Abstract
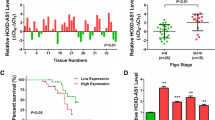
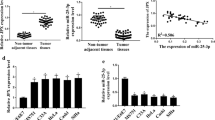
Emerging evidence reveals that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) contribute to human tumorigenesis. Nevertheless, the function of HOXC cluster antisense RNA 3 (HOXC-AS3) in human cervical cancer (CC) remains largely unknown. The levels of HOXC-AS3, miR-105-5p and SOS1 in CC tissues and cells were monitored by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and western blot (WB). Gain- and loss-of-function experiments were conducted to verify the function of HOXC-AS3 and miR-105-5p in CC cells. Meanwhile, cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion were examined by the cell counting kit-8 (CCK8) experiment, colony formation assay, flow cytometry and Transwell assay. Dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay were carried out to test the regulatory interaction of HOXC-AS3, miR-105-5p and SOS1. In addition, in vivo experiment was performed to certain the role of HOXC-AS3 in tumorigenesis of CC. HOXC-AS3 was overexpressed in CC tissues (vs. adjacent normal tissues) and CC cells. Besides, the higher HOXC-AS3 profile was associated with the poorer clinical prognosis of CC patients. Overexpression of HOXC-AS3 promoted cell growth, migration and invasion, hampered apoptosis, whereas knocking down HOXC-AS3 exhibited the reverse effects. MiR-105-5p was a downstream target of HOXC-AS3, and it mediated the HOXC-AS3-induced oncogenic effects. Mechanistically, the bioinformatic analysis illustrated that SOS1 was targeted by miR-105-5p. Up-regulating SOS1 heightened the growth, migration and invasion of CC cells by enhancing the ErbB signaling pathway, which was reversed by miR-105-5p. Up-regulated HOXC-AS3 aggravates CC by promoting SOS1 expression via targeting miR-105-5p.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Baltanás FC, Zarich N, Rojas-Cabañeros JM, Santos E (2020) SOS GEFs in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 2:188445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188445
Bao J, Zou JH, Li CY, Zheng GQ (2016) miR-194 inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis by targeting KDM5B. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20(21):4487–4493
Barra F, Leone Roberti Maggiore U, Bogani G, Ditto A, Signorelli M, Martinelli F, Chiappa V, Lorusso D, Raspagliesi F, Ferrero S (2019) New prophylactics human papilloma virus (HPV) vaccines against cervical cancer. J Obstet Gynaecol 39(1):1–10
Bjurberg M, Beskow C, Kannisto P, Lindahl G (2015) Cervixcancer en klinisk utmaning [Cervical cancer is a clinical challenge]. Lakartidningen 112:DIUS (In Swedish)
Cao L, Jin H, Zheng Y, Mao Y, Fu Z, Li X, Dong L (2019) DANCR-mediated microRNA-665 regulates proliferation and metastasis of cervical cancer through the ERK/SMAD pathway. Cancer Sci 110(3):913–925. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13921
Dong X, Chang M, Song X, Ding S, Xie L, Song X (2020) Plasma miR-1247-5p, miR-301b-3p and miR-105-5p as potential biomarkers for early diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13800
Fumagalli MR, Lionetti MC, Zapperi S, La Porta CAM (2019) Cross-talk between circRNAs and mRNAs modulates MiRNA-mediated circuits and affects melanoma plasticity. Cancer Microenviron 12(2–3):95–104
Hao PQ, Zhang XY, Guo H, Yang Y, An S, Liu Y, Guo XX, Xu TR, Hao Q (2018) Research progress on pathophysiological function of SOS1 protein. Sheng Li Xue Bao 70(5):565–570 (In Chinese)
Hua FF, Liu SS, Zhu LH, Wang YH, Liang X, Ma N, Shi HR (2017) MiRNA-338-3p regulates cervical cancer cells proliferation by targeting MACC1 through MAPK signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21(23):5342–5352. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201712_13919
