
- ERP:
-
Enterprise resource planning
- HF:
-
High frequency
- HIBCC:
-
Health industry business communications council
- HIS:
-
Hospital information system
- IOS:
-
Inter-organizational system
- IT:
-
Information technology
- NPV:
-
Net present value
- OR:
-
Operating room
- RFID:
-
Radio-frequency identification
- ROI:
-
Return on investment
- RTLS:
-
Real time locating system
- RX:
-
Prescription medication
- SCM:
-
Supply chain management
- SGTIN:
-
Serialized global trade identification number
- SKU:
-
Stock keeping unit
- TID:
-
Tag identifier
- TPS:
-
Toyota production system
References
GS1 (2009) Traceability: What’s in it for you: What GS1 can do to help. http://www.gs1.org/docs/traceability/traceability_brochure.pdf. Accessed 24 October 2011.
GS1. (2009) GS1 Standards document business process and system requirements for supply chain traceability: Global traceability standard for healthcare. http://www.gs1.org/docs/gsmp/traceability/Global_Traceability_Standard_Healthcare.pdf Accessed 24 October 2011.
Boeck, H., and Fosso Wamba, S., RFID and buyer-seller relationships in the retail supply chain. Int. J. Retail. Distrib. Manag. 36(6):433–360, 2008. doi:10.1108/09590550810873929.
Voulodimos, A. S., Patrikakis, C. Z., Sideridis, A. B., Ntafis, V. A., and Xylouri, E. M., A complete farm management system based on animal identification using RFID technology. Comput. Electron. Agric. 70(2):380–388, 2010. doi:10.1016/j.compag.2009.07.009.
Ruiz-Garcia, L., Steinberger, G., and Rothmund, M., A model and prototype implementation for tracking and tracing agricultural batch products along the food chain. Food Control 21:112–121, 2010. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2008.12.003.
Kvarnstrom, B., and Vanhatalo, E., Using RFID to improve traceability in process industry Experiments in a distribution chain for iron ore pellets. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 21(1):139–154, 2010. doi:10.1108/17410381011011524.
Palsson, H., and Johansson, O., Supply chain integration obtained through uniquely labelled goods A survey of Swedish manufacturing industries. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 39(1):28–46, 2009. doi:10.1108/09600030910929174.
Wasserman, E., RFID in the Forest. RFID J 8(1):20–28, 2011.
California State Board of Pharmacy (2008) Questions and answers relating to the California electronic prescription drug pedigree law(s). http://www.pharmacy.ca.gov/forms/pedigree_q_and_a.pdf. Accessed 24 October 2011.
Ilie-Zudor, E., Kemény, Z., Van Blommestein, F., Monostori, L., and Van der Meulen, A., A survey of applications and requirements of unique identification systems and RFID techniques. Comput. Ind. 62:227–252, 2011. doi:10.1016/j.compind.2010.10.004.
US Department of Defense,Department of Defense (2008) Guide to uniquely identifying items: Assuring valuation, accountability and control of government property. http://www.acq.osd.mil/dpap/UID/attachments/DoDUIDGuide.pdf Accessed 24 October 2011.
Crounse, B., Feied, C., Jordan, N., Kanhouwa, M., Kavanagh, J., The new world of healthcare work: UK focus international lecture, The Royal Academy of Engineering, London, 2006. www.raeng.org.uk/events/pdf/ukfocus_lecture_summary.pdf Accessed 24 October 2011.
Porter, M. E., Teisberg, E. O., Redefining health care: creating value-based competition on results. Harvard business school publishing, 2006.
Womack, J. P., and Jones, D. T., Lean thinking: banish the waste and create wealth in your corporation. Simon & Schuster, London, 1996.
Black, J., Miller, D., The Toyota way to healthcare excellence: increase efficiency & improve quality with lean. Health Administration Press, 2008.
Womack, J. P., Jones, D. T., and Roos, D., The machine that changed the world: the story of lean production. Rawson Associates, Macmillan Publishing Company, New York, 1991.
Manos, A., Sattler, M., and Alukal, G., Make healthcare lean. Qual. Prog. 39(7):24–30, 2006.
de Souza, L. B., Trends and approaches in lean healthcare. Leadersh Health Serv 22(2):121–139, 2009. doi:10.1108/17511870910953788.
Landry, S., and Beaulieu, M., Achieving lean healthcare by combining the two-bin kanban replenishment system with RFID technology. Intern J Health Manag Inf 1(1):85–98, 2010.
Bendavid, Y., Boeck, H., and Philippe, R., Redesigning the replenishment process of medical supplies in hospitals with RFID. Bus. Process. Manag. J. 16(6):991–1013, 2010. doi:10.1108/14637151011093035.
Nachtmann, H., Pohl, E. A., The state of healthcare logistics, cost and quality improvement opportunies. Center for Innovation in Healthcare Logistics, University of Arkansas, 2009.
