Abstract
Objectives
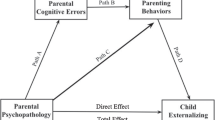
This study used a two-wave design to examine whether (dis)agreement between mothers and adolescents and between fathers and adolescents in reports of on parenting (i.e., support, proactive control, punishment, harsh punishment, and psychological control) was associated with adolescent Externalizing Problem Behavior (EPB; i.e., aggression and rule-breaking behavior) 1 year later.
Methods
Adolescents (N = 1,116, Mage = 13.79) reported on EPB and parenting across both parents, whereas mothers (N = 841) and fathers (N = 724) reported on EPB and their own parenting. As suggested by Laird and De Los Reyes (2013), we used moderated polynomial regressions to investigate informant discrepancy.
Results
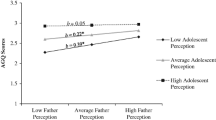
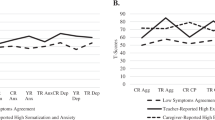
Results indicated that agreement between mothers and adolescents concerning psychological control positively predicted EPB. Furthermore, there were linear and curvilinear associations between adolescent-reported parenting and EPB.
Conclusions
Our findings indicated that the inclusion of multiple informants, and more specifically, the agreement between two informants was important in predicting adolescent problem behavior. Furthermore, it provided support for including both mothers and fathers in future research or clinical programs. Finally, the link between some parenting practices and externalizing problem behavior may be more complex than suggested by previous studies. Concerning clinical implications, the present study provides support for tailoring prevention/intervention programs for the different members of the family.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M. (1991a). Manual for the youth self-report and 1991 profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach, T. M. (1991b). Manual for the child behavior checklist/4-18 and 1991 profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont.
Ahmad, I., Vansteenkiste, M., & Soenens, B. (2013). The relations of Arab Jordanian adolescents’ perceived maternal parenting to teacher-rated adjustment and problems: the intervening role of perceived need satisfaction. Developmental Psychology, 49, 177–183. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0027837.
Aiken, L. S., & West, S. G. (1991). Multiple regression: testing and interpreting interactions. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Armstrong, R. A. (2014). When to use the Bonferroni correction. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics, 34, 502–508. https://doi.org/10.1111/opo.12131.
Barber, B. K. (1996). Parental psychological control: revisiting a neglected construct. Child Development, 67, 3296–3319. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.1996.tb01915.x.
Barber, B. K (2002). Regulation as a multicultural concept and construct for adolescent health and development. Knoxville, TN: University of Tennessee. Unpublished manuscript.
Barber, B. K., Xia, M., Olsen, J. A., Mcneely, C. A., & Bose, K. (2012). Feeling disrespected by parents : refining the measurement and understanding of psychological control. Journal of Adolescence, 35, 273–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2011.10.010.
Baumrind, D. (1991). The influence of parenting style on adolescent competence and substance use. Journal of Early Adolescence, 11, 56–95.
Bender, H. L., Allen, J. P., McElhaney, K. B., Antonishak, J., Moore, C. M., Kelly, H. O., & Davis, S. M. (2007). Use of harsh physical discipline and developmental outcomes in adolescence. Development and Psychopathology, 19, 227–242. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579407070125.
Brand, A. E., & Klimes-Dougan, B. (2010). Emotion socialization in adolescence: the roles of mothers and fathers. New directions for child and adolescent. Development, 128, 85–100. https://doi.org/10.1002/cd.270.
Delhaye, M., Beyers, W., Klimstra, T. A., Linkowski, P., & Goossens, L. (2012). The leuven adolescent perceived parenting scale (LAPPS): reliability and validity with French-speaking adolescents in Belgium. Psychologica Belgica, 52, 289–305. https://doi.org/10.5334/pb-52-4-289.
De Los Reyes, A., & Kazdin, A. E. (2005). Informant discrepancies in the assessment of childhood psychopathology: a critical review, theoretical framework, and recommendations for further study. Psychological Bulletin, 131, 483–509. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.131.4.483.
De Los Reyes, A., Goodman, K. L., Kliewer, W., & Reid-Quiñones, K. (2010). The longitudinal consistency of mother-child reporting discrepancies of parental monitoring and their ability to predict child delinquent behaviors two years later. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 39, 1417–1430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-009-9496-7.
De Los Reyes, A., Augenstein, T. M., Wang, M., Thomas, S. A., & Dabrick, D. (2015). The validity of the multi-informant approach to assessing child and adolescent mental health. Psychological Bulletin, 141, 858–900. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0038498.
De Los Reyes, A., & Ohannessian, C. (2016). Introduction to the special issue: discrepancies in adolescent-parent perceptions of the family and adolescent adjustment. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 45, 1957–1972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-016-0533-z.
Dimler, L. M., Natsuaki, M. N., Hastings, P. D., Zahn-Waxler, C., & Klimes-Dougan, B. (2017). Parenting effects are in the eye of the beholder: parent-adolescent differences in perceptions affects adolescent problem behaviors. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 46, 1076–1088. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-016-0612-1.
