Abstract
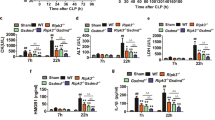
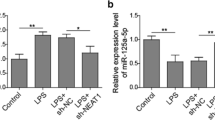
Sepsis is a fetal immunological disorder and its complication worsens in the patients with hemodialysis which may increase the risk of death. In the present study, we aimed to investigate the effect of homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 3 (HIPK3) on inflammatory factors and oxidative stress markers in monocytes of rats with sepsis by regulating the c-Jun amino-terminal kinase (JNK)/c-Jun signaling pathway. A rat model of sepsis was initially established using cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) and was further identified by enlarged spleen tissues, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Monocytes were isolated from rats with CLP-induced sepsis. HIPK3 was observed to be downregulated while JUN was upregulated in monocytes from rats with CLP-induced sepsis. Furthermore, isolated monocytes were transduced with lentiviral vectors expressing HIPK3 or shRNA against HIPK3 to explore the effect of HIPK3 on viability and apoptosis of monocytes as well as inflammatory factors and oxidative stress markers. The obtained data exhibited that overexpression of HIPK3 or inhibition of the JNK signaling pathway enhanced proliferation, reduced apoptosis of monocytes, alleviated inflammation, and oxidative stress injury. Consistently, our results may provide evidence that HIPK3 could inhibit the JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway, thereby potentially retarding the progression of sepsis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated/analyzed during the current study are available.
References
Winters, B.D., M. Eberlein, J. Leung, D.M. Needham, P.J. Pronovost, and J.E. Sevransky. 2010. Long-term mortality and quality of life in sepsis: a systematic review. Critical Care Medicine 38 (5): 1276–1283.
Hotchkiss, R.S., G. Monneret, and D. Payen. 2013. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: from cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy. Nature Reviews Immunology 13 (12): 862–874.
Galley, H.F. 2011. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis. British Journal of Anaesthesia 107 (1): 57–64.
Rhodes, A., L.E. Evans, W. Alhazzani, M.M. Levy, M. Antonelli, R. Ferrer, A. Kumar, J.E. Sevransky, C.L. Sprung, M.E. Nunnally, B. Rochwerg, G.D. Rubenfeld, D.C. Angus, D. Annane, R.J. Beale, G.J. Bellinghan, G.R. Bernard, J.D. Chiche, C. Coopersmith, D.P. De Backer, C.J. French, S. Fujishima, H. Gerlach, J.L. Hidalgo, S.M. Hollenberg, A.E. Jones, D.R. Karnad, R.M. Kleinpell, Y. Koh, T.C. Lisboa, F.R. Machado, J.J. Marini, J.C. Marshall, J.E. Mazuski, L.A. McIntyre, A.S. McLean, S. Mehta, R.P. Moreno, J. Myburgh, P. Navalesi, O. Nishida, T.M. Osborn, A. Perner, C.M. Plunkett, M. Ranieri, C.A. Schorr, M.A. Seckel, C.W. Seymour, L. Shieh, K.A. Shukri, S.Q. Simpson, M. Singer, B.T. Thompson, S.R. Townsend, T. Van der Poll, J.L. Vincent, W.J. Wiersinga, J.L. Zimmerman, and R.P. Dellinger. 2017. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016. Intensive Care Medicine 43 (3): 304–377.
Cecconi, M., L. Evans, M. Levy, and A. Rhodes. 2018. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet 392 (10141): 75–87.
Shalova, I.N., J.Y. Lim, M. Chittezhath, A.S. Zinkernagel, F. Beasley, E. Hernandez-Jimenez, V. Toledano, C. Cubillos-Zapata, A. Rapisarda, J. Chen, K. Duan, H. Yang, M. Poidinger, G. Melillo, V. Nizet, F. Arnalich, E. Lopez-Collazo, and S.K. Biswas. 2015. Human monocytes undergo functional re-programming during sepsis mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Immunity 42 (3): 484–498.
Mukherjee, R., P. Kanti Barman, P. Kumar Thatoi, R. Tripathy, B. Kumar Das, and B. Ravindran. 2015. Non-Classical monocytes display inflammatory features: Validation in Sepsis and Systemic Lupus Erythematous. Scientific Reports 5: 13886.
Chen, J., and E.M. Verheyen. 2012. Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase regulates Yorkie activity to promote tissue growth. Current Biology 22 (17): 1582–1586.
Blaquiere, J.A., and E.M. Verheyen. 2017. Homeodomain-Interacting Protein Kinases: Diverse and Complex Roles in Development and Disease. Current Topics in Developmental Biology 123: 73–103.
Jiang, Z., L. Bo, Y. Meng, C. Wang, T. Chen, C. Wang, X. Yu, and X. Deng. 2018. Overexpression of homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 2 (HIPK2) attenuates sepsis-mediated liver injury by restoring autophagy. Cell Death & Disease 9 (9): 847.
