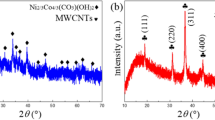
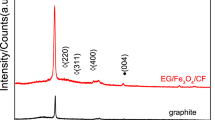
Abstract
Designing the structure with dielectric loss and magnetic loss integrated contributes to expansion of microwave absorption bandwidth. Nanohybrid materials composed of iron oxide (Fe3O4) and multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) were prepared through a newly electrostatic attraction method as high-performance microwave absorbers in the 2–18 GHz band. The nanohybrids are characterized by transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and vector network analysis. Microstructural analysis showed that Fe3O4 and MWCNTs were well-connected through electrostatic interaction in the nanohybrids. The experimental results indicated that MWCNTs/PEDOT: PSS/Fe3O4 possessed higher reflection loss and broader absorption bandwidth than MWCNTs. MWCNTs/SDBS/Fe3O4 had better matching of dielectric loss and magnetic loss, the absorption bandwidth below − 10 dB was up to 8 GHz. This work further reveals that the novel electrostatic attraction method could be efficiently enlarged electromagnetic wave attenuation performance in absorb materials.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seokjin Y, Artavazd KJ, Srivathsava S, Jong-Ryul J, Jihoon C (2017) Controlled morphology of MWCNTs driven by polymer-grafted nanoparticles for enhanced microwave absorption. J Mater Chem C 5:8436–8443
Yi C, Xiaoyun L, Xiaoyang M, Qixin Z, Zhong X, Zhewen H (2014) γ-Fe2O3–MWNT/poly(p-phenylenebenzobisoxazole) composites with excellent microwave absorption performance and thermal stability. Nanoscale 6:6440–6447
Zhang Y, Yi H, Honghui C et al (2016) Composition and structure control of ultralight graphene foam for high-performance microwave absorption. Carbon 105:438–447
Genban S, Bingxiang D, Minhua C, Bingqing W, Changwen H (2011) Hierarchical dendrite-like magnetic materials of Fe3O4, gamma-Fe2O3, and Fe with high performance of microwave absorption. Chem Mater 23:1587–1593
Lei W, Ying H, Xu S, Haijian H, Panbo L, Meng Z, Yan W (2014) Synthesis and microwave absorption enhancement of graphene@Fe3O4@SiO2@NiO nanosheet hierarchical structures. Nanoscale 6:3157–3164
Zhijiang W, Lina Wu, Jigang Z, Baozhong S, Zhaohua J (2014) Enhanced microwave absorption of Fe3O4 nanocrystals after heterogeneously growing with ZnO, nanoshell. RSC Adv 3:3309–3315
Zhu H, Zhang H, Chen Y, Li Z, Zhang D, Zeng G, Huang Y, Wang W, Wu Q, Zhi C (2016) The electromagnetic property and microwave absorption of wormhole-like mesoporous carbons with different surface areas. J Mater Sci 51:9723–9731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0206-z
Danping S, Quan Z, Yanping W, Yujiao W, Wei J, Li Fengsheng (2014) Controllable synthesis of porous Fe3O4@ZnO sphere decorated graphene for extraordinary electromagnetic wave absorption. Nanoscale 6:6557–6562
Liu Q, Zi Z, Zhang M, Zhang P, Pang A, Dai J, Sun Y (2013) Solvothermal synthesis of hollow glass microspheres/Fe3O4 composites as a light weight microwave absorber. J Mater Sci 48:6048–6055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7401-y
Xin T, Fanbin M, Fanchen M, Xiangnan C, Yifan G, Ying W, Wenjun Z, Zuowan Z (2017) Synergistic enhancement of microwave absorption using hybridized polyaniline@helical CNTs with dual chirality. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:15711–15718
Shital PP, Sourav B, Goutam PK, Suryasarathi B (2016) High frequency millimetre wave absorbers derived from polymeric nanocomposites. Polymer 84:398–419
Luo K, Chen W, Xiaowei Y, Xiaomeng F, Wei W, Jianfeng H (2017) Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of a carbon nanotube modified by a tetrapyridinoporphyrazine interface layer. J Mater Chem C 5:7479–7488
Hao S, Renchao C, Xiao Y, Yishu J, Zhibin Y, Jue D, Longbin Q, Huisheng P (2014) Cross-stacking aligned carbon-nanotube films to tune microwave absorption frequencies and increase absorption intensities. Adv. Mater 26: 8120–8125–8
Arup C (2014) Carboxyl-functionalized MWCNT doped poly(o-toluidine) nanohybrids: Synthesis, a characterization with AC electrical and dielectric properties. Synth Met 188:13–20
Bhattacharya P, Sahoo S, Das CK (2013) Microwave absorption behavior of MWCNT based nanocomposites in X-band region. Polym Lett 7(3):212–223
Xu H, Zhiran C, Lifen T, Mengna F, Zejun P, Xiaobo L (2013) Preparation and microwave absorption properties of BaTiO3@MWCNTs core/shell heterostructure. Mater Lett 111:24–27
Cuiling H, Tiehu L, Tingkai Z, Jing L, Wenjuan Z, Yongshuai M (2013) Microwave absorption properties of rare metal-doped multi-walled carbon nanotube/polyvinyl chloride composites. J Reinf Plast Compos 31(22):1526–1531
Zhang L, Shi C, Rhee KY, Zhao NQ (2012) Properties of Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4/carbon nanotubes/polyimide nanocomposites for microwave absorption. Compos Part A 43:2241–2248
Wang Z, Wei G, Zhao G-L (2013) Enhanced electromagnetic wave shielding effectiveness of Fe doped carbon nanotubes/epoxy composites. Appl Phys Lett 103:109–183
MaoSheng C, Jian Y, WeiLi S, DeQing Z, Bo W, HaiBo J, ZhiLing H, Jie Y (2012) Ferrosoferric oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotube vs polyaniline/ferrosoferric oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotube multiheterostructures for highly effective microwave absorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:6949–6956
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Basic Research Project of Shanghai (16JC1403300) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (16ZR1446200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, Z., Qiu, J. Microwave absorption performance of iron oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotubes nanohybrids prepared by electrostatic attraction. J Mater Sci 53, 3640–3646 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1770-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1770-6