Abstract
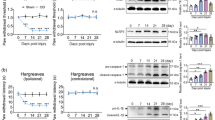
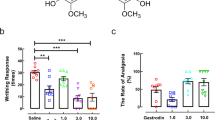
The nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat protein 3 (NLRP3), an intracellular signaling molecule that senses many environmental- and pathogen/host-derived factors, has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several diseases associated with inflammation. It has been suggested that NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitors may have a therapeutic potential in the treatment of NLRP3-related inflammatory diseases. The aim of this study was to determine whether inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome prevents inflammatory hyperalgesia induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in mice as well as changes in expression/activity of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), caspase-1/11, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (NOX), and endothelial/neuronal/inducible nitric oxide synthase (eNOS/nNOS/iNOS) that may regulate NLRP3/apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain (ASC)/pro-caspase-1 inflammasome formation and activity by using a selective NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor, MCC950. Male mice received saline (10 ml/kg; i.p.), LPS (10 mg/kg; i.p.), and/or MCC950 (3 mg/kg; i.p.). Reaction time to thermal stimuli within 1 min was evaluated after 6 h. The mice were killed and the brains, hearts, and lungs were collected for measurement of NF-κB, caspase-1, caspase-11, NLRP3, ASC, NOX subunits (gp91phox; NOX2), and p47phox; NOXO2), nitrotyrosine, eNOS, nNOS, iNOS, and β-actin protein expression, NOS activity, and interleukin (IL)-1β levels. LPS-induced hyperalgesia was associated with a decrease in eNOS, nNOS, and iNOS protein expression and activity as well as an increase in expression of NF-κB p65, caspase-1 p20, caspase-11 p20, NLRP3, ASC, gp91phox, p47phox, and nitrotyrosine proteins in addition to elevated IL-1β levels. The LPS-induced changes were prevented by MCC950. The results suggest that inhibition of NLRP3/ASC/pro-caspase-1 inflammasome formation and activity prevents inflammatory hyperalgesia induced by LPS in mice as well as changes in NF-κB, caspase-11, NOX2, NOXO2, and eNOS/nNOS/iNOS expression/activity.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hwang, S.H., A.T. Wecksler, K. Wagner, and B.D. Hammock. 2013. Rationally designed multitarget agents against inflammation and pain. Current Medicinal Chemistry 20: 1783–1799.
Lei, Y., K. Wang, L. Deng, Y. Chen, E.C. Nice, and C. Huang. 2015. Redox regulation of inflammation: old elements, a new story. Medicinal Research Reviews 35: 306–340.
Turner, M.D., B. Nedjai, T. Hurst, and D.J. Pennington. 2014. Cytokines and chemokines: at the crossroads of cell signalling and inflammatory disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1843: 2563–2582.
Brandes, R.P., N. Weissmann, and K. Schröder. 2014. Nox family NADPH oxidases: molecular mechanisms of activation. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 76: 208–226.
Fujikawa, M., T. Ibukia, K. Matsumurab, and T. Sawaa. 2012. Inflammatory hyperalgesia: the role of the prostaglandin system in the spinal cord. Advences in Neuroimmune Biology 3: 197–207.
Shahabi, P., G. Siest, U.A. Meyer, and S. Visvikis-Siest. 2014. Human cytochrome P450 epoxygenases: variability in expression and role in inflammation-related disorders. Pharmacology and Therapeutics 144: 134–161.
Teixeira, G., C. Szyndralewiez, S. Molango, S. Carnesecchi, F. Heitz, P. Wiesel, and J.M. Wood. 2016. Therapeutic potential of NOX1/4 inhibitors. British Journal of Pharmacology.
Verri, W.A., T.M. Cunha, C.A. Parada, S. Poole, F.Q. Cunha, and S.H. Ferreira. 2006. Hypernociceptive role of cytokines and chemokines: targets for analgesic drug development? Pharmacology and Therapeutics 112(2006): 116–138.