He, Q., J. Shi, H. Sun, J. An, Y. Huang, and M.S. Sheikh. 2010. Characterization of Human Homeodomain-interacting Protein Kinase 4 (HIPK4) as a Unique Member of the HIPK Family. Molecular and Cellular Pharmacology 2 (2): 61–68.
Arai, S., A. Matsushita, K. Du, K. Yagi, Y. Okazaki, and R. Kurokawa. 2007. Novel homeodomain-interacting protein kinase family member, HIPK4, phosphorylates human p53 at serine 9. FEBS Letters 581 (29): 5649–5657.
Blaquiere, J.A., K.K.L. Wong, S.D. Kinsey, J. Wu, and E.M. Verheyen. 2018. Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase promotes tumorigenesis and metastatic cell behavior. Disease Models & Mechanisms 11 (1).
Chen, C.L., C.F. Lin, W.T. Chang, W.C. Huang, C.F. Teng, and Y.S. Lin. 2008. Ceramide induces p38 MAPK and JNK activation through a mechanism involving a thioredoxin-interacting protein-mediated pathway. Blood 111 (8): 4365–4374.
Sawai, M., Y. Ishikawa, A. Ota, and H. Sakurai. 2013. The proto-oncogene JUN is a target of the heat shock transcription factor HSF1. The FEBS Journal 280 (24): 6672–6680.
Brandt, B., E.F. Abou-Eladab, M. Tiedge, and H. Walzel. 2010. Role of the JNK/c-Jun/AP-1 signaling pathway in galectin-1-induced T-cell death. Cell Death & Disease 1: e23.
Nemeth, K., A. Leelahavanichkul, P.S. Yuen, B. Mayer, A. Parmelee, K. Doi, P.G. Robey, K. Leelahavanichkul, B.H. Koller, J.M. Brown, X. Hu, I. Jelinek, R.A. Star, and E. Mezey. 2009. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via prostaglandin E(2)-dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to increase their interleukin-10 production. Nature Medicine 15 (1): 42–49.
Kezic, J.M., and P.G. McMenamin. 2013. The effects of CX3CR1 deficiency and irradiation on the homing of monocyte-derived cell populations in the mouse eye. PLoS One 8 (7): e68570.
Kim, D., and J.Y. Kim. 2014. Anti-CD14 antibody reduces LPS responsiveness via TLR4 internalization in human monocytes. Molecular Immunology 57 (2): 210–215.
Pierrakos, C., and J.L. Vincent. 2010. Sepsis biomarkers: a review. Critical Care 14 (1): R15.
Guerra, F.M., J.L. Gommerman, S.A. Corfe, C.J. Paige, and R. Rottapel. 2012. Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase (HIPK)-1 is required for splenic B cell homeostasis and optimal T-independent type 2 humoral response. PLoS One 7 (4): e35533.
Lan, H.C., H.J. Li, G. Lin, P.Y. Lai, and B.C. Chung. 2007. Cyclic AMP stimulates SF-1-dependent CYP11A1 expression through homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 3-mediated Jun N-terminal kinase and c-Jun phosphorylation. Molecular and Cellular Biology 27 (6): 2027–2036.
Lan, H.C., C.F. Wu, H.M. Shih, and B.C. Chung. 2012. Death-associated protein 6 (Daxx) mediates cAMP-dependent stimulation of Cyp11a1 (P450scc) transcription. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 287 (8): 5910–5916.
Pizzino, G., A. Bitto, G. Pallio, N. Irrera, F. Galfo, M. Interdonato, A. Mecchio, F. De Luca, L. Minutoli, F. Squadrito, and D. Altavilla. 2015. Blockade of the JNK signalling as a rational therapeutic approach to modulate the early and late steps of the inflammatory cascade in polymicrobial sepsis. Mediators of Inflammation 2015: 591572.
Venet, F., and G. Monneret. 2018. Advances in the understanding and treatment of sepsis-induced immunosuppression. Nature Reviews. Nephrology 14 (2): 121–137.
Pelekanou, A., I. Tsangaris, A. Kotsaki, V. Karagianni, H. Giamarellou, A. Armaganidis, and E.J. Giamarellos-Bourboulis. 2009. Decrease of CD4-lymphocytes and apoptosis of CD14-monocytes are characteristic alterations in sepsis caused by ventilator-associated pneumonia: results from an observational study. Critical Care 13 (6): R172.
Hotchkiss, R.S., and S. Opal. 2010. Immunotherapy for sepsis--a new approach against an ancient foe. The New England Journal of Medicine 363 (1): 87–89.