Edwards, J. R. (1994). The study of congruence in organizational behavior research: critique and a proposed alternative. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 58, 51–100.
Enders, C. K. (2001). The performance of the full information maximum likelihood estimator in multiple regression models with missing data. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 61, 713–740.
Gershoff, E. T., & Grogan-Kaylor, A. (2016). Spanking and child outcomes: old controversies and new meta-analyses. Journal of Family Psychology, 30, 453–469. https://doi.org/10.1037/fam0000191.
Grolnick, W. S., & Pomerantz, E. M. (2009). Issues and challenges in studying parental control: toward a new conceptualization. Child Development Perspectives, 3, 165–170. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-8606.2009.00099.x.
Grolnick, W. S., Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (1991). Inner resources for school achievement: Motivational mediators of children’s perceptions oftheir parents. Journal of Educational Psychology, 83, 508–517. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.83.4.508.
Grotevant, H. D., & Cooper, C. R. (1986). Individuation in family relationships: a perspective on individual differences in the development of identity and role-taking skill in adolescence. Human Development, 29, 82–100. https://doi.org/10.1159/000273025.
Guion, K., Mrug, S., & Windle, M. (2009). Predictive value of informant discrepancies in reports of parenting: relations to early adolescents’ adjustment. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37, 17–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-008-9253-5.
Hanisch, C., Hautmann, C., Plück, J., Eichelberger, I., & Döpfner, M. (2014). The prevention program for externalizing problem behavior (PEP) improves child behavior by reducing negative parenting: analysis of mediating processes in a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 55, 473–484. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12177.
IBM Corp (2016). IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 24.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.
Institute for Research and Reform in Education. (1998). Research assessment package for schools (RAPS) manual. Philadelphia, PA. http://www.irre.org/sites/default/files/publication_pdfs/RAPS_manual_entire_1998.pdf.
Jager, J., Bornstein, M. H., Diane, P. L., & Hendricks, C. (2012). Family members‘ unique perspectives of the family: examining their scope, size, and relations to individual adjustment. Journal of Family Psychology, 26, 400–410. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0028330.
Jager, J., Yuen, C. X., Bornstein, M. H., Diane, P. L., & Hendricks, C. (2014). The relations of family members‘ unique and shared perspectives of family dysfunction to dyad adjustment. Journal of Family Psychology, 28, 407–414. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0036809.
Janssens, A., Goossens, L., Van Den Noortgate, W., Colpin, H., Verschueren, K., & Van Leeuwen, K. (2015). Parents’ and adolescents’ perspectives on parenting: evaluating conceptual structure, measurement invariance, and criterion validity. Assessment, 22(4), 473–489. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191114550477.
Janssens, A., Van Den Noortgate, W., Goossens, L., Verschueren, K., Colpin, H., Claes, S., Van Heel, M., & Van Leeuwen, K. (2017). Adolescent externalizing behaviour, psychological control, and peer rejection: transactional links and dopaminergic moderation. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 35, 420–438.
Jeynes, W. H. (2016). Meta-analysis on the roles of fathers in parenting: are they unique? Marriage & Family Review, 52, 665–688. https://doi.org/10.1080/01494929.2016.1157121.
Kakihara, F., Tilton-Weaver, L., Kerr, M., & Stattin, H. (2010). The relationship of parental control to youth adjustment: do youth’s feelings about their parents play a role? Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 39, 1442–1456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-009-9479-8.
King Baudouin Foundation. (2008). Het kind in een nieuw samengesteld gezin [The child in a blended family]. https://www.kbsfrb.be/~/media/Files/Bib/Publications/Older/PUB-1838-NieuwSamengesteldeGezinnen.pdf.
Laible, D. J., & Carlo, G. (2004). The differential relations of maternal and paternal support and control to adolescent social competence, self-worth, and sympathy. Faculty Publications Department of Psychology, 30, 1–14.
Laible, D. J., Carlo, G., & Raffaelli, M. (2000). The differential relations of parent and peer attachment to adolescent adjustment. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 29, 45–59.
Laird, R. D., & De Los Reyes, A. (2013). Testing informant discrepancies as predictors of early adolescent psychopathology: why difference scores cannot tell you what you want to know and how polynomial regression may. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 41, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-012-9659-y.
Laird, R. D., & Weems, C. F. (2011). The equivalence of regression models using difference scores and models using separate scores for each informant: implications for the study of informant discrepancies. Psychological Assessment, 23, 388–397. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0021926.
Lansford, J. E., Criss, M. M., Laird, R. D., Shaw, D. S., Pettit, G. S., Bates, J. E., & Dodge, K. A. (2011). Reciprocal relations between parents’ physical discipline and children’s externalizing behavior during middle childhood and adolescence. Development and Psychopathology, 23, 225–238. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579410000751.
Larzelere, R. E., & Kuhn, B. R. (2005). Comparing child outcomes of physical punishment and alternative disciplinary tactics: a meta-analysis. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 8, 1–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-005-2340-z.