Tunctan, B., B. Korkmaz, A.N. Sari, M. Kacan, D. Unsal, M.S. Serin, C.K. Buharalioglu, S. Sahan-Firat, W.H. Schunck, J.R. Falck, and K.U. Malik. 2012. A novel treatment strategy for sepsis and septic shock based on the interactions between prostanoids, nitric oxide, and 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid. Anti-inflammatory and Anti-allergy Agents in Medicinal Chemistry 11: 121–150.
Barrot, M. 2012. Tests and models of nociception and pain in rodents. Neuroscience 211: 39–50.
Cahill, C.M., A. Dray, and T.J. Coderre. 1998. Priming enhances endotoxin-induced thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia in rats. Brain Research 808: 13–22.
Calil, I.L., A.C. Zarpelon, A.T. Guerrero, J.C. Alves-Filho, S.H. Ferreira, F.Q. Cunha, T.M. Cunha, and W.A. Verri. 2014. Lipopolysaccharide induces inflammatory hyperalgesia triggering a TLR4/MyD88-dependent cytokine cascade in the mice paw. PLoS ONE 9: e90013.
Kamei, J., Y. Iwamoto, T. Suzuki, M. Misawa, Y. Kasuya, H. Nagase, T. Okutomi, G. Soma, and D. Mizuno. 1994. Antinociceptive effect of lipopolysaccharide from Pantoea agglomerans on streptozocosin-induced diabetic mice. European Journal of Pharmacology 251: 95–98.
Kanaan, S.A., N.E. Saade, J.J. Haddad, A.M. Abdelnoor, S.F. Atweh, S.J. Jabbur, and B. Safieh-Garabedian. 1996. Endotoxin-induced local inflammation and hyperalgesia in rats and mice: a new model for inflammatory. Pain 66: 373–379.
Kanaan, S.A., B. Safieh-Garabedian, J.J. Haddad, S.F. Atweh, A.M. Abdelnoor, S.J. Jabbur, and N.A. Saade. 1997. Effects of various analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs on endotoxin-induced hyperalgesia in rats and mice. Pharmacology 54: 285–297.
Benson, S., H. Engler, M. Schedlowski, and S. Elsenbruch. 2012. Experimental endotoxemia as a model to study neuroimmune mechanisms in human visceral pain. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1262: 108–117.
Hori, T., T. Oka, M. Hosoi, M. Abe, and K. Oka. 2000. Hypothalamic mechanisms of pain modulatory actions of cytokines and prostaglandin E2. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 917: 106–120.
Meirer, K., D. Steinhilber, and E. Proschak. 2014. Inhibitors of the arachidonic acid cascade: interfering with multiple pathways. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology 114: 83–91.
Petho, G., and P.W. Reeh. 2012. Sensory and signaling mechanisms of bradykinin, eicosanoids, platelet-activating factor, and nitric oxide in peripheral nociceptors. Physiological Reviews 92: 1699–1775.
Salvemini, D., J.W. Little, T. Doyle, and W.L. Neumann. 2011. Roles of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in pain. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 51: 951–966.
Serhan, C.N., S. Yacoubian, and R. Yang. 2008. Anti-inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediators. Annual Review of Pathology 3: 279–312.
Buharalioglu, K., O. Ozbasoglu, B. Korkmaz, T. Cuez, S. Sahan-Firat, A. Yalcin, and B. Tunctan. 2009. Thalidomide potentiates analgesic effect of COX inhibitors on endotoxin-induced hyperalgesia by modulating TNF-α, PGE and NO synthesis in mice. FASEB Journal 23: 742.4.
Kehl, L.J., K.J. Kovacs, and A.A. Larson. 2004. Tolerance develops to the effect of lipopolysaccharides on movement-evoked hyperalgesia when administered chronically by a systemic but not an intrathecal route. Pain 111: 104–115.
Raghavendra, V., J.N. Agrewala, and S.K. Kulkarni. 2000. Melatonin reversal of lipopolysaccharides-induced thermal and behavioral hyperalgesia in mice. European Journal of Pharmacology 395: 15–21.
