Abstract
Background
Even though upper blepharoplasty is one of the most commonly performed procedures in esthetic surgery, there is still no consensus regarding the management of the orbicularis oculi muscle (OOM).
Aim
To compare outcomes of upper eyelid blepharoplasty with or without OOM excision using surface electromyography in a 12 month follow-up.
Methods
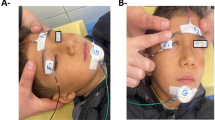
A prospective, randomized, single-blinded comparative split-face study was conducted on 26 patients with dermatochalasis. Skin-only upper blepharoplasty was performed on a randomly selected side, and on the contralateral side, a strip of OOM was resected as well. The functional outcomes were assessed using sEMG, and the esthetics were evaluated independently by the operating surgeon, blinded patients, and three blinded ophthalmic surgeons.
Results
The RMS values of maximal contraction of the OOM were statistically significantly lower two weeks after blepharoplasty than the values before surgery in both groups (p < 0,001) and reached the preoperative values after six months. Lagophthalmos occurred in 2 cases in the skin-muscle group (7.69%), and no incidence of lagophthalmos was observed in the skin group. There were comparable esthetic outcomes on both operated sides.
Conclusions
This study is an objective and quantitative report using surface electromyography on upper blepharoplasty with or without a strip of OOM excision. Our results showed that OOM fully recovers after the stripping procedure. The resection of the skin-OOM flap showed no difference in long-term cosmetic results. Therefore, we recommend OOM preservation during upper blepharoplasty unless muscle excision is well-grounded.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data relevant to the study are included in the article.
References
Friedland JA, Lalonde DH, Rohrich RJ (2010) An evidence-based approach to blepharoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 126(6):2222–2229. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181f949a2
Gradinger GP (1988) Cosmetic upper blepharoplasty. Clin Plast Surg 15(2):289–297
Assumpção EAD’ (1999) Blepharoplasty: a personal tactical approach. Aesthet Plast Surg 23(1):128–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002669900238
Carroll RP, Mahanti RL (1992) En bloc resection in upper eyelid blepharoplasty. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 8(1):47–49. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002341-199203000-00008
Furnas DW (1981) The orbicularis oculi muscle: management in blepharoplasty. Clinic Plast Surg 8(4):687–715
Loeb R (1977) Necessity for partial resection of the orbicularis oculi muscle in blepharoplasties in some young patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 60(2):176–178. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-197708000-00003
Rohrich RJ, Coberly DM, Fagien S, Stuzin JM (2004) Current concepts in aesthetic upper blepharoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 113(3):32e–42e. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000105684.06281.32
Fagien S (2002) Advanced rejuvenative upper blepharoplasty: enhancing aesthetics of the upper periorbita. Plast Reconstr Surg 110(1):278–291. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-200207000-00047
Hoorntje LE, van der Lei B, Stollenwerck GA, Kon M (2010) Resecting orbicularis oculi muscle in upper eyelid blepharoplasty–a review of the literature. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63(5):787–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2009.02.069
Kiang L, Deptula P, Mazhar M, Murariu D, Parsa FD (2014) Muscle-sparing blepharoplasty: a prospective left-right comparative study. Arch Plast Surg 41(05):576–583. https://doi.org/10.5999/aps.2014.41.5.576
Saadat D, Dresner SC (2004) Safety of blepharoplasty in patients with preoperative dry eyes. Arch Facial Plast Surg 6(2):101–104. https://doi.org/10.1001/archfaci.6.2.101
Reaz MBI, Hussain MS, Mohd-Yasin F (2006) Techniques of EMG signal analysis: detection, processing, classification and applications. Biol Proced Online 8(1):11–35. https://doi.org/10.1251/bpo115
Baker TJ (1981) Upper blepharoplasty. Clinic Plast Surg 8(4):635–641
Courtiss EH (1981) Selection of alternatives in esthetic blepharoplasty. Clinic Plast Surg 8(4):739–755
Nemoto Y (2001) Facial nerve anatomy in eyelids and periorbit. Japn J Ophthalmol 45(5):445–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-5155(01)00381-1
DiFrancesco LM, Anjema CM, Codner MA, McCord CD, English J (2005) Evaluation of conventional subciliary incision used in blepharoplasty: preoperative and postoperative videography and electromyography findings. Plast Reconstr Surg 116(2):632–639. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000173446.21513.47
Wong C-H, Mendelson B (2015) Midcheek lift using facial soft-tissue spaces of the midcheek. Plast Reconstr Surg 136(6):1155–1165. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000001826
Krajewska-Węglewicz L, Banach M, Filipiak E, Sempińska-Szewczyk J, Skopiński P, Dorobek M (2022) The Feasibility of surface electromyography in monitoring orbicularis oculi recovery after anterior approach levator aponeurosis advancement. J Clinic Med 11(3):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030731
Mayr-Riedler MS, Broer PN, Hirtler L, Grill C (2023) Sensory innervation of the upper eyelid and its implication for upper eyelid surgery. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0000000000002350
Lessa S, Pontello J, Wanick R, Flores E, Costa W, Sampaio FJ (2019) Histopathological characteristics of the orbicularis oculi muscle after lower blepharoplasty with or without myotomy. Aesthetic Plast Surg 43(3):673–679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-018-01305-1
Putterman AM (1990) Patient satisfaction in oculoplastic surgery. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina 21(1):15–21
Klassen AF, Cano SJ, Grotting JC, Baker SB, Carruthers J, Carruthers A, Van Laeken N, Sykes JM, Schwitzer JA, Pusic AL (2017) FACE-Q eye module for measuring patient-reported outcomes following cosmetic eye treatments. JAMA Facial Plast Surg 19(1):7–14. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamafacial.2016.1018
Damasceno RW, Cariello AJ, Cardoso EB, Viana GA, Osaki MH (2011) Upper blepharoplasty with or without resection of the orbicularis oculi muscle: a randomized double-blind left-right study. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 27(3):195–197. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0b013e318201d659
Flowers RS (1991) Periorbital aesthetic surgery for men: eyelids and related structures. Clinic Plast Surg 18(4):689–729
Fagien S (2010) The role of the orbicularis oculi muscle and the eyelid crease in optimizing results in aesthetic upper blepharoplasty: a new look at the surgical treatment of mild upper eyelid fissure and fold asymmetries. Plast Reconstr Surg 125(2):653–666. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181c87cc6
Dericioğlu V, Şan B, Sevik MO, Akkaya Turhan S (2023) Skin-Only Versus Skin-Plus-Orbicularis Resection Blepharoplasty: An Elaborated Analysis of Early- and Long-Term Effects on Corneal Nerves, Meibomian Glands, Dry Eye Parameters, and Eyebrow Position. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0000000000002376
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LKW: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, review and editing; MD: methodology, supervision, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Ethical approval
This study involves human participants and was approved by the Central Clinical Hospital of the Ministry of Interior and Administration Ethics Committee. All participants were treated in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate
Participants gave informed consent to participate in the study before taking part.
Consent for publication
Patients provided informed consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Krajewska-Węglewicz, L., Dorobek, M. The evaluation of the skin-muscle and only-skin upper blepharoplasty featuring surface electromyography: a single-masked, randomized split-face prospective study. Int Ophthalmol 43, 3979–3987 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-023-02801-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-023-02801-3