Abstract
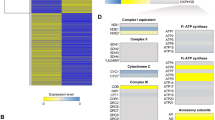
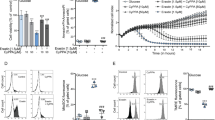
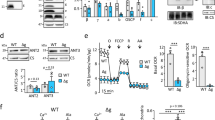
The highly abundant voltage-dependent anion-selective channel (VDAC) allows transit of metabolites across the mitochondrial outer membrane. Previous studies in Neurospora crassa showed that the LoPo strain, expressing 50% of normal VDAC levels, is indistinguishable from wild-type (WT). In contrast, the absence of VDAC (ΔPor-1), or the expression of an N-terminally truncated variant VDAC (ΔN2-12porin), is associated with deficiencies in cytochromes b and aa3 of complexes III and IV and concomitantly increased alternative oxidase (AOX) activity. These observations led us to investigate complex I and complex II activities in these strains, and to explore their mitochondrial bioenergetics. The current study reveals that the total NADH dehydrogenase activity is similar in mitochondria from WT, LoPo, ΔPor-1 and ΔN2-12porin strains; however, in ΔPor-1 most of this activity is the product of rotenone-insensitive alternative NADH dehydrogenases. Unexpectedly, LoPo mitochondria have increased complex II activity. In all mitochondrial types analyzed, oxygen consumption is higher in the presence of the complex II substrate succinate, than with the NADH-linked (complex I) substrates glutamate and malate. When driven by a combination of complex I and II substrates, membrane potentials (Δψ) and oxygen consumption rates (OCR) under non-phosphorylating conditions are similar in all mitochondria. However, as expected, the induction of state 3 (phosphorylating) conditions in ΔPor-1 mitochondria is associated with smaller but significant increases in OCR and smaller decreases in Δψ than those seen in wild-type mitochondria. High ROS production, particularly in the presence of rotenone, was observed under non-phosphorylating conditions in the ΔPor-1 mitochondria. Thus, the absence of VDAC is associated with increased ROS production, in spite of AOX activity and wild-type OCR in ΔPor-1 mitochondria.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banh S, Treberg JR (2013) The pH sensitivity of H2O2 metabolism in skeletal muscle mitochondria. FEBS Lett 587:1799–1804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2013.04.035
Banh S, Wiens L, Sotiri E, Treberg JR (2015) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production by fish muscle mitochondria: potential role in acute heat-induced oxidative stress. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 191:99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2015.10.001
Bayrhuber M, Meins T, Habeck M, Becker S, Giller K, Villinger S, Vonrhein C, Griesinger C, Zweckstetter M, Zeth K (2008) Structure of the human voltage-dependent anion channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:15370–15375. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0808115105
Blachly-Dyson E, Song J, Wolfgang WJ, Colombini M, Forte M (1997) Multicopy suppressors of phenotypes resulting from the absence of yeast VDAC encode a VDAC-like protein. Mol Cell Biol 17:5727–5738
Bleier L, Drose S (2013) Superoxide generation by complex III: from mechanistic rationales to functional consequences. Biochim Biophys Acta 1827:1320–1331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.12.002
Brand MD (2010) The sites and topology of mitochondrial superoxide production. Exp Gerontol 45:466–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2010.01.003
Budzinska M, Galganska H, Wojtkowska M, Stobienia O, Kmita H (2007) Effects of VDAC isoforms on CuZn-superoxide dismutase activity in the intermembrane space of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 357:1065–1070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.04.090
Carneiro P, Duarte M, Videira A (2012) Disruption of alternative NAD(P)H dehydrogenases leads to decreased mitochondrial ROS in Neurospora crassa. Free Radic Biol Med 52:402–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.10.492
Chowdhury SR, Djordjevic J, Albensi BC, Fernyhough P (2016) Simultaneous evaluation of substrate-dependent oxygen consumption rates and mitochondrial membrane potential by TMRM and safranin in cortical mitochondria. Biosci Rep 38:00286
Colombini M (1979) A candidate for the permeability pathway of the outer mitochondrial membrane. Nature 279:643–645
Colot HV, Park G, Turner GE, Ringelberg C, Crew CM, Litvinkova L, Weiss RL, Borkovich KA, Dunlap JC (2006) A high-throughput gene knockout procedure for Neurospora reveals functions for multiple transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:10352–10357. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0601456103