Romanovsky, A.A., V.A. Kulchitsky, N.V. Akulich, S.V. Koulchitsky, C.T. Simons, D.I. Sessler, and V.N. Gourine. 1996. First and second phases of biphasic fever: two sequential stages of the sickness syndrome? American Journal of Physiology 271: R244–R253.
Saade, N.E., P.G. Abou Jaoude, F.A. Saadeh, S. Hamoui, B. Safieh-Garabedian, S.A. Kanaan, S.F. Atweh, and S.J. Jabbur. 1997. Fos-like immunoreactivity induced by intraplantar injection of endotoxin and its reduction by morphine. Brain Research 769: 57–65.
Safieh-Garabedian, B., S. Poole, J.J. Haddad, C.A. Massaad, S.J. Jabbur, and N.E. Saade. 2002. The role of the sympathetic efferents in endotoxin-induced localized inflammatory hyperalgesia and cytokine upregulation. Neuropharmacology 42: 864–872.
Shavit, Y., E. Cohen, R. Gagin, R. Avitsur, Y. Pollak, G. Chaikin, G. Wolf, and R. Yirmiya. 1998. Effects of prenatal morphine exposure on NK cytotoxicity and responsiveness to LPS in rats. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 59: 835–841.
Talhouk, R.S., N.E. Saade, G. Mouneimne, C.A. Masaad, and B. Safieh-Garabedian. 2004. Growth hormone releasing hormone reverses endotoxin-induced localized inflammatory hyperalgesia without reducing the upregulated cytokines, nerve growth factor and gelatinase activity. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 28: 625–631.
Tunctan, B., E. Ozveren, B. Korkmaz, C.K. Buharalioglu, L. Tamer, U. Degirmenci, and U. Atik. 2006. Nitric oxide reverses endotoxin-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia via inhibition of prostacyclin production in mice. Pharmacological Research 53: 177–192.
Wu, H.E., H.S. Sun, C.W. Cheng, M. Terashvili, and L.F. Tseng. 2006. dextro-Naloxone or levo-naloxone reverses the attenuation of morphine antinociception induced by lipopolysaccharide in the mouse spinal cord via a non-opioid mechanism. European Journal of Neuroscience 24: 2575–2580.
Zhou, M., H. Wang, J. Suolangjiba Kou, and B. Yu. 2008. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg. leaves extract. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 117: 345–350.
de Zoete, M., N.W. Palm, S. Zhu, and R.A. Flavell. 2014. Inflammasomes. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 6: a016287.
Jo, E.K., J.K. Kim, D.M. Shin, and C. Sasakawa. 2016. Molecular mechanisms regulating NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cellular & Molecular Immunology 13: 148–159.
Man, S.M., and T.D. Kanneganti. 2015. Regulation of inflammasome activation. Immunological Reviews 265: 6–21.
Shao, B.Z., Z.Q. Xu, B.Z. Han, D.F. Su, and C. Liu. 2015. NLRP3 inflammasome and its inhibitors: a review. Frontiers in Pharmacology 6: 62.
Shi, F., M. Kouadir, and Y. Yang. 2015. Inflammasome activation in protein misfolding diseases. Life Sciences 135: 9–14.
Butts, B., R.A. Gary, S.B. Dunbar, and J. Butler. 2015. The importance of NLRP3 inflammasome in heart failure. Journal of Cardiac Failure 21: 586–593.
De Nardo, D., C.M. De Nardo, and E. Latz. 2014. New insights into mechanisms controlling the NLRP3 inflammasome and its role in lung disease. American Journal of Pathology 184: 42–54.
Freeman, L.C., and J.P. Ting. 2016. The pathogenic role of the inflammasome in neurodegenerative diseases. Journal of Neurochemistry 136: 29–38.
Hosseinian, N., Y. Cho, R.F. Lockey, and N. Kolliputi. 2015. The role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in pulmonary diseases. Therapeutic Advances in Respiratory Disease 9: 188–197.
Hutton, H.L., J.D. Ooi, S.R. Holdsworth, and A.R. Kitching. 2016. The NLRP3 inflammasome in kidney disease and autoimmunity. Nephrology.
