Abstract
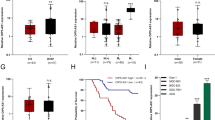
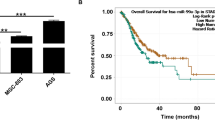
Gastric cancer (GC) remains a major cause of cancer-related deaths. Increasing studies suggest that cancer development is accompanied by the deregulation of circular RNAs. We investigated the function of circ_0003159 in GC. The expression levels of circ_0003159, miR-221-3p/miR-222-3p and leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR) mRNA were measured by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Cell colony formation ability was assessed by colony formation assay, and cell viability was assessed by cell counting kit-8 assay. Cell apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry assay and caspase3 activity. Cell migration and invasion were assessed by transwell assay. Glycolysis energy metabolism was assessed by 5’-triphosphate production, glucose uptake and lactate production. The protein levels of related marker proteins and LIFR were detected by western blot. The relationship between circ_0003159 and miR-221-3p/miR-222-3p, or LIFR and miR-221-3p/miR-222-3p was obtained from bioinformatics tools and verified by dual-luciferase reporter assay. A cancer tumorogenicity xenograft experiment in nude mice was conducted to determine the role of circ_0003159 in tumor growth by AGS cells. Our results showed that circ_0003159 expression was decreased in GC tissues and cells. Circ_0003159 overexpression sequestered GC cell viability, migration, invasion and glycolysis and induced cell apoptosis. MiR-221-3p and miR-222-3p were targets of circ_0003159, and the inhibition of miR-221-3p and miR-222-3p also blocked GC cell viability, migration, invasion and glycolysis and promoted cell apoptosis. LIFR was a common target of miR-221-3p and miR-222-3p. Interestingly, LIFR knockdown reversed the effects of circ_0003159 overexpression on GC cell behaviors. Circ_0003159 increased the expression level of LIFR by targeting miR-221-3p and miR-222-3p. The tumorigenicity assay showed that circ_0003159 overexpression inhibited tumor growth in vivo. In conclusion, circ_0003159 inhibited GC development in vitro and in vivo by enriching the level of LIFR via direct binding to miR-221-3p/miR-222-3p.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi T, Kimoto T (1976) Human cell line (HGC-27) derived from the metastatic lymph node of gastric cancer. Acta Medica Okayama 30(3):215
Ala U (2020) Competing endogenous RNAs, non-coding rnas and diseases: an intertwined story. Cells 9(7):1574
Barranco SC et al (1983) Establishment and characterization of an in vitro model system for human adenocarcinoma of the stomach. Cancer Res 43(4):1703–1709
Bolha L, Ravnik-Glavac M, Glavac D (2017) Circular RNAs: biogenesis, function, and a role as possible cancer biomarkers. Int J Genomics 2017:6218353
Bray F et al (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424
Cervantes A et al (2013) Current questions for the treatment of advanced gastric cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 39(1):60–67
Chen Y, Wang X (2020) miRDB: an online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res 48(D1):D127–D131
Chen D et al (2012) LIFR is a breast cancer metastasis suppressor upstream of the Hippo-YAP pathway and a prognostic marker. Nat Med 18(10):1511–1517
Chipman LB, Pasquinelli AE (2019) miRNA targeting: growing beyond the seed. Trends Genet 35(3):215–222
Dong Y et al (2019) miR-221-3p and miR-15b-5p promote cell proliferation and invasion by targeting Axin2 in liver cancer. Oncol Lett 18(6):6491–6500
Fang J et al (2019) A novel circular RNA, circFAT1(e2), inhibits gastric cancer progression by targeting miR-548g in the cytoplasm and interacting with YBX1 in the nucleus. Cancer Lett 442:222–232
He J et al (2017) Circular RNAs and cancer. Cancer Lett 396:138–144
Hsiao KY, Sun HS, Tsai SJ (2017) Circular RNA - New member of noncoding RNA with novel functions. Exp Biol Med (maywood) 242(11):1136–1141
Ke Y, Ning T, Wang B (1994) Establishment and characterization of a SV40 transformed human fetal gastric epithelial cell line-GES-1. Zhonghua zhong liu za zhi Chin J Oncol 16(1):7
Li JH et al (2014) starBase v20: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D92–D97
Lin S et al (2020) Oncogenic circular RNA Hsa-circ-000684 interacts with microRNA-186 to upregulate ZEB1 in gastric cancer. FASEB J 34(6):8187–8203
Liu B et al (2014) Elevated MiR-222–3p promotes proliferation and invasion of endometrial carcinoma via targeting ERalpha. PLoS ONE 9(1):e87563
