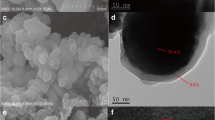
Abstract
A novel magnetically hyper-cross-linked polymer (Fe3O4@HCP-NH2) was prepared in this study, which combined the advantage of the amino-modified HCP-NH2 and the magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. The Fe3O4@HCP-NH2 composite has a high specific surface area (532.62 m2 g−1), well-developed mesoporous (0.3786 cm3 g−1) and good magnetic property. This Fe3O4@HCP-NH2 composite exhibits excellent adsorption ability for tetracycline, and the maximum adsorption capacity calculated by Langmuir model at 298 K is up to 694 mg g−1. The adsorption mechanisms could be attributed to the complexation interactions, hydrogen bonding and cation exchange, and the dominant interaction was the surface complexation which was elucidated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis. In addition, the composite can be rapidly separated and maintains high adsorption performance after five regeneration cycles. More importantly, it can be used as a broad-spectrum and highly efficient adsorbent for organic contaminants including methyl orange, methylene blue, bisphenol A and 2,4-dichlorophenol removal from contaminated water. This work demonstrated that the Fe3O4@HCP-NH2 composite would be the most promising candidates for application in the adsorption of organic pollutants.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petrović M, Gonzalez S, Barceló D (2003) Analysis and removal of emerging contaminants in wastewater and drinking water. Trends Anal Chem 22(10):685–696
Bui XT, Vo TPT, Ngo HH, Guo WS, Nguyen TT (2016) Multicriteria assessment of advanced treatment technologies for micropollutants removal at large-scale applications. Sci Total Environ 563–564:1050–1067
Shen J, Xue JJ, He GY, Ni J, Chen ZX, Tang B, Zhou ZW, Chen HQ (2018) Construction of 3D marigold-like Bi2WO6/Ag2O/CQDs heterostructure with superior visible-light active photocatalytic activity toward tetracycline degradation and selective oxidation. J Mater Sci 53(17):12040–12055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2479-x
Gao P, Xu W, Ruan X, Qian Y, Xue G, Jia H (2018) Long-term impact of a tetracycline concentration gradient on the bacterial resistance in anaerobic-aerobic sequential bioreactors. Chemosphere 205:308–316
Zhu Z, Zhang M, Wang W, Zhou Q, Liu F (2018) Efficient and synergistic removal of tetracycline and Cu(II) using novel magnetic multi-amine resins. Sci Rep 8(1):4762
Mohan D, Singh KP, Singh VK (2008) Wastewater treatment using low cost activated carbons derived from agricultural byproducts—a case study. J Hazard Mater 152(3):1045–1053
Minceva M, Fajgar R, Markovska L, Meshko V (2008) Comparative study of Zn2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ removal from water solution using natural clinoptilolitic zeolite and commercial granulated activated carbon. Equilibrium of adsorption. Sep Sci Technol 43(8):2117–2143
Budd PM, Ghanem BS, Makhseed S, Mckeown NB, Msayib KJ, Tattershall CE (2004) Polymers of intrinsic microporosity (PIMs): robust, solution-processable, organic nanoporous materials. Chem Commun 2(2):230–231
Han SS, Furukawa H, Yaghi OM (2008) Covalent organic frameworks as exceptional hydrogen storage materials. J Am Chem Soc 130(35):11580–11581
Ben T, Ren H, Ma S, Cao D, Lan J, Jing X, Wang W, Xu J, Deng F, Simmons JM (2010) Targeted synthesis of a porous aromatic framework with high stability and exceptionally high surface area. Angew Chem 121(50):9621–9624
Germain J, Hradil J, Fréchet JMJ, Svec F (2006) High surface area nanoporous polymers for reversible hydrogen storage. Chem Mater 18(18):4430–4435
Dawson R, Stevens LA, Drage TC, Snape CE, Smith MW, Adams DJ, Cooper AI (2012) Impact of water coadsorption for carbon dioxide capture in microporous polymer sorbents. J Am Chem Soc 134(26):10741–10744
Li B, Gong R, Wang W, Huang X, Wang Z, Li H, Hu C, Tan B (2011) A new strategy to microporous polymers: knitting rigid aromatic building blocks by external cross-linker. Macromolecules 44(8):2410–2414
Bratkowska D, Davies A, Fontanals N, Cormack PA, Borrull F, Sherrington DC, Marcé RM (2015) Hypercrosslinked strong anion-exchange resin for extraction of acidic pharmaceuticals from environmental water. J Sep Sci 35(19):2621–2628
Jia Z, Wang K, Li T, Tan B, Gu Y (2016) Functionalized hypercrosslinked polymers with knitted N-heterocyclic carbene-copper complexes as efficient and recyclable catalysts for organic transformations. Catal Sci Technol 6(12):4345–4355