Lambert, D., Supply chain management, process, partnership, performance, 3rd edition. Supply chain management institute, Sarasota, Florida, 2008.
Sarac, A., Absi, N., and Dauzere-Peres, S., A literature review on the impact of RFID technologies on supply chain management. Intern J Prod Econ 128:77–95, 2010. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2010.07.039.
Kumar, S., Swanson, E., and Tran, T., RFID in the healthcare supply chain: usage and application. Intern J Healthc Qual Assur 22(1):67–81, 2009. doi:10.1108/09526860910927961.
Chow, G., and Heaver, T., Logistics in the Canadian health care industry. Can Logist J 1(1):29–74, 1994.
Ontario Buys & Healthcare Supply Network. Supply chain modernization in Ontario health care: Improving patient care, enhancing service levels and reducing costs: A report on the e-supply chain project. Ontario Ministry of Finance, 2007. http://www.hscn.org/PDFs/eSupplyChainReport_FINAL_web_ENG.pdf Accessed 10 January 2011.
Friesen, S., Rattling the supply chain: The opportunity for supply chain management in healthcare. University of Waterloo, 2005. http://infranet.uwaterloo.ca/infranet/s200503.htm. Accessed 24 October 2011.
Stanley InnerSpace. RFID enabled clinical supply management solution, 2010. http://www.stanleyinnerspace.com/node/158. Accessed 24 October 2011.
Harrop, P., Das, R., Holland, G., RFID for Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals 2009–2019. IDTechEx, 2009.
Van Oranje, C., Schindler, R., Vilamovska, A. M., Botterman, M., Policy options for radio frequency identification (RFID) application in healthcare; a prospective view: Final report (Deliverable 5), 2010. http://www.rand.org/pubs/technical_reports/2010/RAND_TR767-1.pdf. Accessed 24 October 2011.
GS1 Canada. EPC/RFID in Healthcare. GS1 knowledge center, 2010. http://www.gs1ca.org/page.asp?intPageID=1428. Accessed 24 October 2011.
Wicks, A. M., Visich, J. K., and Li, S., Radio frequency identification applications in healthcare. Int. J. Healthc. Technol. Manag. 7(6):522–40, 2006.
Edwards, J., RFID Smart Shelves and Cabinets. RFID Journal, 2009. http://www.rfidjournal.com/article/view/5140. Accessed 24 October 2011.
Yin, R. K., Case study research: Design and methods, 3rd edition. Sage, Thousand Oaks, 2002.
Kaplan, R. S., and Anderson, S. R., Time-driven activity-based costing: Simpler and more powerful path to higher profits. Harvard Business School Press, Boston, 2007.
Bunduchi, R., Weisshaar, C., and Smart, A. U., Mapping the benefits and costs associated with process innovation: The case of RFID adoption. Technovation 31(9):505–521, 2011. doi:10.1016/j.technovation.2011.04.001.
Bendavid, Y., Ng, E., Developing an RFID Business Case and Calculating the ROIRFID Preconference: RFID for Warehouse and Inventory Management. RFID Journal Live 2011, ninth annual conference and exhibition, Orlando, 2011.
Smart, A. U., Bunduchi, R., and Gerst, M., The costs of adoption of RFID technologies in supply networks. Int J Oper Prod Manag 30(4):423–447, 2010. doi:10.1108/01443571011029994.
Bahri, S., Managing the implementation of an innovative technology in: a hospital a case study. J. Syst. Inf. Technol. 11(3):269–285, 2009. doi:10.1108/13287260910983632.
Roberti, M., Labor savings can be illusive. RFID J 7(6):6–7, 2010.
Health Industry Business Communications Council. ANSI approves HIBCC standard that addresses RFID/medical device safety concerns, 2009. http://www.hibcc.org/RFID.htm. Accessed 24 October 2011.
GS1 (2011) GS1 Healthcare Newsletter, No. 22, Quarter 2. http://www.gs1.org/docs/healthcare/GS1_Healthcare_Newsletter_22_Q2_2011.pdf. Accessed 24 October 2011.
Bendavid, Y., and Boeck, H., Using RFID to improve hospital supply chain management for high value and consignment items. Procedia Comput Sci 5:849–856, 2011. doi:10.1016/j.procs.2011.07.117.
Acknowledgment
The authors are grateful to (i) the CHUM for providing access to the field of research and for their time in reviewing the paper, (ii) the team of Logi-D for their immense support in this research and for providing us access to all relevant data to build the business case (iii) the reviewers for their useful comments on the first version of the paper. This article is an updated and extended version of a shorter paper presented at The Fifth International Workshop on RFID Technology—Concepts, Applications, Challenges (IWRT 2011) in Niagara Falls, Canada [43].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bendavid, Y., Boeck, H. & Philippe, R. RFID-Enabled Traceability System for Consignment and High Value Products: A Case Study in the Healthcare Sector. J Med Syst 36, 3473–3489 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-011-9804-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-011-9804-0