Abstract
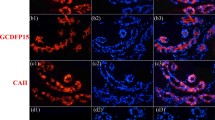
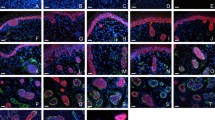
Eccrine sweat gland (ESG) and hair follicle (HF) are different skin appendages but share many common development characteristics. Although the morphology of adult ESG and HF is obviously different, it is difficult to distinguish ESG placodes from HFs placodes morphologically. To study the fate determination of ESG and HF, specific antigen markers for ESG placodes and HF placodes must be found first to distinguish them. In the study, we detected the expression of commonly used keratins 4, 5, 7–10, 12, 14, 15, 17–20, 27 and 73, and the reported ESG and HF specific markers, P-cadherin, Lymphoid enhancer factor 1 (LEF1), LIM Homeobox gene 2 (LHX2), Na+/K+-ATPase (NKA) and Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransporter 1 (NKCC1) in ESG and HF placodes by single-immunofluorescence staining and double-immunofluorescence staining. To further verify the results of immunofluorescence staining, Western blot (WB) was used to detect the differential antigen and some co-expressed antigens of ESG and HF placodes. The results showed that both ESG and HF placodes expressed K4/5/14/1517/18, P-cadherin and LEF1, neither expressed K7/8/9/10/12/19/20/27/73, NKA or NKCC1. HF placodes specifically expressed LHX2. Combination of LHX2 and co-expressed antigen K14, can distinguish ESG placodes from HF placodes. We conclude that LHX2 is a specific marker for HF placodes, and ESG placodes and HF placodes can be distinguished by double immunofluorescence staining of the specific marker LHX2 and the co-expressed markers, such as K4, K5, K14, K15, K17, K18, P-cadherin and LEF1.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn Y (2015) Signaling in tooth, hair, and mammary placodes. Curr Top Dev Biol 111:421–459
Aldea D, Kokalari B, Luckhart C, Aharoni A, Albert PR, Kamberov YG (2019) The Transcription factor deaf1 modulates engrailed-1 expression to regulate skin appendage fate. J Invest Dermatol 139:2378–2381
Buffoli B, Rinaldi F, Labanca M, Sorbellini E, Trink A, Guanziroli E, Rezzani R, Rodella LF (2014) The human hair: from anatomy to physiology. Int J Dermatol 53:331–341
Cao L, Chen L, Li H, Wei Z, Xie S, Zhang M, Lin Y, Huang H (2019) Differential antigen expression between human eccrine sweat glands and hair follicles/pilosebaceous units. J Mol Histol 50:335–342
Cui CY, Yin M, Sima J, Childress V, Michel M, Piao Y, Schlessinger D (2014) Involvement of Wnt, Eda and Shh at defined stages of sweat gland development. Development 141:3752–3760
Fuchs E (2016) Epithelial skin biology: three decades of developmental biology, a hundred questions answered and a thousand new ones to address. Curr Top Dev Biol 116:357–374
Kamberov YG, Guhan SM, DeMarchis A, Jiang J, Wright SS, Morgan BA, Sabeti PC, Tabin CJ, Lieberman DE (2018) Comparative evidence for the independent evolution of hair and sweat gland traits in primates. J Hum Evol 125:99–105
Kim DK, Holbrook KA (1995) The appearance, density, and distribution of Merkel cells in human embryonic and fetal skin: their relation to sweat gland and hair follicle development. J Invest Dermatol 104:411–416
Li H, Li X, Zhang B, Zhang M, Chen W, Tang S, Fu X (2016) Changes in keratins and alpha-smooth muscle actin during three-dimensional reconstitution of eccrine sweat glands. Cell Tissue Res 365:113–122
Lu CP, Polak L, Keyes BE, Fuchs E (2016) Spatiotemporal antagonism in mesenchymal-epithelial signaling in sweat versus hair fate decision. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aah6102
Martel JL, Miao JH, Badri T (2021) Anatomy, Hair Follicle. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL),
Miura K, Akashi T, Ando N, Ayabe S, Kayamori K, Namiki T, Eishi Y (2018) Homeobox transcriptional factor engrailed homeobox 1 is expressed specifically in normal and neoplastic sweat gland cells. Histopathology 72:1199–1208
Moll R, Divo M, Langbein L (2008) The human keratins: biology and pathology. Histochem Cell Biol 129:705–733
Niemann C, Horsley V (2012) Development and homeostasis of the sebaceous gland. Semin Cell Dev Biol 23:928–936
Poblet E, Jimenez F, Ortega F (2004) The contribution of the arrector pili muscle and sebaceous glands to the follicular unit structure. J Am Acad Dermatol 51:217–222
Rhee H, Polak L, Fuchs E (2006) Lhx2 maintains stem cell character in hair follicles. Science 312:1946–1949
Saga K (2002) Structure and function of human sweat glands studied with histochemistry and cytochemistry. Prog Histochem Cytochem 37:323–386
Schneider MR, Schmidt-Ullrich R, Paus R (2009) The hair follicle as a dynamic miniorgan. Curr Biol 19:R132-142
Silva LMA, Hsieh R, Lourenco SV, Valente NYS, Paiva GR, Fernandes JD (2020) Immunostaining study of cytokeratins in human hair follicle development. An Bras Dermatol 95:278–282
Strnad P, Guldiken N, Helenius TO, Misiorek JO, Nystrom JH, Lahdeniemi IA, Silvander JS, Kuscuoglu D, Toivola DM (2016) Simple Epithelial Keratins Methods Enzymol 568:351–388
Tornqvist G, Sandberg A, Hagglund AC, Carlsson L (2010) Cyclic expression of lhx2 regulates hair formation. PLoS Genet 6:e1000904
Tzchori I, Day TF, Carolan PJ, Zhao Y, Wassif CA, Li L, Lewandoski M, Gorivodsky M, Love PE, Porter FD, Westphal H, Yang Y (2009) LIM homeobox transcription factors integrate signaling events that control three-dimensional limb patterning and growth. Development 136:1375–1385
Vaidya MM, Kanojia D (2007) Keratins: markers of cell differentiation or regulators of cell differentiation? J Biosci 32:629–634
Wollina U, Schaarschmidt HH, Hipler C, Knopf B (1989) Distribution of glycoconjugates in human skin appendages. Acta Histochem 87:87–93
Zhang M, Zeng S, Zhang L, Li H, Chen L, Zhang X, Li X, Lin C, Shu S, Xie S, He Y, Mao X, Peng L, Shi L, Yang L, Tang S, Fu X (2014) Localization of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase alpha/beta, Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl-cotransporter 1 and aquaporin-5 in human eccrine sweat glands. Acta Histochem 116:1374–1381
Zhang M, Li H, Xie S, Chen L (2018) Time course of differentiation of different cell types in 3D-reconstructed eccrine sweat glands. J Mol Histol 49:567–575
Acknowledgements
The manuscript was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81772102, 82172231).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare we have no competing financial, personal or other relationships with other people or organizations.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, M., Zhao, J., Du, L. et al. The combination of hair follicle-specific marker LHX2 and co-expressed marker can distinguish between sweat gland placodes and hair placodes in rat. J Mol Histol 52, 1225–1232 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10023-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10023-z