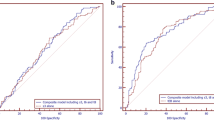
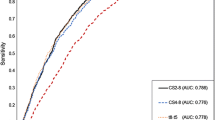
Abstract
Purpose
To demonstrate whether the standard morphokinetic markers used for embryo selection have a similar relationship to blastocyst formation and implantation in two large clinical data sets.
Methods
This is a retrospective cohort analysis striving to answer two distinct questions utilizing data sets from two large IVF clinics. Blastocysts (BL) and implanted blastocysts (I) in both clinics, IVI-Valencia (BL = 11,414, I = 479) and WMC (BL = 15,902; I = 337), were cultured in a time-lapse system (EmbryoScope, Vitrolife, Sweden). The study was designed to assess the relationship between early morphokinetic hallmarks and BL development, with a secondary analysis of implantation rates following single-embryo day 3 and day 5 transfers.
Results
We performed a detailed graphical analysis for t3, t5, duration of the second cell cycle (cc2) (t3-t2), and the ratio (t5-t3)/(t5-t2). The t5 timing was not affected between the clinics. However, Weill Cornell Medicine’s (WCM) proportions were significantly affected by having BL vs. not. A significant decrease of blastocysts with longer t5 in WCM data, while t5 was more informative in the IVI data set for the implantation rate.
Conclusions
Morphokinetic intervals for early cleavages were distributed differently between the clinics. Incorporation of embryo-selection algorithms depends on the individual clinic’s selected developmental hallmarks, all of which must be validated before incorporation into clinical practice.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kupka MS, D’Hooghe T, Ferraretti AP, de Mouzon J, Erb K, Castilla JA, et al. Assisted reproductive technology in Europe, 2011: results generated from European registers by ESHRE. Hum Reprod (Oxford, England). 2016;31(2):233–48.
Ferraretti AP, Goossens V, Kupka M, Bhattacharya S, de Mouzon J, Castilla JA, et al. Assisted reproductive technology in Europe, 2009: results generated from European registers by ESHRE. Hum Reprod (Oxford, England). 2013;28(9):2318–31.
Herrero J, Meseguer M. Selection of high potential embryos using time-lapse imaging: the era of morphokinetics. Fertil Steril. 2013;99(4):1030–4.
Montag M, Toth B, Strowitzki T. New approaches to embryo selection. Reprod BioMed Online. 2013;27(5):539–46.
Basile N, Vime P, Florensa M, Aparicio Ruiz B, Garcia Velasco JA, Remohi J, et al. The use of morphokinetics as a predictor of implantation: a multicentric study to define and validate an algorithm for embryo selection. Hum Reprod (Oxford, England). 2015;30(2):276–83.
Campbell A, Fishel S, Bowman N, Duffy S, Sedler M, Hickman CF. Modelling a risk classification of aneuploidy in human embryos using non-invasive morphokinetics. Reprod BioMed Online. 2013;26(5):477–85.
Coticchio G, Mignini Renzini M, Novara PV, Lain M, De Ponti E, Turchi D, et al. Focused time-lapse analysis reveals novel aspects of human fertilization and suggests new parameters of embryo viability. Human Reprod (Oxford, England). 2018;33(1):23–31.
Zaninovic N, Irani M, Meseguer M. Assessment of embryo morphology and developmental dynamics by time-lapse microscopy: is there a relation to implantation and ploidy? Fertil Steril. 2017;108(5):722–9.
Rubio I, Galan A, Larreategui Z, Ayerdi F, Bellver J, Herrero J, et al. Clinical validation of embryo culture and selection by morphokinetic analysis: a randomized, controlled trial of the EmbryoScope. Fertil Steril. 2014;102(5):1287–94.e5.
Lemmen JG, Agerholm I, Ziebe S. Kinetic markers of human embryo quality using time-lapse recordings of IVF/ICSI-fertilized oocytes. Reprod BioMed Online. 2008;17(3):385–91.
Meseguer M, Rubio I, Cruz M, Basile N, Marcos J, Requena A. Embryo incubation and selection in a time-lapse monitoring system improves pregnancy outcome compared with a standard incubator: a retrospective cohort study. Fertil Steril. 2012;98(6):1481–9.e10.
Meseguer M, Herrero J, Tejera A, Hilligsoe KM, Ramsing NB, Remohi J. The use of morphokinetics as a predictor of embryo implantation. Hum Reprod (Oxford, England). 2011;26(10):2658–71.
Chamayou S, Patrizio P, Storaci G, Tomaselli V, Alecci C, Ragolia C, et al. The use of morphokinetic parameters to select all embryos with full capacity to implant. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2013;30(5):703–10.
Cruz M, Garrido N, Herrero J, Perez-Cano I, Munoz M, Meseguer M. Timing of cell division in human cleavage-stage embryos is linked with blastocyst formation and quality. Reprod BioMed Online. 2012;25(4):371–81.
Dal Canto M, Coticchio G, Mignini Renzini M, De Ponti E, Novara PV, Brambillasca F, et al. Cleavage kinetics analysis of human embryos predicts development to blastocyst and implantation. Reprod BioMed Online. 2012;25(5):474–80.
Kirkegaard K, Kesmodel US, Hindkjaer JJ, Ingerslev HJ. Time-lapse parameters as predictors of blastocyst development and pregnancy outcome in embryos from good prognosis patients: a prospective cohort study. Hum Reprod (Oxford, England). 2013;28(10):2643–51.
Wong CC, Loewke KE, Bossert NL, Behr B, De Jonge CJ, Baer TM, et al. Non-invasive imaging of human embryos before embryonic genome activation predicts development to the blastocyst stage. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(10):1115–21.