Court DA, Kleene R, Neupert W, Lill R (1996) Role of the N- and C-termini of porin in import into the outer membrane of Neurospora mitochondria. FEBS Lett 390:73–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(96)00629-1
Davis RH, de Serres FJ (1970) Genetic and microbiological research techniques for Neurospora crassa. Methods Enzymol 17:79–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(71)17168-6
Earley FG, Ragan CI (1984) Photoaffinity labelling of mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase with arylazidoamorphigenin, an analogue of rotenone. Biochem J 224:525–534. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2240525
Elbaz-Alon Y (2017) Mitochondria–organelle contact sites: the plot thickens. Biochem Soc Trans 45:477–488. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20160130
El-Khoury R, Dufour E, Rak M et al (2013) Alternative oxidase expression in the mouse enables bypassing cytochrome c oxidase blockade and limits mitochondrial ROS overproduction. PLoS Genet 9:e1003182. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003182
Ferens FG, Spicer V, Krokhin OV, Motnenko A, Summers WAT, Court DA (2017) A deletion variant partially complements a porin-less strain of Neurospora crassa. Biochem Cell Biol 95:318–327. https://doi.org/10.1139/bcb-2016-0166
Frazier AE, Thorburn DR (2012) Biochemical analyses of the electron transport chain complexes by spectrophotometry. Methods Mol Biol:49–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-504-6_4
Galganska H, Budzinska M, Wojtkowska M, Kmita H (2008) Redox regulation of protein expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria: possible role of VDAC. Arch Biochem Biophys 479:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2008.08.010
Galganska H, Karachitos A, Wojtkowska M, Stobienia O, Budzinska M, Kmita H (2010) Communication between mitochondria and nucleus : putative role for VDAC in reduction / oxidation mechanism. BBA - Bioenerg 1797:1276–1280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.02.004
Geula S, Ben-Hail D, Shoshan-Barmatz V (2012) Structure-based analysis of VDAC1: N-terminus location, translocation, channel gating and association with anti-apoptotic proteins. Biochem J 444:475–485. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20112079
Gonçalves AP, Videira A (2015) Mitochondrial type II NAD(P)H dehydrogenases in fungal cell death. Microb Cell 2:68–73. https://doi.org/10.15698/mic2015.03.192
Guardiani C, Magrì A, Karachitos A, di Rosa MC, Reina S, Bodrenko I, Messina A, Kmita H, Ceccarelli M, de Pinto V (2018) yVDAC2, the second mitochondrial porin isoform of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1859:270–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2018.01.008
Han D, Antunes F, Canali R, Rettori D, Cadenas E (2003) Voltage-dependent anion channels control the release of the superoxide anion from mitochondria to cytosol. J Biol Chem 278:5557–5563
Harkness TAA, Nargang FE, Van Der Klei I et al (1994) A crucial role of the mitochondrial protein import receptor MOM19 for the biogenesis of mitochondria. J Cell Biol 124:637–648
Head SA, Shi W, Zhao L, Gorshkov K, Pasunooti K, Chen Y, Deng Z, Li RJ, Shim JS, Tan W, Hartung T, Zhang J, Zhao Y, Colombini M, Liu JO (2015) Antifungal drug itraconazole targets VDAC1 to modulate the AMPK/mTOR signaling axis in endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112:E7276–E7285. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1512867112
Hiller S, Garces RG, Malia TJ, Orekhov VY, Colombini M, Wagner (2008) Solution structure of the integral human membrane protein VDAC-1 in detergent micelles. Science 321:1206–1210. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1161302
Hoffman DL, Brookes PS (2009) Oxygen sensitivity of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation depends on metabolic conditions. J Biol Chem 284:16236–16245. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M809512200
Jastroch M, Divakaruni AS, Mookerjee S, Treberg JR, Brand MD (2010) Mitochondrial proton and electron leaks. Essays Biochem 47:53–67. https://doi.org/10.1042/bse0470053
Joseph-Horne T, Hollomon DW, Wood PM (2001) Fungal respiration: a fusion of standard and alternative components. Biochim Biophys Acta 1504:179–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2728(00)00251-6