Yao S, Yang X, Yu M, Zhang Y, Jiang JX (2014) High surface area hypercrosslinked microporous organic polymer networks based on tetraphenylethylene for CO2 capture. J Mater Chem A 2(21):8054–8059
Huang J, Deng R, Huang K (2011) Equilibria and kinetics of phenol adsorption on a toluene-modified hyper-cross-linked poly(styrene-co-divinylbenzene) resin. Chem Eng J 171(3):951–957
Zhang C, Zhu PC, Tan L, Liu JM, Tan B, Yang XL, Xu HB (2015) Triptycene-based hyper-cross-linked polymer sponge for gas storage and water treatment. Macromolecules 48(23):8509–8514
Pan L, Xu MY, Liu ZL, Du BB, Yang KH, Wu L, He P, He YJ (2016) Facile method for the synthesis of Fe3O4@HCP core-shell porous magnetic microspheres for fast separation of organic dyes from aqueous solution. RSC Adv 6(53):47530–47535
Li Q, Zhan Z, Jin S, Tan B (2017) Wettable magnetic hypercrosslinked microporous nanoparticle as an efficient adsorbent for water treatment. Chem Eng J 326:8509–8514
Shao L, Li Y, Zhang T, Liu M, Huang J (2017) Controllable synthesis of polar modified hyper-cross-linked resins and their adsorption of 2-naphthol and 4-hydroxybenzoic acid from aqueous solution. Ind Eng Chem Res 56(11):47530–47535
Dawson R, Ratvijitvech T, Corker M, Laybourn A, Khimyak YZ, Cooper AI, Adams DJ (2012) Microporous copolymers for increased gas selectivity. Polym Chem 3(8):2034–2038
Samanta P, Chandra P, Desai AV, Ghosh SK (2017) Chemically stable microporous hyper-cross-linked polymer (HCP): an efficient selective cationic dye scavenger from aqueous medium. Mater Chem Front 1(7):1384–1388
He Y, Xu T, Hu J, Peng C, Yang Q, Wang H, Liu H (2017) Amine functionalized 3D porous organic polymer as an effective adsorbent for removing organic dyes and solvents. RSC Adv 7(48):30500–30505
Shi S, Fan Y, Huang Y (2013) Facile low temperature hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic mesoporous carbon nanocomposite for adsorption removal of ciprofloxacin antibiotics. Ind Eng Chem Res 52(7):2604–2612
Yang X, Li B, Majeed I, Liang L, Long X, Tan B (2013) Magnetic microporous polymer nanoparticles. Polym Chem 4(5):1425–1429
Savva I, Marinica O, Papatryfonos C, Vekas L, Krasiachristoforou T (2015) Evaluation of electrospun polymer–Fe3O4 nanocomposite mats in malachite green adsorption. RSC Adv 5(21):16484–16496
Jiang Z, Tijing LD, Amarjargal A, Park CH, An KJ, Shon HK, Kim CS (2015) Removal of oil from water using magnetic bicomponent composite nanofibers fabricated by electrospinning. Compos Part B 77:311–318
Chen Y, Liu K (2016) Preparation and characterization of nitrogen-doped TiO2/diatomite integrated photocatalytic pellet for the adsorption-degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride using visible light. Chem Eng J 302:682–696
Wang K, Jia Z, Yang X, Wang L, Gu Y, Tan B (2017) Acid and base coexisted heterogeneous catalysts supported on hypercrosslinked polymers for one-pot cascade reactions. J Catal 348:168–176
Liu J, Sun Z, Deng Y, Zou Y, Li C, Guo X, Xiong L, Gao Y, Li F, Zhao D (2009) Highly water-dispersible biocompatible magnetite particles with low cytotoxicity stabilized by citrate groups. Angew Chem Int Ed 48(32):5875–5879
Mu J, Chen B, Guo Z, Zhang M, Zhang Z, Zhang P, Shao C, Liu Y (2011) Highly dispersed Fe3O4 nanosheets on one-dimensional carbon nanofibers: synthesis, formation mechanism, and electrochemical performance as supercapacitor electrode materials. Nanoscale 3(12):5034–5040
Zhou G, Wang DW, Li F, Zhang L, Li N, Wu ZS, Wen L, Lu GQ, Cheng HM (2010) Graphene-wrapped Fe3O4 anode material with improved reversible capacity and cyclic stability for lithium ion batteries. Chem Mater 22(18):5306–5313
Minitha CR, Arachy MMS (2018) Influence of Fe3O4 nanoparticles decoration on dye adsorption and magnetic separation properties of Fe3O4/rGO nanocomposites. Sep Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1446986
Ma Y, Zhou Q, Zhou S, Wang W, Jin J, Xie J, Li A, Shuang CA (2014) A bifunctional adsorbent with high surface area and cation exchange property for synergistic removal of tetracycline and Cu2+. Chem Eng J 258:26–33
Li Q, Snoeyink VL, Mariñas BJ, Campos C (2003) Pore blockage effect of NOM on atrazine adsorption kinetics of PAC: the roles of PAC pore size distribution and NOM molecular weight. Water Res 37(20):4863–4872
Guerra W, Silva-Caldeira PP, Terenzi H, Pereira-Maia EC (2016) Impact of metal coordination on the antibiotic and non-antibiotic activities of tetracycline-based drugs. Coord Chem Rev 327–328:188–199