Campbell A, Fishel S, Bowman N, Duffy S, Sedler M, Thornton S. Retrospective analysis of outcomes after IVF using an aneuploidy risk model derived from time-lapse imaging without PGS. Reprod BioMed Online. 2013;27(2):140–6.
Chawla M, Fakih M, Shunnar A, Bayram A, Hellani A, Perumal V, et al. Morphokinetic analysis of cleavage stage embryos and its relationship to aneuploidy in a retrospective time-lapse imaging study. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2015;32(1):69–75.
Vera-Rodriguez M, Chavez SL, Rubio C, Reijo Pera RA, Simon C. Prediction model for aneuploidy in early human embryo development revealed by single-cell analysis. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7601.
Liu Y, Chapple V, Feenan K, Roberts P, Matson P. Time-lapse deselection model for human day 3 in vitro fertilization embryos: the combination of qualitative and quantitative measures of embryo growth. Fertil Steril. 2016;105(3):656–62.e1.
Milewski R, Kuc P, Kuczynska A, Stankiewicz B, Lukaszuk K, Kuczynski W. A predictive model for blastocyst formation based on morphokinetic parameters in time-lapse monitoring of embryo development. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2015;32(4):571–9.
Milewski R, Milewska AJ, Kuczynska A, Stankiewicz B, Kuczynski W. Do morphokinetic data sets inform pregnancy potential? J Assist Reprod Genet. 2016;33(3):357–65.
Racowsky C, Kovacs P, Martins WP. A critical appraisal of time-lapse imaging for embryo selection: where are we and where do we need to go? J Assist Reprod Genet. 2015;32(7):1025–30.
Kaser DJ, Racowsky C. Clinical outcomes following selection of human preimplantation embryos with time-lapse monitoring: a systematic review. Hum Reprod Update. 2014;20(5):617–31.
Barrie A, Homburg R, McDowell G, Brown J, Kingsland C, Troup S. Examining the efficacy of six published time-lapse imaging embryo selection algorithms to predict implantation to demonstrate the need for the development of specific, in-house morphokinetic selection algorithms. Fertil Steril. 2017;107(3):613–21.
Barrie A, Taylor E, Schnauffer K, Kingsland C, Troup S. An examination of embryo morphokinetics and utilisation in single step and sequential media systems. Hum Reprod (Oxford, England). 2015;30:282.
Ciray HN, Aksoy T, Goktas C, Ozturk B, Bahceci M. Time-lapse evaluation of human embryo development in single versus sequential culture media--a sibling oocyte study. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2012;29(9):891–900.
Freour T, Dessolle L, Lammers J, Lattes S, Barriere P. Comparison of embryo morphokinetics after in vitro fertilization-intracytoplasmic sperm injection in smoking and nonsmoking women. Fertil Steril. 2013;99(7):1944–50.
Wolff HS, Fredrickson JR, Walker DL, Morbeck DE. Advances in quality control: mouse embryo morphokinetics are sensitive markers of in vitro stress. Hum Reprod (Oxford, England). 2013;28(7):1776–82.
Garrido N, Zuzuarregui JL, Meseguer M, Simon C, Remohi J, Pellicer A. Sperm and oocyte donor selection and management: experience of a 10 year follow-up of more than 2100 candidates. Hum Reprod (Oxford, England). 2002;17(12):3142–8.
Veeck LL, Zaninovic N. An atlas of human blastocysts. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2003. 286 Pages
Motato Y, de los Santos MJ, Escriba MJ, Ruiz BA, Remohi J, Meseguer M. Morphokinetic analysis and embryonic prediction for blastocyst formation through an integrated time-lapse system. Fertil Steril. 2016;105(2):376–84.e9.
The Istanbul consensus workshop on embryo assessment: proceedings of an expert meeting. Hum Reprod (Oxford, England) 2011;26(6):1270–1283.
Cobo A, Meseguer M, Remohi J, Pellicer A. Use of cryo-banked oocytes in an ovum donation programme: a prospective, randomized, controlled, clinical trial. Hum Reprod (Oxford, England). 2010;25(9):2239–46.
Kuwayama M, Vajta G, Kato O, Leibo SP. Highly efficient vitrification method for cryopreservation of human oocytes. Reprod BioMed Online. 2005;11(3):300–8.
Li R, Pedersen KS, Liu Y, Pedersen HS, Laegdsmand M, Rickelt LF, et al. Effect of red light on the development and quality of mammalian embryos. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2014;31(7):795–801.
Petersen BM, Boel M, Montag M, Gardner DK. Development of a generally applicable morphokinetic algorithm capable of predicting the implantation potential of embryos transferred on day 3. Hum Reprod (Oxford, England). 2016;31(10):2231–44.
Pribenszky C, Matyas S, Kovacs P, Losonczi E, Zadori J, Vajta G. Pregnancy achieved by transfer of a single blastocyst selected by time-lapse monitoring. Reprod BioMed Online. 2010;21(4):533–6.
Kirkegaard K, Hindkjaer JJ, Ingerslev HJ. Effect of oxygen concentration on human embryo development evaluated by time-lapse monitoring. Fertil Steril. 2013;99(3):738–44.e4.
Wale PL, Gardner DK. Time-lapse analysis of mouse embryo development in oxygen gradients. Reprod BioMed Online. 2010;21(3):402–10.
Pribenszky C, Nilselid AM, Montag M. Time-lapse culture with morphokinetic embryo selection improves pregnancy and live birth chances and reduces early pregnancy loss: a meta-analysis. Reprod BioMed Online. 2017;35(5):511–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplemental Table 1
(DOCX 17kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaninovic, N., Nohales, M., Zhan, Q. et al. A comparison of morphokinetic markers predicting blastocyst formation and implantation potential from two large clinical data sets. J Assist Reprod Genet 36, 637–646 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-018-1396-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-018-1396-x