Klingenberg M (2008) The ADP and ATP transport in mitochondria and its carrier. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1778:1978–2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.04.011
Kmita H, Stobienia O, Michejda J (1999) The access of metabolites into yeast mitochondria in the presence and absence of the voltage dependent anion selective channel (YVDAC1). Acta Biochim Pol 46:991–1000 10824870
Krüger V, Becker T, Becker L, Montilla-Martinez M, Ellenrieder L, Vögtle FN, Meyer HE, Ryan MT, Wiedemann N, Warscheid B, Pfanner N, Wagner R, Meisinger C (2017) Identification of new channels by systematic analysis of the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Cell Biol 216:3485–3495. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201706043
Lambert AJ, Brand MD (2004) Superoxide production by NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I) depends on the pH gradient across the mitochondrial inner membrane. Biochem J 382:511–517
Lee AC, Xu X, Blachly-Dyson E, Forte M, Colombini M (1998) The role of yeast VDAC genes on the permeability of the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Membr Biol 161:173–181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002329900324
Liu Y, Fiskum G, Schubert D (2002) Generation of reactive oxygen species by the mitochondrial electron transport chain. J Neurochem 80:780–787. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0022-3042.2002.00744.x
Ma X, Jin M, Cai Y, Xia H, Long K, Liu J, Yu Q, Yuan J (2011) Mitochondrial electron transport chain complex III is required for antimycin a to inhibit autophagy. Chem Biol 18:1474–1481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.08.009
Mailloux RJ (2015) Teaching the fundamentals of electron transfer reactions in mitochondria and the production and detection of reactive oxygen species. Redox Biol 4:381–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.02.001
Maldonado EN, Sheldon KL, DeHart DN et al (2013) Voltage-dependent anion channels modulate mitochondrial metabolism in cancer cells: regulation by free tubulin and erastin. J Biol Chem 288:11920–11929. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.433847
Marques I, Duarte M, Assunção J, Ushakova AV, Videira A (2005) Composition of complex I from Neurospora crassa and disruption of two “accessory” subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1707:211–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2004.12.003
Marques I, Dencher NA, Videira A, Krause F (2007) Supramolecular organization of the respiratory chain in Neurospora crassa mitochondria. Eukaryot Cell 6:2391–2405
Maxwell DP, Wang Y, Mcintosh L, Kende HJ (1999) The alternative oxidase lowers mitochondrial reactive oxygen production in plant cells. Plant Biol 96:8271–8276
McCluskey K, Wiest A, Plamann M (2010) The fungal genetics stock center: a repository for 50 years of fungal genetics research. J Biosci 35:119–126
Michejda J, Guo XJ, Lauquin GJM (1990) The respiration of cells and mitochondria of porin deficient yeast mutants is coupled. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 171:354–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291X(90)91401-D
Møller IM (2001) Plant mitochondria and oxidative stress: Electron transport, NADPH turnover, and metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52:561–591
Muller FL, Liu Y, Abdul-Ghani MA, Lustgarten MS, Bhattacharya A, Jang YC, Van Remmen H (2008) High rates of superoxide production in skeletal-muscle mitochondria respiring on both complex I- and complex II-linked substrates. Biochem J 409:491–499. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20071162
Munro D, Treberg JR (2017) A radical shift in perspective: mitochondria as regulators of reactive oxygen species. J Exp Biol 220:1170–1180. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.132142
Nargang FE, Rapaport D (2007) Neurospora crassa as a model organism for mitochondrial biogenesis. Methods Mol Biol 372:107–123
Popp B, Court DA, Benz R, Neupert W, Lill R (1996) The role of the N and C termini of recombinant Neurospora mitochondrial porin in channel formation and voltage-dependent gating. J Biol Chem 271:13593–13599. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.271.23.13593
Quinlan CL, Gerencser AA, Treberg JR, Brand MD (2011) The mechanism of superoxide production by the antimycin-inhibited mitochondrial Q-cycle. J Biol Chem 286:31361–31372. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.267898
