Abstract
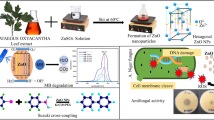
This work reports an innovative, effortless and inexpensive method for the preparation of ZnO nanoparticles by green approach using leaf extract of Piper betleas a reducing-stabilizing negotiator. The prepared ZnO NPs were characterized through XRD, FTIR, UV–Visible spectroscopy, and EDX etc. The band gap energy of the sample was estimated as 3.41 eV which is larger than the bulk ZnO (Eg = 3.37 eV). The observed blue shift is attributed to the quantum confinement of excitons. FTIR analysis showed the presence of alkaloids, flavonoids, polyphenols, and terpenoid. TEM analysis showed that each nanoparticle comprised of 1 to 2 nano-crystallites. Photocatalytic activity results revealed that ZnO-NPs prepared through green synthesis route were found to be efficient in the degradation of toxic reactive red dye with degradation efficiency of 96.4% having high photodegradation rate-constant of 1.6 × 10–2 min−1. As an antimicrobial agent, the ZnO NPs are effective against both gram-positive (Bacillus subtilis) and negative bacteria (Escherichia coli), with the zones of clearance as 16.4 and 14.3 mm, respectively. Therefore, present research signifies an effective approach to utilize as-prepared ZnO NPs as efficient photocatalysts as well as antimicrobial agent.










Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
23 November 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02204-3
References
M. Islam, K. M. F. Hasan, H. Deb, A. M. M. Faisal, and W. Xu (2016). Am. J. Polym. Sci. Eng. 12, 1.
K. Singh and S. Arora (2011). Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41, 807.
A. Stolz (2001). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 56, 69.
Z. L. Wang (2004). Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 55, 159.
S. H. Fatma and J. Psikol (2019). Islam 6, 51.
N. A. Ibrahim, A. Hashem, and M. H. Abou-Shosha (1997). Polym. Plast. Tech. Eng. 36, 963.
S. Cao, H. Wang, H. Li, J. Chen, and Z. Zang (2020). Chem. Eng. J. 394, 124903.
C. Li, Z. Zang, C. Han, Z. Hu, X. Tang, J. Du, Y. Leng, and K. Sun (2017). Nano Energy 40, 195.
Z. Zang, X. Zeng, J. Du, M. Wang, and X. Tang (2016). Opt. Lett. 41, 3463.
C. Li, C. Han, Y. Zhang, Z. Zang, M. Wang, X. Tang, and J. Du (2017). Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 172, 341.
Z. Zang (2018). Appl. Phys. Lett. 112, 042106.
S. Basak, P. Singh, and M. Rajurkar (2016). J. Pathog. 1, 4065603.
S. M. Dizaj, F. Lotfipour, M. Barzegar-Jalali, M. H. Zarrintan, and K. Adibkia (2014). Mater. Sci. Eng. C 44, 278.
Z. Lixiong, J. Mengdong, and M. Enze (1997). Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 105C, 2211.
N. A. Ibrahim, A. A. Nada, B. M. Eid, M. Al-Moghazy, A. G. Hassabo, and N. Y. Abou-Zeid (2018). Adv. Nat. Sci: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9, 035014.
N. A. Ibrahim, A. A. Nada, A. G. Hassabo, B. M. Eid, A. M. N. El-Deen, and N. Y. Abou-Zeid (2017). Chem. Pap. 71, 1365.
N. A. Ibrahim, B. M. Eid, E. A. El-Aziz, T. M. A. Elmaaty, and S. M. Ramadan (2017). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 105, 769.
N. Kaur, J. Singh, G. Kaur, S. Kumar, D. Kukkar, and M. Rawat (2019). Micro Nano Lett. 14, 856.
I. Musa and N. Qamhieh (2019). Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 14, 119.
J. Singh, V. Kumar, K. H. Kim, and M. Rawat (2019). Environ. Res. 177, 108569.
S. Kaur, J. Singh, R. Rawat, S. Kumar, H. Kaur, K. Venkateswara Rao, and M. Rawat (2018). J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 11679.
S. Chaudhary, S. Kumar, A. Umar, J. Singh, M. Rawat, and S. K. Mehta (2017). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 243, 579.
C. H. Wu (2008). J. Hazard. Mater. 153, 1254.
S. Amisha, K. Selvam, N. Sobana, and M. Swaminathan (2008). J. Korean Chem. Soc. 52, 66.
K. Mehrotra, G. S. Yablonsky, and A. K. Ray (2005). Chemosphere 60, 1427.
K. Hayat, M. A. Gondal, M. M. Khaled, and S. Ahmed (2010). J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 45, 1413.
J. Singh, S. Kaur, G. Kaur, S. Basu, and M. Rawat (2019). Green Process. Synth. 8, 272.
S. S. Dakshayani, M. B. Marulasiddeshwara, M. N. S. Kumar, G. Ramesh, P. R. Kumar, S. Devaraja, and R. Hosamani (2019). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 131, 787.
S. Ganesan, I. G. Babu, D. Mahendran, P. I. Arulselvi, N. Elangovan, N. Geetha, and P. Venkatachalam (2016). Ann. Phytomed. An Int. J. 5, 69.
Acknowledgements
Arashdeep Singh and Vikas Goyal has equal contributed in this work. The authors gratefully acknowledge, Vice Chancellor, Dr. Prit Pal Singh, Sri Guru Granth Sahib World University, Fatehgarh Sahib, Punjab (India) for research lab facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Author notes
Deceased: Mohit Rawat.
- Mohit Rawat
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goyal, V., Singh, A., Singh, J. et al. Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as Efficient Photocatalytic and Antimicrobial Agent. J Clust Sci 33, 2551–2558 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02108-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02108-2