Im, H., and A.J. Ammit. 2015. The NLRP3 inflammasome: role in airway inflammation. Clinical and Experimental Allergy 44: 160–172.
Ozaki, E., M. Campbell, and S.L. Doyle. 2015. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in chronic inflammatory diseases: current perspectives. Journal of Inflammation Research 8: 15–27.
Paramel, G.V., A. Sirsjö, and K. Fransen. 2015. Role of genetic alterations in the NLRP3 and CARD8 genes in health and disease. Mediators of Inflammation 2015: 846782.
Szabo, G., and T. Csak. 2012. Inflammasomes in liver diseases. Journal of Hepatology 57: 642–654.
Tong, Y., Z.H. Ding, F.X. Zhan, L. Cai, X. Yin, J.L. Ling, J.J. Ye, S.Y. Hou, Z. Lu, Z.H. Wang, and J.F. Liu. 2015. The NLRP3 inflammasome and stroke. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 8: 4787–4794.
Wen, H., J.P. Ting, and L.A. O’Neill. 2012. A role for the NLRP3 inflammasome in metabolic diseases-did Warburg miss inflammation? Nature Immunology 13: 352–357.
Coll, R.C., A.A. Robertson, J.J. Chae, S.C. Higgins, R. Munoz-Planillo, M.C. Inserra, I. Vetter, L.S. Dungan, B.G. Monks, A. Stutz, D.E. Croker, M.S. Butler, M. Haneklaus, C.E. Sutton, G. Nunez, E. Latz, D.L. Kastner, K.H. Mills, S.L. Masters, K. Schroder, M.A. Cooper, and L.A. O’Neill. 2015. A small-molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Nature Medicine 21: 248–255.
Tunctan, B., A. Dolunay, S.P. Senol, M. Temiz Resitoglu, D.S. Guden, A.N. Sari, and S. Sahan Firat. 2016. Inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia in mice: contribution of NF-κB, caspase-1/11, ASC, NADPH oxidase, and NOS isoforms. 7th European Congress of Pharmacology (EPHAR2016), Turkey. http://ephar2016.org/post_congress_book.pdf. Accessed 8 Aug 2016.
Turner, R.A. 1965. Analgesics. Screening Methods in Pharmacology. New York: Academic.
Bradford, M.M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry 72: 248–254.
Cuez, T., B. Korkmaz, C.K. Buharalioglu, S. Sahan-Firat, J. Falck, K.U. Malik, and B. Tunctan. 2010. A synthetic analogue of 20-HETE, 5,14-HEDGE, reverses endotoxin-induced hypotension via increased 20-HETE levels associated with decreased iNOS protein expression and vasodilator prostanoid production in rats. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology 106: 378–388.
Tunctan, B., B. Korkmaz, A.N. Sari, M. Kacan, D. Unsal, M.S. Serin, C.K. Buharalioglu, S. Sahan-Firat, T. Cuez, W.H. Schunck, J.R. Falck, and K.U. Malik. 2013. 5,14-HEDGE, a 20-HETE mimetic, reverses hypotension and improves survival in a rodent model of septic shock: contribution of soluble epoxide hydrolase, CYP2C23, MEK1/ERK1/2/IKKβ/IκB-α/NF-κB pathway, and proinflammatory cytokine formation. Prostaglandins and Other Lipid Mediators 102–103: 31–41.
Tunctan, B., B. Korkmaz, A.N. Sari, M. Kacan, D. Unsal, M.S. Serin, C.K. Buharalioglu, S. Sahan-Firat, T. Cuez, W.H. Schunck, V.L. Manthati, J.R. Falck, and K.U. Malik. 2013. Contribution of iNOS/sGC/PKG pathway, COX-2, CYP4A1, and gp91(phox) to the protective effect of 5,14-HEDGE, a 20-HETE mimetic, against vasodilation, hypotension, tachycardia, and inflammation in a rat model of septic shock. Nitric Oxide 33: 18–41.