Leung, J. T. Y., & Shek, D. T. L. (2014). Parent-adolescent discrepancies in perceived parenting characteristics and adolescent developmental outcomes in poor Chinese families. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 23, 200–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-013-9775-5.
Little, R. J. A. (1988). A test of missing completely at random for multivariate data with missing values. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 83, 1198–1202.
Mabbe, E., Soenens, B., Vansteenkiste, M., & Van Leeuwen, K. (2016). Do personality traits moderate relations between psychologically controlling parenting and problem behavior in adolescents? Journal of Personality, 84, 381–392. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004.
Mackenbach, J. D., Ringoot, A. P., van der Ende, J., Verhulst, F. C., Jaddoe, V. W. V., Hofman, A., & Tiemeier, H. W. (2014). Exploring the relation of harsh parental discipline with child emotional and behavioral problems by using multiple informants: the generation R study. PLoS ONE, 9, e104793.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (1998–2012). Mplus user’s guide. 7th ed Los Angeles, CA: Muthén & Muthén.
Nelson, D. A., & Crick, N. R. (2002). Parental psychological control: Implications for childhood physical and relational aggression. In B. K. Barber (Ed.) Intrusive parenting: how psychological control affects children and adolescents. (pp. 168–189). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Odhayani, A. I., Watson, W. J., & Watson, L. (2013). Behavioural consequences of child abuse. Canadian Family Physician, 59, 831–836.
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J. Y., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88, 879–903.
Research Department of the Flemish Government. (2010). Activiteitsgraad naar geslacht, leeftijdsgroep en internationale vergelijking, in %. [Activity level by sex, age group and international comparison, in %]. http://bi-vijf-zes.deboeck.com/public/modele/bi-vijf-zes/content/bivijf/Module%203/Hoofdstuk%204/activiteitsgraad%20internationaal.
Research Department of the Flemish Government. (2011). Scholingsgraad van de bevolking (25–64 jaar), in % [Educational attainment in the population aged 25–64 years, in %]. www4dar.vlaanderen.be/sites/svr/Cijfers/Exceltabellen/onderwijs/kwaliteitszorg/ONDEKWAL012.xlsx.
Russell, J. D., Graham, R. A., Neil, E. L., & Weems, C. F. (2016). Agreement in youth-parent perceptions of parenting behaviors: a case for testing measurement invariance in reporter discrepancy research. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 45, 2094–2107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-016-0495-1.
Schludermann, E. H., & Schludermann, S. M. (1988). Children’s report on Parent Behavior (CRPBI-108, CRPBI-30) for older children and adolescents (Tech. Rep.). Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada: University of Manitoba, Department of Psychology.
Soenens, B., Sierens, E., Vansteenkiste, M., Dochy, F., & Goossens, L. (2012). Psychologically controlling teaching: Examining outcomes, antecedents, and mediators. Journal of Educational Psychology, 104(1), 108–120. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0025742.
Soenens, B., Vansteenkiste, M., Luyckx, K., & Goossens, L. (2006). Parenting and adolescent problem behavior: an integrated model with adolescent self-disclosure and perceived parental knowledge as intervening variables. Developmental Psychology, 42, 305–318. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.42.2.305.
Van Heel, M., Bijttebier, P., Claes, S., Colpin, H., Goossens, L., Van Den Noortgate, W., Verschueren, K., & Van Leeuwen, K. (2019). Measuring parenting throughout adolescence. Assessment, 26, 111–124. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191116686827.
Leeuwen, Van, K., Vermulst, A., Kroes, G., Meyer, De, R., Nguyen, L., & Veerman, J. W. (2013). Verkorte Schaal voor Ouderlijk Gedrag (VSOG): handleiding [Brief Scale of parental behavior: manual]. Nijmegen, The Netherlands: Praktikon.
Yaban, E. H., Say, M., Tepe, Y. K., & Sayil, M. (2014). Are discrepancies in perceptions of psychological control related to maladjustment? A study of adolescents and their parents in Turkey. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 38, 550–562. https://doi.org/10.1177/0165025414537880.
Acknowledgements
The research reported in this manuscript was supported by a Concerted Research Action grant (GOA/12/009) from the KU Leuven Research Fund.
Funding
This research was funded by a Concerted Research Action grant (GOA/12/009) from the KU Leuven Research Fund.
Author Contributions
M.V.H. and K.V.L. designed the current study. M.V.H. was responsible for data analysis and report writing. P.B., L.C., H.C., W.V.D.N., K.V. and K.V.L. provided feedback on the manuscript. L.G., H.C., W.V.D.N., K.V. and K.V.L. were involved in the conceptualization of the research project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Permission for the study was obtained from the institutional review board of the KU Leuven (ML7972). Written parental consent was obtained for the present study. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Heel, M., Bijttebier, P., Colpin, H. et al. Adolescent-Parent Discrepancies in Perceptions of Parenting: Associations with Adolescent Externalizing Problem Behavior. J Child Fam Stud 28, 3170–3182 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-019-01493-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-019-01493-7