Abstract
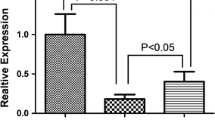
MicroRNA-155 (miR155) has been demonstrated as a central regulator of immune responses induced by inflammatory mediators. Previous studies suggest that miR155 may play adverse effects in various diseases. We hereby explored the roles of miR155 in the pathogenesis of Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were separated from GBS patients and healthy controls. Expression of miR155 in PBMCs was detected by quantitative PCR. An inhibitor of miR155 was transfected into the cultured PBMCs and the GBS-related cytokines were detected. Significantly, our study demonstrated that miR155 was downregulated in PBMCs from GBS patients and silencing of miR155 profoundly promoted the production of Th1-type cytokines in vitro. Our data effectively demonstrate a protective role of miR155 in GBS, which suggests that miR155 may be a promising target for the therapy of the disease.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hughes, R.A., R.D. Hadden, N.A. Gregson, and K.J. Smith. 1999. Pathogenesis of Guillain–Barre syndrome. Journal of Neuroimmunology 100: 74–97.
Nyati, K.K., K.N. Prasad, A. Rizwan, A. Verma, and V.K. Paliwal. 2011. TH1 and TH2 response to Campylobacter jejuni antigen in Guillain–Barre syndrome. Archives of Neurology 68: 445–452.
van Doorn, P.A., L. Ruts, and B.C. Jacobs. 2008. Clinical features, pathogenesis, and treatment of Guillain–Barre syndrome. Lancet Neurology 7: 939–950.
Hughes, R.A., A.V. Swan and P.A. van Doorn. 2010. Intravenous immunoglobulin for Guillain–Barre syndrome. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews CD002063.
van Doorn, P.A., K. Kuitwaard, C. Walgaard, R. van Koningsveld, L. Ruts, and B.C. Jacobs. 2010. IVIG treatment and prognosis in Guillain–Barre syndrome. Journal of Clinical Immunology 30(Suppl 1): S74–S78.
Alshekhlee, A., Z. Hussain, B. Sultan, and B. Katirji. 2008. Guillain–Barre syndrome: incidence and mortality rates in US hospitals. Neurology 70: 1608–1613.
Willison, H.J., and N. Yuki. 2002. Peripheral neuropathies and anti-glycolipid antibodies. Brain 125: 2591–2625.
Hafer-Macko, C.E., K.A. Sheikh, C.Y. Li, T.W. Ho, D.R. Cornblath, G.M. McKhann, A.K. Asbury, and J.W. Griffin. 1996. Immune attack on the Schwann cell surface in acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Annals of Neurology 39: 625–635.
Lee, R.C., R.L. Feinbaum, and V. Ambros. 1993. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75: 843–854.
O'Neill, L.A., F.J. Sheedy, and C.E. McCoy. 2011. MicroRNAs: the fine-tuners of Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature Reviews Immunology 11: 163–175.
Ha, T.Y. 2011. The role of microRNAs in regulatory T cells and in the immune response. Immune Network 11: 11–41.
Tam, W., D. Ben-Yehuda, and W.S. Hayward. 1997. bic, a novel gene activated by proviral insertions in avian leukosis virus-induced lymphomas, is likely to function through its noncoding RNA. Molecular and Cellular Biology 17: 1490–1502.
Thai, T.H., D.P. Calado, S. Casola, K.M. Ansel, C. Xiao, Y. Xue, A. Murphy, D. Frendewey, D. Valenzuela, J.L. Kutok, M. Schmidt-Supprian, N. Rajewsky, G. Yancopoulos, A. Rao, and K. Rajewsky. 2007. Regulation of the germinal center response by microRNA-155. Science 316: 604–608.
Rodriguez, A., E. Vigorito, S. Clare, M.V. Warren, P. Couttet, D.R. Soond, S. van Dongen, R.J. Grocock, P.P. Das, E.A. Miska, D. Vetrie, K. Okkenhaug, A.J. Enright, G. Dougan, M. Turner, and A. Bradley. 2007. Requirement of bic/microRNA-155 for normal immune function. Science 316: 608–611.
Taganov, K.D., M.P. Boldin, K.J. Chang, and D. Baltimore. 2006. NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 103: 12481–12486.
Vigorito, E., K.L. Perks, C. Abreu-Goodger, S. Bunting, Z. Xiang, S. Kohlhaas, P.P. Das, E.A. Miska, A. Rodriguez, A. Bradley, K.G. Smith, C. Rada, A.J. Enright, K.M. Toellner, I.C. Maclennan, and M. Turner. 2007. microRNA-155 regulates the generation of immunoglobulin class-switched plasma cells. Immunity 27: 847–859.
Wang, Y.Z., Q.H. Liang, H. Ramkalawan, Y.L. Wang, Y.F. Yang, W.B. Zhou, F.F. Tian, J. Li, and H. Yang. 2012. Expression of Toll-like receptors 2, 4 and 9 in patients with Guillain–Barre syndrome. Neuroimmunomodulation 19: 60–68.
van der Meche, F.G., and P.I. Schmitz. 1992. A randomized trial comparing intravenous immune globulin and plasma exchange in Guillain–Barre syndrome. Dutch Guillain-Barre Study Group. The New England Journal of Medicine 326: 1123–1129.
