Abstract
Purpose
To present patients who suffered damage to the inferior oblique muscle branch of the oculomotor nerve during orbital fat decompression.
Methods
This study was a retrospective chart review of all patients who underwent orbital decompression surgery between April 2009 and June 2016 by the authors.
Results
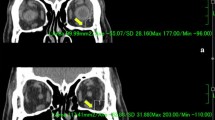
Among 414 sides from 226 consecutive patients who underwent orbital decompression, the inferior oblique muscle branch was injured in two sides (0.5%) of two patients. Both patients showed hypotropia and incyclotropia immediately after surgery. Within 6 months of injury, ocular deviation on primary gaze had mostly resolved after conservative treatment. None of the patients underwent strabismus surgery. Postoperative computed tomographic images demonstrated that the affected branch was indistinct 3–4 mm posterior to the inferior oblique muscle.
Conclusions
This report indicates that injury to the inferior oblique muscle nerve branch can occur at a point posterior to the inferior oblique muscle during orbital fat decompression; however, the resulting ocular deviation improves considerably within 6 months of injury.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben Simon GJ, Wang L, McCann JD, Goldberg RA (2004) Primary-gaze diplopia in patients with thyroid-related orbitopathy undergoing deep lateral orbital decompression with intraconal fat debulking: a retrospective analysis of treatment outcome. Thyroid 14:379–383
Lee KH, Jang SY, Lee SY, Yoon JS (2014) Graded decompression of orbital fat and wall in patients with Graves’ orbitopathy. Korean J Ophthalmol 28:1–11
Serafino M, Fogagnolo P, Trivedi RH, Saunders RA, Nucci P (2010) Torsional diplopia after orbital decompression and strabismus surgery. Eur J Ophthalmol 20:437–441
Garrity JA, Saggau DD, Gorman CA, Bartley GB, Fatourechi V, Hardwiq PW, Dyer JA (1992) Torsional diplopia after tranantral orbital decompression and extraocular muscle surgery associated with Graves’ orbitopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 113:363–373
Tsutsumi S, Nakamura M, Tabuchi T, Yasumoto Y, Ito M (2013) An anatomic study of the inferior oblique nerve with high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Surg Radiol Anat 35:377–383
Richter DF, Stoff A, Olivari N (2007) Transpalpebral decompression of endocrine ophthalmopathy by intraorbital fat removal (Olivari technique): experience and progression after more than 3000 operations over 20 years. Plast Reconstr Surg 120:109–123
Trokel S, Kazim M, Moor S (1993) Orbital fat removal: decompression for Graves orbitopathy. Ophthalmology 100:674–682
O’Malley MR, Meyer DR (2009) Transconjunctival fat removal combined with conservative medial wall/floor orbital decompression for Graves orbitopathy. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 25:206–210
Takahashi Y, Sabundayo MS, Miyazaki H, Mito H, Kakizaki H (2017) Incarceration of the inferior oblique muscle branch of the oculomotor nerve in patients with orbital floor trapdoor fracture. Graefe Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 255:2059–2065
Takahashi Y, Kakizaki H, Kohjima K, Nakano T, Asamoto K, Ichinose A, Iwaki M (2013) Inferior oblique muscle origin: horizontal location in relation to ala nasi and its gender difference. Ann Plast Surg 70:88–90
Sabundayo MS, Kakizaki H, Takahashi Y (2018) Normative measurements of inferior oblique muscle thickness in Japanese by magnetic resonance imaging using a new technique. Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-017-3871-y
Takahashi Y, Kitaguchi Y, Sabundayo MS, Kakizaki H (2017) Orbital fat volume in the inferolateral quadrant in Japanese: a guide for orbital fat decompression without injury to the oculomotor nerve. Int Ophthalmol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0756-3
Acknowledgements
Meeting Presentation Part of this study was presented at the 41th Orbital Society Meeting, Brisbane, September 2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicting interests related to this manuscript.
Human Participants and/or Animals; Informed consent
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of our institution (2016-H273) and adhered to the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki tenets. The IRB granted a waiver of informed consent for this study based on the ethical guidelines for medical and health research involving human subjects established by the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology and by the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare. The waiver was granted since the study was a retrospective chart review, not an interventional study, and it would be difficult to obtain consent from patients who had been treated several years prior. Nevertheless, at the request of the IRB, we published an outline of the study, available for public viewing, on the Aichi Medical University website. This also provided patients the opportunity to decline participation; however, none of the patients declined to participate. Personal identifiers were removed from the records prior to data analysis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, Y., Kakizaki, H. Damage to the inferior oblique muscle branch of the oculomotor nerve: a complication during orbital fat decompression. Int Ophthalmol 39, 711–716 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-018-0856-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-018-0856-8