Abstract
Introduction
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), have been frequently reported to regulate various diseases including hypertension. However, the biological role and regulatory mechanism of miR-20b-5p are unclear in hypertension. The current study aimed to investigate the role of miR-20b-5p in hypertension.
Methods
Bioinformatics analysis (starBase: http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn) and a wide range of experiments including blood pressure detection, morphometric sampling by electron microscopy, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), CCK-8, western blot, luciferase reporter, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and Masson trichrome staining assays were used to explore the function and mechanism of miR-20b-5p in hypertension.
Results
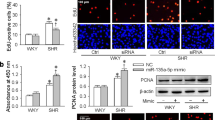
MiR-20b-5p level was significantly upregulated in Spontaneously hypertensive rats’ (SHRs’) thoracic aortic vascular tissues. In function, miR-20b-5p silencing inhibited the proliferation and migration of aortic smooth muscle cells (ASMCs) of SHRs. In mechanism, we predicted 10 potential target mRNAs for miR-20b-5p. After prediction by bioinformatics, MAGI3 was validated to bind with miR-20b-5p. Rescue assays showed that MAGI3 silencing reversed the inhibitive influence of miR-20b-5p depletion on cell proliferation and migration.
Conclusions
MiR-20b-5p contributed to the dysfunction of ASMCs by targeting MAGI3 in hypertension. This new discovery provided a potential novel insight for hypertension treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Bhaskaran M, Mohan M (2014) MicroRNAs: history, biogenesis, and their evolving role in animal development and disease. Vet Pathol 51:759–774. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300985813502820
Dluzen DF et al (2017) MicroRNAs modulate oxidative stress in hypertension through PARP-1. Regul Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:3984280. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3984280
Doroszko A, Janus A, Szahidewicz-Krupska E, Mazur G, Derkacz A (2016) Resistant hypertension. Adv Clin Exp Med 25:173–183. https://doi.org/10.17219/acem/58998
Doyle AE (1991) Hypertension and vascular disease. Am J Hypertens 4:103s–106s. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/4.2.103s
Egan Benova T, Szeiffova Bacova B, Viczenczova C, Diez E, Barancik M, Tribulova N (2016) Protection of cardiac cell-to-cell coupling attenuate myocardial remodeling and proarrhythmia induced by hypertension. Physiol Res 65(Suppl 1):S29-42. https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.933391
Elliott WJ (2007) Systemic hypertension. Curr Probl Cardiol 32:201–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2007.01.002
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Filipowicz W (2010) Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem 79:351–379. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060308-103103
Fernandes J, Vieira AS, Kramer-Soares JC, Da Silva EA, Lee KS, Lopes-Cendes I, Arida RM (2018) Hippocampal microRNA-mRNA regulatory network is affected by physical exercise. Biochim Biophys Acta 1862:1711–1720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.05.004
Fritschka E, Distler A (1989) Treatment of hypertension in the aged. Fortschr Med 107:662–666
Hao H, Gabbiani G, Bochaton-Piallat ML (2003) Arterial smooth muscle cell heterogeneity: implications for atherosclerosis and restenosis development. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:1510–1520. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.Atv.0000090130.85752.Ed
Hromadnikova I, Kotlabova K, Dvorakova L, Krofta L (2019a) Postpartum profiling of microRNAs involved in pathogenesis of cardiovascular/cerebrovascular diseases in women exposed to pregnancy-related complications. Int J Cardiol 291:158–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.05.036
Hromadnikova I, Kotlabova K, Dvorakova L, Krofta L (2020) Evaluation of vascular endothelial function in young and middle-aged women with respect to a history of pregnancy, pregnancy-related complications, classical cardiovascular risk factors, and epigenetics. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020430
Hromadnikova I, Kotlabova K, Dvorakova L, Krofta L, Sirc J (2019b) Postnatal expression profile of microRNAs associated with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in children at the age of 3 to 11 years in relation to previous occurrence of pregnancy-related complications. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030654
Huang Y (2018) The novel regulatory role of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Mol Med 22:5768–5775. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13866
Iadecola C, Davisson RL (2008) Hypertension and cerebrovascular dysfunction. Cell Metab 7:476–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2008.03.010
Jordan J (2017) Device-based approaches for the treatment of arterial hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 19:59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-017-0755-9
Judd E, Calhoun DA (2014) Apparent and true resistant hypertension: definition, prevalence and outcomes. J Hum Hypertens 28:463–468. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.140
