Abstract
Purpose
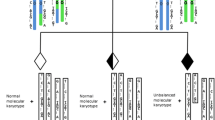
Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) using Karyomapping is used to screen embryos for single gene disorders prior to implantation. While Karyomapping is not designed to screen for abnormalities in chromosome copy number, this testing is based upon a genome-wide analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) and, as such, some chromosome abnormalities are detected. The aim of this study was to validate whether Karyomapping could provide reliable and accurate PGT for a paternal 46,XY,t(10;19)(p15;p13.3) reciprocal translocation.
Methods
Feasibility/validation for PGT was performed using DNA from the couple, as well as DNA from the paternal parents and from a previous unbalanced pregnancy. Karyomapping was performed using Illumina’s HumanKaryomap-12 BeadChip microarray technology. SNP analysis was performed using BlueFuse Multi software (Illumina). Transmission of the translocation was assessed through the analysis of SNP markers on the chromosome regions of interest.
Results
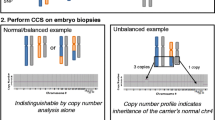
PGT-SR was determined to be feasible as chromosomal SNP analysis could reliably distinguish normal/balanced outcomes from all unbalanced outcomes. The couple transferred a normal/balanced embryo in an elective single embryo transfer procedure following 2 IVF/PGT-SR cycles. A clinical pregnancy was achieved.
Conclusion
This is the first report of PGT-SR test validation using Karyomapping for a 46,XY,t(10;19)(p15;p13.3) reciprocal translocation. Karyomapping may offer a means of detecting unbalanced forms of chromosome rearrangements when other PGT platforms fail.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katz MG, Fitzgerald L, Bankie A, Savulescu J, Cram DS. Issues and concerns of couples presenting for preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD). Prenat Diagn. 2002;22:1117–22.
Handyside AH, Harton GL, Mariani B, Thornhill AR, Affara N, Shaw MA, et al. Karyomapping: a universal method for genome wide analysis of genetic disease based on mapping crossovers between parental haplotypes. J Med Genet. 2010;47:651–8.
Natesan S, Bladon A, Coskun S, Qubbaj W, Prates R, Munne S, et al. Genome-wide karyomapping accurately identifies the inheritance of single-gene defects in human preimplantation embryos in vitro. Genet Med. 2014;16:838–45.
Griffin D, Gould R. What is Karyomapping and where does it fit in the world of preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD)? Med Res Arch. 2017;5(6):1–18.
Cuman C, Beyer CE, Brodie D, Fullston T, Lin JI, Willats E, et al. Defining the limits of detection for chromosome rearrangements in the preimplantation embryo using next generation sequencing. Hum Reprod. 2018;33(8):1566–76.
A technical guide to Karyomapping – phasing single gene defects. Illumina; 2015.
Infinium Karyomapping Assay Protocol Guide. 2015.
Kuliev A, Verlinsky O, Rechitsky S. Safety, accuracy and reproductive outcome of preimplantation genetic diagnosis. J IVF Reprod Med Genet. 2013;1:116.
Natesan S, Handyside A, Thornhill C, Ottolini K, Sage M, Summers M, et al. Live birth after PGD with confirmation by a comprehensive approach (Karyomapping) for simultaneous detection of monogenic and chromosomal disorders. Reprod BioMed Online. 2014;29:600–5.
Sarasa J, Wheeler K, Lansdowne L, Raberi A, Babariya D, Wells D. Clinical experience using single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) arrays for preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) of chromosomal translocations. Conferene paper P-658. Hum Reprod. 2015;30:403.
Giménez C, Sarasa J, Arjona C, Vilamajó E, Martínez-Pasarell O, Wheeler K, et al. Karyomapping allows preimplantation genetic diagnosis of a de-novo deletion undetectable using conventional PGD technology. Reprod BioMed Online. 2015;31(6):770–5.
Stock-Myer S, Twomey A, Tang P, Kohfahl A, Martic M. PGD for reciprocal translocation and CNVs using Karyomapping. Australian Society of Diagnostic Genomics Abstract, 2017.
Colls P, Escudero T, Fischer J, Cekleniak NA, Ben-Ozer S, Meyer B, et al. Validation of array comparative genome hybridization for diagnosis of translocations in preimplantation human embryos. Reprod BioMed Online. 2012;24(6):621–9.
Lai H, Chuang T, Wong L, Lee M, Hsieh C, Wang H, et al. Identification of mosaic and segmental aneuploidies by next-generation sequencing in preimplantation genetic screening can improve clinical outcomes compared to array-comparative genomic hybridization. Mol Cytogenet. 2017;10:14.
Vera-Rodriguez M, Michel C, Mercader A, Bladon A, Rodrigo L, Kokocinski F, et al. Distribution patterns of segmental aneuploidies in human blastocysts identified by next-generation sequencing. Fertil Steril. 2016;105(4):1047–55.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the staff at Monash IVF clinic for referring and coordinating the couple and the genetics staff at Monash IVF for their genetic analysis and contributions towards this paper.
Authors’ roles
Claire E Beyer—case study concept and design, data acquisition, study execution, analysis, manuscript drafting, interpretation of data.
Amy Lewis—data acquisition, study execution, analysis, manuscript drafting, interpretation of data.
Elissa Willats—Manuscript drafting, interpretation of data.
Jayne Mullen—Manuscript review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beyer, C.E., Lewis, A., Willats, E. et al. Preimplantation genetic testing using Karyomapping for a paternally inherited reciprocal translocation: a case study. J Assist Reprod Genet 36, 951–963 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-019-01413-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-019-01413-0