Quinlan CL, Orr AL, Perevoshchikova IV, Treberg JR, Ackrell BA, Brand MD (2012) Mitochondrial complex II can generate reactive oxygen species at high rates in both the forward and reverse reactions. J Biol Chem 287:27255–27264. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.374629
Reina S, Palermo V, Guarnera A, Guarino F, Messina A, Mazzoni C, de Pinto V (2010) Swapping of the N-terminus of VDAC1 with VDAC3 restores full activity of the channel and confers anti-aging features to the cell. FEBS Lett 584:2837–2844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2010.04.066
Schein SJ, Colombini M, Finkelstein A (1976) Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a voltage-dependent anion-selective channel obtained from paramecium mitochondria. J Membr Biol 30:99–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869662
Schlossmann J, Dietmeier K, Pfanner N, Neupert W (1994) Specific recognition of mitochondrial preproteins by the cytosolic domain of the import receptor MOM72. J Biol Chem 269:11893–11901
Schneider H, Arretz M, Wachter E, Neupert W (1990) Matrix processing peptidase of mitochondria. Structure-function relationships. J Biol Chem 265:9881–9887
Shoshan-Barmatz V, De S (2017) Mitochondrial VDAC, the Na+/Ca2+exchanger, and the Ca2+uniporter in Ca2+dynamics and signaling. Adv Exp Med Biol 981:323–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55858-5_13
Shoshan-Barmatz V, De Pinto V, Zweckstetter M et al (2010) VDAC, a multi-functional mitochondrial protein regulating cell life and death. Mol Asp Med 31:227–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2010.03.002
Shuvo SR, Ferens FG, Court DA (2016) The N-terminus of VDAC: structure, mutational analysis, and a potential role in regulating barrel shape. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1858:1350–1361
Shuvo SR, Kovaltchouk U, Zubaer A, Kumar A, Summers WAT, Donald LJ, Hausner G, Court DA (2017) Functional characterization of an N-terminally truncated mitochondrial porin expressed in Neurospora crassa. Can J Microbiol 63:730–738. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2016-0764
Summers WAT, Wilkins JA, Dwivedi RC, Ezzati P, Court DA (2012) Mitochondrial dysfunction resulting from the absence of mitochondrial porin in Neurospora crassa. Mitochondrion 12:220–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2011.09.002
Tanton LL, Nargang CE, Kessler KE, Li Q, Nargang FE (2003) Alternative oxidase expression in Neurospora crassa. Fungal Genet Biol 39:176–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1087-1845(03)00002-1
Tewari D, Majumdar D, Vallabhaneni S, Bera AK (2017) Aspirin induces cell death by directly modulating mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC). Sci Rep 7:45184. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45184
Tomasello MF, Guarino F, Reina S, Messina A, De Pinto V (2013) The voltage-dependent anion selective channel 1 (VDAC1) topography in the mitochondrial outer membrane as detected in intact cell. PLoS One 8(12):e81522. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0081522
Treberg JR, Quinlan CL, Brand MD (2011) Evidence for two sites of superoxide production by mitochondrial NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I). J Biol Chem 286:27103–27110. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.252502
Ujwal R, Cascio D, Colletier JP, Faham S, Zhang J, Toro L, Ping P, Abramson J (2008) The crystal structure of mouse VDAC1 at 2.3 A resolution reveals mechanistic insights into metabolite gating. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:17742–7. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0809634105
Videira A, Duarte M (2002) From NADH to ubiquinone in Neurospora mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1555:187–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2728(02)00276-1
Villa-Cuesta E, Holmbeck MA, Rand DM (2014) Rapamycin increases mitochondrial efficiency by mtDNA-dependent reprogramming of mitochondrial metabolism in Drosophila. J Cell Sci 127:2282–2290. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.142026
Young MJ, Bay DC, Hausner G, Court DA (2007) The evolutionary history of mitochondrial porins. BMC Evol Biol 7:31