Kabekkodu SP, Shukla V, Varghese VK, D’Souza J, Chakrabarty S, Satyamoorthy K (2018) Clustered miRNAs and their role in biological functions and diseases. Biol Rev 93(4):1955–86
Kriegel AJ, Baker MA, Liu Y, Liu P, Cowley AW Jr, Liang M (2015) Endogenous microRNAs in human microvascular endothelial cells regulate mRNAs encoded by hypertension-related genes. Hypertension (Dallas, TX: 1979) 66:793–799. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.115.05645
Lee SJ, Ritter SL, Zhang H, Shim H, Hall RA, Yun CC (2011) MAGI-3 competes with NHERF-2 to negatively regulate LPA2 receptor signaling in colon cancer cells. Gastroenterology 140:924–934. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2010.11.054
Li D et al (2019) Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes cardiac remodeling in hypertensive rats by inhibiting the transcription of MyoD. Aging 11:8792–8809. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102265
Ma Q et al (2015) MAGI3 suppresses glioma cell proliferation via upregulation of PTEN expression. Biomed Environ Sci 28:502–509. https://doi.org/10.3967/bes2015.072
Nara Y et al (1988) A new approach to the prevention of hypertensive cardiovascular diseases by controlling the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells Journal of hypertension. Supplement 6:S246–S247. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004872-198812040-00074
Qi JC et al (2019) miR-20b-5p, TGFBR2, and E2F1 form a regulatory loop to participate in epithelial to mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer. Front Oncol 9:1535. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.01535
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ (2017) MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16:203–222. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.246
Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR, Soleymani Fard S, Ghaffari SH (2019) An overview of microRNAs: biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell Physiol 234:5451–5465. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27486
Semplicini A, Maresca A, Sartori M, Calò L, Pessina AC (2001) Hypertension and cerebrovascular diseases: a specific role of vascular protection for the prevention of dementia. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 38(Suppl 2):S79-82. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005344-200111002-00019
Shah M, Julu POO, Monro JA, Coutinho J, Ijeh C, Puri BK (2018) Neuromuscular taping reduces blood pressure in systemic arterial hypertension. Med Hypotheses 116:30–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2018.04.014
Špinar J, Vítovec J, Špinarová L, Bendová M (2015) Combination treatment of hypertension in 2015. Vnitr Lek 61:458–465
Tai L, Huang CJ, Choo KB, Cheong SK, Kamarul T (2020) Oxidative stress down-regulates MiR-20b-5p, MiR-106a-5p and E2F1 expression to suppress the G1/S transition of the cell cycle in multipotent stromal cells. Int J Med Sci 17:457–470. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.38832
Tang B, Bao N, He G, Wang J (2019) Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates autophagy via the miR-20b-5p/ATG7 axis in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Gene 686:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.10.059
Villela PB, Klein CH, Oliveira GMM (2018) Cerebrovascular and hypertensive diseases as multiple causes of death in Brazil from 2004 to 2013. Public Health 161:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2018.04.006
Wander PL et al (2020) Short Report: Circulating microRNAs are associated with incident diabetes over 10 years in Japanese Americans. Sci Rep 10:6509. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63606-3
Weng Q et al (2020) Integrated analyses identify miR-34c-3p/MAGI3 axis for the Warburg metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma. FASEB J 34:5420–5434. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201902895R
Xhignesse P, Krzesinski F, Krzesinski JM (2018) Hypertensive crisis. Rev Med Liege 73:326–332
Ying SY, Chang DC, Lin SL (2018) The MicroRNA. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton, NJ) 1733:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7601-0_1
You H, Zhang L, Chen Z, Liu W, Wang H, He H (2019) MiR-20b-5p relieves neuropathic pain by targeting Akt3 in a chronic constriction injury rat model. Synapse (New York, NY) 73:e22125. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.22125
Zhu K et al (2019) Downregulation of circRNA DMNT3B contributes to diabetic retinal vascular dysfunction through targeting miR-20b-5p and BAMBI. EBioMedicine 49:341–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.10.004
Acknowledgements
We appreciate all participators in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
The Ethics Committee of The Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University approved this study. The animal management obtained the approval from the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of The Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, M., Yu, T. MiR-20b-5p contributes to the dysfunction of vascular smooth muscle cells by targeting MAGI3 in hypertension. J Mol Histol 53, 187–197 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10050-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10050-w