O'Connell, R.M., D. Kahn, W.S. Gibson, J.L. Round, R.L. Scholz, A.A. Chaudhuri, M.E. Kahn, D.S. Rao, and D. Baltimore. 2010. MicroRNA-155 promotes autoimmune inflammation by enhancing inflammatory T cell development. Immunity 33: 607–619.
Ray, D., S. Culine, A. Tavitain, and F. Moreau-Gachelin. 1990. The human homologue of the putative proto-oncogene Spi-1: characterization and expression in tumors. Oncogene 5: 663–668.
DeKoter, R.P., J.C. Walsh, and H. Singh. 1998. PU.1 regulates both cytokine-dependent proliferation and differentiation of granulocyte/macrophage progenitors. The EMBO Journal 17: 4456–4468.
Martinez-Nunez, R.T., F. Louafi, P.S. Friedmann, and T. Sanchez-Elsner. 2009. MicroRNA-155 modulates the pathogen binding ability of dendritic cells (DCs) by down-regulation of DC-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3 grabbing non-integrin (DC-SIGN). The Journal of Biological Chemistry 284: 16334–16342.
Ekerfelt, C., C. Dahle, R. Weissert, M. Kvarnstrom, T. Olsson, and J. Ernerudh. 2001. Transfer of myelin-specific cells deviated in vitro towards IL-4 production ameliorates ongoing experimental allergic neuritis. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 123: 112–118.
Bhatheja, K., and J. Field. 2006. Schwann cells: origins and role in axonal maintenance and regeneration. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology 38: 1995–1999.
Bremer, J., T. O'Connor, C. Tiberi, H. Rehrauer, J. Weis, and A. Aguzzi. 2010. Ablation of Dicer from murine Schwann cells increases their proliferation while blocking myelination. PloS One 5: e12450.
Dugas, J.C., T.L. Cuellar, A. Scholze, B. Ason, A. Ibrahim, B. Emery, J.L. Zamanian, L.C. Foo, M.T. McManus, and B.A. Barres. 2010. Dicer1 and miR-219 Are required for normal oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination. Neuron 65: 597–611.
Kominato, Y., D. Galson, W.R. Waterman, A.C. Webb, and P.E. Auron. 1995. Monocyte expression of the human prointerleukin 1 beta gene (IL1B) is dependent on promoter sequences which bind the hematopoietic transcription factor Spi-1/PU.1. Molecular and Cellular Biology 15: 58–68.
Fasanaro, P., S. Greco, M. Ivan, M.C. Capogrossi, and F. Martelli. 2010. microRNA: emerging therapeutic targets in acute ischemic diseases. Pharmacology and Therapeutics 125: 92–104.
Zhu, J., E. Mix, and H. Link. 1998. Cytokine production and the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune neuritis and Guillain–Barre syndrome. Journal of Neuroimmunology 84: 40–52.
Zhu, J., E. Mix, T. Olsson, and H. Link. 1994. Cellular mRNA expression of interferon-gamma, IL-4 and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) by rat mononuclear cells stimulated with peripheral nerve myelin antigens in experimental allergic neuritis. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 98: 306–312.
Kutty, R.K., C.N. Nagineni, W. Samuel, C. Vijayasarathy, J.J. Hooks, and T.M. Redmond. 2010. Inflammatory cytokines regulate microRNA-155 expression in human retinal pigment epithelial cells by activating JAK/STAT pathway. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 402: 390–395.
Ceppi, M., P.M. Pereira, I. Dunand-Sauthier, E. Barras, W. Reith, M.A. Santos, and P. Pierre. 2009. MicroRNA-155 modulates the interleukin-1 signaling pathway in activated human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106: 2735–2740.
Banerjee, A., F. Schambach, C.S. DeJong, S.M. Hammond, and S.L. Reiner. 2010. Micro-RNA-155 inhibits IFN-gamma signaling in CD4+ T cells. European Journal of Immunology 40: 225–231.
Lu, F., A. Weidmer, C.G. Liu, S. Volinia, C.M. Croce, and P.M. Lieberman. 2008. Epstein–Barr virus-induced miR-155 attenuates NF-kappaB signaling and stabilizes latent virus persistence. Journal of Virology 82: 10436–10443.
Wang, Y.Z., Q.H. Liang, H. Ramkalawan, W. Zhang, W.B. Zhou, B. Xiao, F.F. Tian, H. Yang, J. Li, Y. Zhang, and N.A. Xu. 2012. Inactivation of TLR9 by a suppressive oligodeoxynucleotides can ameliorate the clinical signs of EAN. Immunological Investigations 41: 171–182.
Tang, Y., X. Luo, H. Cui, X. Ni, M. Yuan, Y. Guo, X. Huang, H. Zhou, N. de Vries, P.P. Tak, S. Chen, and N. Shen. 2009. MicroRNA-146A contributes to abnormal activation of the type I interferon pathway in human lupus by targeting the key signaling proteins. Arthritis and Rheumatism 60: 1065–1075.
Acknowledgments
We thank Jun-Mei Zhang and Qun Liu for their technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YZ., Feng, XG., Shi, QG. et al. Silencing of miR155 Promotes the Production of Inflammatory Mediators in Guillain–Barré Syndrome In Vitro . Inflammation 36, 337–345 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-012-9551-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-012-9551-5