Liu L et al (2019) lncRNA GAS5 inhibits cell migration and invasion and promotes autophagy by targeting miR-222-3p via the GAS5/PTEN-signaling pathway in CRC. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 17:644–656
Liu J et al (2020) Circular RNA circ-MAT2B facilitates glycolysis and growth of gastric cancer through regulating the miR-515-5p/HIF-1alpha axis. Cancer Cell Int 20:171
Lopez-Jimenez E, Rojas AM, Andres-Leon E (2018) RNA sequencing and prediction tools for circular RNAs analysis. Adv Exp Med Biol 1087:17–33
Lu J et al (2019) Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001368 suppresses the progression of gastric cancer by regulating miR-6506-5p/FOXO3 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 512(1):29–33
Luo Q et al (2015) LIFR functions as a metastasis suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma by negatively regulating phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway. Carcinogenesis 36(10):1201–1212
McLean MH, El-Omar EM (2014) Genetics of gastric cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(11):664–674
Pereira AL et al (2020) The biological role of sponge circular RNAs in gastric cancer: main players or coadjuvants? Cancers (basel) 12(7):1982
Shao Y et al (2017) Global circular RNA expression profile of human gastric cancer and its clinical significance. Cancer Med 6(6):1173–1180
Shi J et al (2017) MicroRNA-221-3p plays an oncogenic role in gastric carcinoma by inhibiting PTEN expression. Oncol Res 25(4):523–536
Sui W et al (2017) Circular RNA and gene expression profiles in gastric cancer based on microarray chip technology. Oncol Rep 37(3):1804–1814
Sun S, Wang H, Ji M (2019) Overexpression of miR-222-3p promotes the proliferation and inhibits the apoptosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells via suppressing PPP2R2A. Technol Cancer Res Treat 18:1533033819892256
Tian M et al (2018) Reduced expression of circRNA hsa_circ_0003159 in gastric cancer and its clinical significance. J Clin Lab Anal 32(3):e22281
Wang J et al (2020) Hsa_circ_0003159 inhibits gastric cancer progression by regulating miR-223-3p/NDRG1 axis. Cancer Cell Int 20:57
Wu D et al (2019a) Serum biomarker panels for the diagnosis of gastric cancer. Cancer Med 8(4):1576–1583
Wu XG et al (2019b) Cancer-derived exosomal miR-221-3p promotes angiogenesis by targeting THBS2 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Angiogenesis 22(3):397–410
Xu G et al (2020) Circular RNA circNRIP1 sponges microRNA-138-5p to maintain hypoxia-induced resistance to 5-fluorouracil through HIF-1alpha-dependent glucose metabolism in gastric carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res 12:2789–2802
Yuan LW, Yamashita H, Seto Y (2016) Glucose metabolism in gastric cancer: the cutting-edge. World J Gastroenterol 22(6):2046–2059
Zhang J et al (2017a) Circular RNA_LARP4 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by sponging miR-424-5p and regulating LATS1 expression. Mol Cancer 16(1):151
Zhang L et al (2017b) Prognostic value of candidate microRNAs in gastric cancer: a validation study. Cancer Biomark 18(3):221–230
Zhang F et al (2018) miR-589 promotes gastric cancer aggressiveness by a LIFR-PI3K/AKT-c-Jun regulatory feedback loop. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37(1):152
Zhang Y et al (2019) Combined detection of serum MiR-221-3p and MiR-122-5p expression in diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer. J Gastric Cancer 19(3):315–328
Zhao JH et al (2016) A novel long noncoding RNA-LOWEG is low expressed in gastric cancer and acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting cell invasion. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142(3):601–609
Zhou CF et al (2019) Cervical squamous cell carcinoma-secreted exosomal miR-221-3p promotes lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis by targeting VASH1. Oncogene 38(8):1256–1268
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region [Grant No. 2018MS08050]; Baotou Medical College Yang Fan Project [Grant No. BYJJ-YF-2018028].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, L., Yan, B., Jin, G. et al. Circ_0003159 upregulates LIFR expression through competitively binding to miR-221-3p/miR-222-3p to block gastric cancer development. J Mol Histol 53, 173–186 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10044-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10044-8