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Discovery Grants (DG) from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) to DAC and JRT, the Canada Research Chairs (CRC) program to JRT and the Faculty of Science (DC). SRS acknowledges support from the Faculty of Graduate Studies at the University of Manitoba and DG funds awarded to DAC. LMW was supported by DG and CRC funds to JRT. The authors thank Mr. Erwin J. Taguiam, Department of Microbiology, for excellent technical assistance, Dr. Frank Nargang, University of Alberta, for antibodies, and Dr. Richard Sparling, Department of Microbiology, for very valuable discussions and reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 51 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 1
Mitochondrial intactness assays. a) Mitochondrial oxygen consumption in the presence of succinate by exogenous cytochrome c in different strains. The OCR (state 3) following the addition of exogenous cytochrome c is presented for 7 biological replicates of all strains except ΔN2-12Por, for which there were 8. Average values are presented and error bars indicate standard deviation; there were no statistically significant differences among the preparations, as assessed using the students’ t-test. Increases of less than 20% indicate high quality mammalian mitochondria suitable for bioenergetics assays (Banh et al. 2015). b) Protease treatment of mitochondria. Two samples of mitochondria were mixed in SR buffer at 30 °C in the Oroboros respirometry chamber. In one chamber the standard cytochrome c-based intactness assay was carried out. For the experiments shown, the ratios of OCR ± cytochrome c addition were WT: 1.2; LoPo: 1.1; ΔPor-1: 1.2; Δ2-12Porin: 1.1. From the other chamber, two 500 μl samples were taken at each time point; one was kept on ice (-protK) and the other was protease-treated (+ protK) on ice as described in Materials and Methods. Lanes 1, samples taken prior to the beginning of the experiment (unmixed); lanes 2, samples taken at the same time as the addition of cytochrome c (after 10–15 min of mixing) and lanes 3, samples taken at the end of the experiment (15–20 min). Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose and probed with antibodies against Tom70 (70-kDa subunit of the translocase of the outer membrane), CCHL (cytochrome c heme lyase; 38 kDa) and MPP (α-subunit of the mitochondrial-processing peptidase, 63 kDa). (PPTX 3.10 mb)
Supplementary Figure 2
OCR in the presence and absence of TMRM. Oxygen consumption rates were measured for mitochondria from each strain, following the sequential addition of GMS, ADP, and oligomycin. Data obtained in the presence (grey bars) and absence (white bars) of TMRM are presented as average OCR for 3 biological replicates of ΔN2-12Por and LoPo and 4 biological replicates for WT and ΔPor-1; error bars indicate standard deviations. The star indicates a statistically significant difference (p > 0.05) between the OCR in the presence and absence of TMRM (Student’s t test). (PPTX 151 kb)
Supplementary Figure 3
Membrane potential and oxygen consumption rates of mitochondria respiring on complex I (GM) and complex II (S) and all three (GMS) substrates. OCR (a) and Δψ (b) data were collected simultaneously by combined respirometry and fluorescence in the presence of the indicated substrates. a) Oxygen consumption rates in mitochondria. OCR was measured as described in materials and methods, following sequential addition of substrate (state 2), ADP (state 3) and oligomycin (state 4o). b) Mitochondrial ΔΨ as estimated by quenching of the fluorescent dye TMRM. For each of the indicated strains, state 2 data indicate the relative TMRM fluorescence in the presence of substrate (ΔFA/FT × 100; see Fig. 3), state 3 data show the degree of quenching of fluorescence (depolarization of mitochondria) in the presence of ADP (ΔFB/FT × 100), and state 4o data represent the quenching observed in the presence of oligomycin (ΔFC/FT × 100). The data presented are ranges obtained from 2 biological replicates, each of which was examined under all three substrate combinations. The top of the bar indicates the lowest value obtained, and the top of the error bar indicates the highest value. Given the small sample size, statistical support for apparent differences cannot be obtained. Black, WT; white, LoPo; grey, ΔPor-1; hatched, ΔN2-12Por. (PPTX 6.91 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shuvo, S.R., Wiens, L.M., Subramaniam, S. et al. Increased reactive oxygen species production and maintenance of membrane potential in VDAC-less Neurospora crassa mitochondria. J Bioenerg Biomembr 51, 341–354 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-019-09807-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-019-09807-6