Guney, H.Z., C.Z. Gorgun, B. Tunctan, O. Uludag, U. Hodoglugil, N. Abacioglu, and H. Zengil. 1998. Circadian-rhythm-dependent effects of L-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester (L-NAME) on morphine-induced analgesia. Chronobiology International 15: 283–289.
de Moura, R.S., A.A. Rios, E.J. Santos, A.B. Nascimento, A. de Castro Resende, M.L. Neto, L.F. de Oliveira, A.C. Ribeiro, and T. Tano. 2004. Role of the NO-cGMP pathway in the systemic antinociceptive effect of clonidine in rats and mice. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 78: 247–253.
Park, Y.H., C.Y. Shin, T.S. Lee, I.H. Huh, and U.D. Sohn. 2000. The role of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 on the hyperalgesia induced by excitatory amino acids in rats. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 52: 431–436.
Blantz, R.C., and K. Munger. 2002. Role of nitric oxide in inflammatory conditions. Nephron 90: 373–378.
Guzik, T.J., R. Korbut, and T.J. Adamek-Guzik. 2003. Nitric oxide and superoxide in inflammation and immune regulation. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 54: 469–487.
Tunctan, B., and S. Altug. 2004. The use of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors in inflammatory diseases: a novel class of anti-inflammatory agents. Current Medicinal Chemistry: Anti-Inflammatory & Anti-Allergy Agents 3: 271–301.
Vanegas, H. 2004. To the descending pain-control system in rats, inflammation-induced primary and secondary hyperalgesia are two different things. Neuroscience Letters 361: 225–228.
Wu, C.C. 2004. Nitric oxide and inflammation. Current Medicinal Chemistry: Anti-Inflammatory & Anti-Allergy Agents 3: 217–222.
Tunctan, B., S. Altug, O. Uludag, and N. Abacioglu. 2000. Time-dependent variations in serum nitrite, 6-keto-prostaglandin F1α and thromboxane B2 levels induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. Biological Rhythm Research 31: 499–513.
Tunctan, B., S. Altug, O. Uludag, B. Demirkay, and N. Abacioglu. 2003. Effects of cyclooxygenase inhibitors on nitric oxide production and survival in a mice model of sepsis. Pharmacological Research 48: 37–48.
Tunctan, B., O. Uludag, S. Altug, and N. Abacioglu. 1998. Effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibition in lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis in mice. Pharmacological Research 38: 405–411.
Ahn, H., J. Kim, E.B. Jeung, and G.S. Lee. 2014. Dimethyl sulfoxide inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Immunobiology 219: 315–322.
Du, R.H., J. Tan, N. Yan, L. Wang, C. Qiao, J.H. Ding, M. Lu, and G. Hu. 2014. Kir6.2 knockout aggravates lipopolysaccharide-induced mouse liver injury via enhancing NLRP3 inflammosome activation. Journal of Gastroenterology 49: 727–736.
Han, J.W., D.W. Shim, W.Y. Shin, K.H. Heo, S.B. Kwak, E.J. Sim, J.H. Jeong, T.B. Kang, and K.H. Lee. 2015. Anti-inflammatory effect of emodin via attenuation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16: 8102–8109.
Kim, S.J., and S.M. Lee. 2013. NLRP3 inflammasome activation in D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver failure: role of heme oxygenase-1. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 65: 997–1004.
Py, B.F., M. Jin, B.N. Desai, A. Penumaka, H. Zhu, M. Kober, A. Dietrich, M.M. Lipinski, T. Henry, D.E. Clapham, and J. Yuan. 2014. Caspase-11 controls interleukin-1β release through degradation of TRPC1. Cell Reports 6: 1122–1128.
Shim, D.W., H.J. Shin, J.W. Han, Y.E. Ji, C.H. Jang, S. Koppula, T.B. Kang, and K.H. Lee. 2015. A novel synthetic derivative of melatonin, 5-hydroxy-2’-isobutyl-streptochlorin (HIS), inhibits inflammatory responses via regulation of TRIF-dependent signaling and inflammasome activation. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 284: 227–235.