Zhang, Y., Y. Zhou, J. Lou, J. Li, L. Bo, K. Zhu, X. Wan, X. Deng, and Z. Cai. 2010. PD-L1 blockade improves survival in experimental sepsis by inhibiting lymphocyte apoptosis and reversing monocyte dysfunction. Critical Care 14 (6): R220.
Shan, K., C. Liu, B.H. Liu, X. Chen, R. Dong, X. Liu, Y.Y. Zhang, B. Liu, S.J. Zhang, J.J. Wang, S.H. Zhang, J.H. Wu, C. Zhao, and B. Yan. 2017. Circular Noncoding RNA HIPK3 Mediates Retinal Vascular Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 136 (17): 1629–1642.
Lee, S.H., S.W. Park, C.W. Pyo, N.K. Yoo, J. Kim, and S.Y. Choi. 2009. Requirement of the JNK-associated Bcl-2 pathway for human lactoferrin-induced apoptosis in the Jurkat leukemia T cell line. Biochimie 91 (1): 102–108.
Neisch, A.L., O. Speck, B. Stronach, and R.G. Fehon. 2010. Rho1 regulates apoptosis via activation of the JNK signaling pathway at the plasma membrane. The Journal of Cell Biology 189 (2): 311–323.
Wang, H.Q., B.Q. Liu, Y.Y. Gao, X. Meng, Y. Guan, H.Y. Zhang, and Z.X. Du. 2009. Inhibition of the JNK signalling pathway enhances proteasome inhibitor-induced apoptosis of kidney cancer cells by suppression of BAG3 expression. British Journal of Pharmacology 158 (5): 1405–1412.
Said, E.A., F.P. Dupuy, L. Trautmann, Y. Zhang, Y. Shi, M. El-Far, B.J. Hill, A. Noto, P. Ancuta, Y. Peretz, S.G. Fonseca, J. Van Grevenynghe, M.R. Boulassel, J. Bruneau, N.H. Shoukry, J.P. Routy, D.C. Douek, E.K. Haddad, and R.P. Sekaly. 2010. Programmed death-1-induced interleukin-10 production by monocytes impairs CD4+ T cell activation during HIV infection. Nature Medicine 16 (4): 452–459.
Urbahn, M.A., S.C. Kaup, F. Reusswig, I. Kruger, M. Spelleken, K. Jurk, M. Klier, P.A. Lang, and M. Elvers. 2018. Phospholipase D1 regulation of TNF-alpha protects against responses to LPS. Scientific Reports 8 (1): 10006.
Li, R., J. Shang, W. Zhou, L. Jiang, D. Xie, and G. Tu. 2018. Overexpression of HIPK2 attenuates spinal cord injury in rats by modulating apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 103: 127–134.
Shen, J., T. Yang, Y. Xu, Y. Luo, X. Zhong, L. Shi, T. Hu, T. Guo, Y. Nie, F. Luo, and Q. Lin. 2018. delta-Tocotrienol, Isolated from Rice Bran, Exerts an Anti-Inflammatory Effect via MAPKs and PPARs Signaling Pathways in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Macrophages. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19 (10).
Tao, J., Y. Wei, and T. Hu. 2016. Flavonoids of Polygonum hydropiper L. attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury via suppressing phosphorylation in MAPKs pathways. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 16: 25.
Kenzel, S., G. Mancuso, R. Malley, G. Teti, D.T. Golenbock, and P. Henneke. 2006. c-Jun kinase is a critical signaling molecule in a neonatal model of group B streptococcal sepsis. Journal of Immunology 176 (5): 3181–3188.
Miksa, M., D. Amin, R. Wu, A. Jacob, M. Zhou, W. Dong, W.L. Yang, T.S. Ravikumar, and P. Wang. 2008. Maturation-induced down-regulation of MFG-E8 impairs apoptotic cell clearance and enhances endotoxin response. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 22 (6): 743–748.
Saito, C., J.J. Lemasters, and H. Jaeschke. 2010. c-Jun N-terminal kinase modulates oxidant stress and peroxynitrite formation independent of inducible nitric oxide synthase in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 246 (1–2): 8–17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ben Liu, QiuyueHou, Yuhong Ma, and Xuehua Han wrote the paper and conceived and designed the experiments; Ben Liu, Xuehua Han, and QiuyueHou analyzed the data; Ben Liu and Yuhong Ma collected the data for this study. All the authors have read and approved the final submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal experiments were conducted under the approval of the Animal Ethics Committee of Huai’an Hospital Affiliated of Xuzhou Medical University. The experimental procedures were performed in compliance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the US National Institutes of Health.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Hou, Q., Ma, Y. et al. HIPK3 Mediates Inflammatory Cytokines and Oxidative Stress Markers in Monocytes in a Rat Model of Sepsis Through the JNK/c-Jun Signaling Pathway. Inflammation 43, 1127–1142 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01200-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01200-5