Gu C, Karthikeyan KG, Sibley SD, Pedersen JA (2007) Complexation of the antibiotic tetracycline with humic acid. Chemosphere 66(8):1494–1501
Li W, Wang J, He G, Yu L, Noor N, Sun Y, Zhou X, Hu J, Parkin IP (2017) Enhanced adsorption capacity of ultralong hydrogen titanate nanobelts for antibiotics. J Mater Chem A 5(9):4352–4358
Huang YM, Lee XQ, Grattieri M, Macazo FC, Cai R, Minteer SD (2018) A sustainable adsorbent for phosphate removal: modifying multi-walled carbon nanotubes with chitosan. J Mater Sci 53(17):12641–12649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2494-y
Widiastuti N, Wu H, Ang HM, Zhang D (2011) Removal of ammonium from greywater using natural zeolite. Desalination 277(1):15–23
Tian C, Zhao J, Zhang J, Chu S, Dang Z, Lin Z, Xing B (2017) Enhanced removal of roxarsone by Fe3O4@3D graphene nanocomposite: synergistic adsorption and mechanism. Environ Sci Nano 4(11):2134–2143
Liu Q, Zhong LB, Zhao QB, Frear C, Zheng YM (2015) Synthesis of Fe3O4/polyacrylonitrile composite electrospun nanofiber mat for effective adsorption of tetracycline. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(27):14573–14583
Zhang D, Niu H, Zhang X, Meng Z, Cai Y (2011) Strong adsorption of chlorotetracycline on magnetite nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 192(3):1088–1093
Jia D, Sun SP, Wu Z, Wang N, Jin Y, Dong W, Chen XD, Ke Q (2017) TCE degradation in groundwater by chelators-assisted Fenton-like reaction of magnetite: sand columns demonstration. J Hazard Mater 346:124–132
Hashemikia S, Hemmatinejad N, Ahmadi E, Montazer M (2015) Optimization of tetracycline hydrochloride adsorption on amino modified SBA-15 using response surface methodology. J Colloid Interface Sci 443:105–114
Kang J, Liu HJ, Zheng YM, Qu JH, Chen JP (2010) Systematic study of synergistic and antagonistic effects on adsorption of tetracycline and copper onto a chitosan. J Colloid Interface Sci 344(1):117–125
Zhang L, Song X, Liu X, Yang L, Pan F, Lv J (2011) Studies on the removal of tetracycline by multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem Eng J 178(24):26–33
Xiong W, Zeng G, Yang Z, Zhou Y, Zhang C, Cheng M, Liu Y, Hu L, Wan J, Zhou C (2018) Adsorption of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solutions on nanocomposite multi-walled carbon nanotube functionalized MIL-53(Fe) as new adsorbent. Sci Total Environ 627:235–244
Gao Y, Li Y, Zhang L, Huang H, Hu J, Shah SM, Su X (2012) Adsorption and removal of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solution by graphene oxide. J Colloid Interface Sci 368(1):540–546
Chen SQ, Chen YL, Jiang H (2017) Slow pyrolysis magnetization of hydrochar for effective and highly stable removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution. Ind Eng Chem Res 56(11):3059–3066
Ma J, Yu F, Zhou L, Jin L, Yang M, Luan J, Tang Y, Fan H, Yuan Z, Chen J (2012) Enhanced adsorptive removal of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution by alkali-activated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(11):5749–5760
Xu L, Wang J (2012) Fenton-like degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol using Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Appl Catal B Environ 123–124(30):117–126
Huang YQ, Wong CK, Zheng JS, Bouwman H, Barra R, Wahlström B, Neretin L, Wong MH (2012) Bisphenol A (BPA) in China: a review of sources, environmental levels, and potential human health impacts. Environ Int 42(1):91–99
Ou HJ, Zhang W, Yang XF, Liao GY, Xia H, Wang DS (2018) One-pot synthesis of g-C3N4-doped rich-amine porous organic polymer for chlorophenol removal. Environ Sci Nano 5(1):169–182
Shen X, Chen X, Sun D, Wu T, Li Y (2018) Fabrication of a magnetite/diazonium functionalized-reduced graphene oxide hybrid as an easily regenerated adsorbent for efficient removal of chlorophenols from aqueous solution. RSC Adv 8(14):7351–7360
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Scientific Foundation of China (21477118, 51478445) and the Open Projects Foundation (No. 1604) State Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber and Cable Manufacture Technology (YOFC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, A., Yang, X., You, Q. et al. Magnetically hyper-cross-linked polymers with well-developed mesoporous: a broad-spectrum and highly efficient adsorbent for water purification. J Mater Sci 54, 2712–2728 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2967-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2967-z