Tianzhu, Z., Y. Shihai, and D. Juan. 2014. The effects of morin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by suppressing the lung NLRP3 inflammasome. Inflammation 37: 1976–1983.
Toldo, S., E. Mezzaroma, M.D. McGeough, C.A. Pena, C. Marchetti, C. Sonnino, B.W. Van Tassell, F.N. Salloum, N.F. Voelkel, H.M. Hoffman, and A. Abbate. 2015. Independent roles of the priming and the triggering of the NLRP3 inflammasome in the heart. Cardiovascular Research 105: 203–212.
Yoon, S.J., J.Y. Park, S. Choi, J.B. Lee, H. Jung, T.D. Kim, S.R. Yoon, I. Choi, S. Shim, and Y.J. Park. 2015. Ginsenoside Rg3 regulates S-nitrosylation of the NLRP3 inflammasome via suppression of iNOS. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 463: 1184–1189.
Zhang, Y., L. Liu, Y.L. Peng, Y.Z. Liu, T.Y. Wu, X.L. Shen, J.R. Zhou, D.Y. Sun, A.J. Huang, X. Wang, Y.X. Wang, and C.L. Jiang. 2014. Involvement of inflammasome activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced mice depressive-like behaviors. CNS Neuroscience and Therapeutics 20: 119–124.
Hernandez-Cuellar, E., K. Tsuchiya, H. Hara, R. Fang, S. Sakai, I. Kawamura, S. Akira, and M. Mitsuyama. 2012. Cutting edge: nitric oxide inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome. Journal of Immunology 189: 5113–5117.
Mao, K., S. Chen, M. Chen, Y. Ma, Y. Wang, B. Huang, Z. He, Y. Zeng, Y. Hu, S. Sun, J. Li, X. Wu, X. Wang, W. Strober, C. Chen, G. Meng, and B. Sun. 2013. Nitric oxide suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation and protects against LPS-induced septic shock. Cell Research 23: 201–212.
Park, Y.J., S.J. Yoon, H.W. Suh, D.O. Kim, J.R. Park, H. Jung, T.D. Kim, S.R. Yoon, J.K. Min, H.J. Na, S.J. Lee, H.G. Lee, Y.H. Lee, H.B. Lee, and I. Choi. 2013. TXNIP deficiency exacerbates endotoxic shock via the induction of excessive nitric oxide synthesis. PLoS Pathogens 9: e1003646.
Bulua, A.C., A. Simon, R. Maddipati, M. Pelletier, H. Park, K.Y. Kim, M.N. Sack, D.L. Kastner, and R.M. Siegel. 2011. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species promote production of proinflammatory cytokines and are elevated in-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). Journal of Experimental Medicine 208: 519–533.
Liao, P.C., L.K. Chao, J.C. Chou, W.C. Dong, C.N. Lin, C.Y. Lin, A. Chen, S.M. Ka, C.L. Ho, and K.F. Hua. 2013. Lipopolysaccharide/adenosine triphosphate-mediated signal transduction in the regulation of NLRP3 protein expression and caspase-1-mediated interleukin-1β secretion. Inflammation Research 62: 89–96.
Coll, R.C., A. Robertson, M. Butler, M. Cooper, and L.A. O’Neill. 2011. The cytokine release inhibitory drug CRID3 targets ASC oligomerisation in the NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasomes. PLoS ONE 6: e29539.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experiments were carried out according to the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, and the study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Mersin University School of Medicine.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
Financial support was provided by grants from the TUBITAK (SBAG-S215047) and the Mersin University (BAP-2016-1-TP2-1427). The results of this study were included in the Master’s Thesis of Pharm. M.S. Abdurrahman Dolunay.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dolunay, A., Senol, S.P., Temiz-Resitoglu, M. et al. Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Prevents LPS-Induced Inflammatory Hyperalgesia in Mice: Contribution of NF-κB, Caspase-1/11, ASC, NOX, and NOS Isoforms. Inflammation 40, 366–386 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0483-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0483-3