Abstract
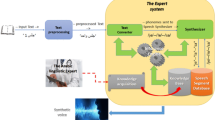
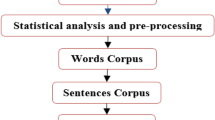
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has many applications such as Speech recognition, Speech understanding, and Speech synthesis. Several approaches have been proposed in the literature in dealing with NLP. This paper describes an ongoing research project that tackles Speech Arabic Synthesis using multi-agent system techniques. The system consists of five modules (agents): the User Interface Agent (UIA), the Facilitator Agent (FA), the Preprocessing Agent (PPA), the Orthographic and Phonetic Transcription Agent, and the Speech Generation Agent. These agents are communicating with each other to construct agent sub societies representing the user input. All the agents are cognitive, work together, and communicate with the Knowledge-Base and the Sound Segments Database to generate Arabic speech signals. We used 800 Arabic sentences and asked 10 listeners with different levels of knowledge of the Arab language to accomplish the evaluation perception process. The system presents in general a Success Rate of 86% for the set of 800 tested sentences.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelkefi, M. (2016). Conversational agent for mobile learning: A review and a proposalof a Multilanguage text-to-speech agent, “MobiSpeech.”. In IEEE tenth international conferenceon research challenges in information science (RCIS). https://doi.org/10.1109/rcis.2016.7549294
Aloulou, C. H. (2002). MASPAR: A multi-agent system forparsing Arabic. In IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics. https://doi.org/10.1109/icsmc.2002.1175732
Boersma, P. (2013). PRAAT: Doing phonetics by computer. University of Amsterdam. Phonetic Sciences. Retrieved from http://www.praat.org/
Boulid, Y. S. (2016). Segmentation approach of Arabic manuscripts textlines based on multi-agent systems. International Journal of Computer Information Systems and Industrial Management Applications, 8, 173–183.
Dragicevic, P. (2004). From A model of interaction in input for interactive systems multi-devices highly configurable. A PhD thesis, The University of Nantes, The National College of Industrial.
Eide, E. A. (2004). A corpus-based approach to expressive speech synthesis. In 5th ISCA Speech Synthesis Workshop, Pittsburgh
Ekpenyong, M. E., & Urua, E.-A. (2013). Agent-based framework for intelligent natural language interface. Telecommunication Systems, 52, 1423–1433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-011-9620-3
Ferber, J. (1999). Multi-agent systems: An introduction to distributed artificial intelligence. Addison-Wesley Longman.
Gouiouez, M. (2018). Multi-agent system for Arabic text categorization. Lecture notes in networks and systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74500-8_15
Halabi, N. (2016). Modern standard Arabic phonetics for speech synthesis. Ph.D Thesis, University of Southampton.
Hemalatha, S. (2017). Unsupervised segmentation of remote sensing images using FD based texture analysis model and ISODATA. International Journal of Ambient Computing and Intelligence, 8(3), 58–75. https://doi.org/10.4018/ijaci.2017070104
Karima, A. Z. (2005). Arabic text categorization: A comparative study of different representation modes. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 38, 1–5.
Khosravy, M. G. (2017). Brain action inspired morphological image enhancement. Modeling and Optimization in Science and Technologies. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-50920-4_15
Maalai, S., & Addou, M. (2011). A new approach of designing Multi-Agent Systems With a practical sample. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications. https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2011.021126
Mahmoud, M. (2017). Using a multi agents system in teaching the Arabic grammar. WSEAS Transactions on Computer Research, 5(20), 147–154.
Mahmoud, M. (2018). A multiagents based intelligent tutoring system for teaching Arabic grammar. International Journal of Education and Learning Systems, 3, 52–59.
Open Agent Architecture (OAA). (n.d.). Retrieved from Developer’s Guide, Version 2.3.2. http://www.ai.sri.com/~oaa
Oprea, M. (2004). Applications of multi-agent systems. In R. Reis (Ed.), Information technology. IFIP International Federation for Information Processing (Vol. 157). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-8159-6_9
Pavon, J. G.-S. (2004). Methodologies for developing multi-agent systems. Journal of Universal Computer Science, 10(4), 359–374.
Ricordel, P. A. (2002). Volcano, a vowels oriented multi-agent platform. In B. Dunin-Keplicz & E. Nawarecki (Eds.), From theory to practice in multi-agent systems. Lecture notes in computer science (Vol. 2296, pp. 253–262). Springer.
Taha, M., Helmy, A., & Alez, R. (2007). Multi-agent based arabic speechrecognition. In IEEE/WIC/ACM international conferences on web intelligence and intelligent agenttechnology—workshops, Silicon Valley, CA (pp. 433–436).
Tebbi, H., Hamadouche, M., & Azzoune, H. (2018a). A new hybrid approach for speech synthesis: Application to the Arabic language. International Journal of Speech Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-9499-4
Tebbi, H., Hamadouche, M., & Azzoune, H. (2018b). An Arabic expert system for voice synthesis. Expert Systems. https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12284
Weiss, G., Braubach, L., & Giorgini, P. (2010). Intelligent agents. In H. Bidgoli (Ed.), The handbook of technology management (Vol. 3, pp. 360–372). Wiley.
Zouaoui, S., & Rezeg, K. (2019). Ontological approach based on multi-agent system for indexing and filtering arabic documents. Journal of Digital Information Management, 17(3), 145–163. https://doi.org/10.6025/jdim/2019/17/3/145-163
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tebbi, H., Hamadouche, M. Multi-agent based Arabic speech synthesis. Int J Speech Technol (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-022-09975-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-022-09975-8