Jiang B, Sun R, Fang S, Qin C, Pan X, Peng L, Li Y, Li G (2016) Lnc-CC3 increases metastasis in cervical cancer by increasing Slug expression. Oncotarget 7(27):41650–41661. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9519
Jin L, Ji J, Shi L, Jin S, Pei L (2019) lncRNA HAND2-AS1 inhibits cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by downregulating ROCK1 in HPV-positive and negative cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Ther Med 18(4):2512–2518. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7830
Juan C, Hua Q, Ruping Z, Tingting W (2018) miRNA-489 as a biomarker in diagnosis and treatment of cervical cancer. Bratisl Lek Listy 119(5):278–283. https://doi.org/10.4149/BLL_2018_052
Li J, Li Z, Zheng W, Li X, Wang Z, Cui Y, Jiang X (2017) LncRNA-ATB: an indispensable cancer-related long noncoding RNA. Cell Prolif 50(6):e12381
Lin C, Gao B, Yan X, Lei Z, Chen K, Li Y, Zeng Q, Chen Z, Li H (2018) MicroRNA 628 suppresses migration and invasion of breast cancer stem cells through targeting SOS1. Onco Targets Ther 11:5419–5428
Liu Q, Guo X, Que S, Yang X, Fan H, Liu M, Li X, Tang H (2017) LncRNA RSU1P2 contributes to tumorigenesis by acting as a ceRNA against let-7a in cervical cancer cells. Oncotarget 8(27):43768–43781. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10844
Ni YJ, Lu J, Zhou HM (2019) Propofol suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells via regulating miR-29/MMP-2 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(23):10177. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201912_19649
Qiannan E, Wang C, Gu X, Gan X, Zhang X, Wang S, Ma J, Zhang L, Zhang R, Su L (2020) Competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) regulation network of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA during the process of the nickel-induced steroidogenesis disturbance in rat Leydig cells. Toxicol In Vitro 63:104721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2019.104721
Sadri Nahand J, Moghoofei M, Salmaninejad A, Bahmanpour Z, Karimzadeh M, Nasiri M, Mirzaei HR, Pourhanifeh MH, Bokharaei-Salim F, Mirzaei H, Hamblin MR (2020) Pathogenic role of exosomes and microRNAs in HPV-mediated inflammation and cervical cancer: a review. Int J Cancer 146(2):305–320
Saito T, Kurashige J, Nambara S, Komatsu H, Hirata H, Ueda M, Sakimura S, Uchi R, Takano Y, Shinden Y, Iguchi T, Eguchi H, Ehata S, Murakami K, Sugimachi K, Mimori K (2015) A long non-coding RNA activated by transforming growth factor-β is an independent prognostic marker of gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 22(Suppl 3):S915–S922. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4554-8
Shi SH, Jiang J, Zhang W, Sun L, Li XJ, Li C, Ge QD, Zhuang ZG (2020) A novel lncRNA HOXC-AS3 acts as a miR-3922-5p sponge to promote breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Invest 38(1):1–12
Shima H, Kida K, Adachi S, Yamada A, Sugae S, Narui K, Miyagi Y, Nishi M, Ryo A, Murata S, Taniguchi H, Ichikawa Y, Ishikawa T, Endo I (2018) Lnc RNA H19 is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients and promotes cancer stemness. Breast Cancer Res Treat 170(3):507–516. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-018-4793-z
Wang X, Sun Y, Xu T, Qian K, Huang B, Zhang K, Song Z, Qian T, Shi J, Li L (2019) HOXB13 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of glioblastoma through transcriptional upregulation of lncRNA HOXC-AS3. J Cell Biochem 120(9):15527–15537. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28819
Wei WF, Zhou CF, Wu XG, He LN, Wu LF, Chen XJ, Yan RM, Zhong M, Yu YH, Liang L, Wang W (2017) MicroRNA-221-3p, a TWIST2 target, promotes cervical cancer metastasis by directly targeting THBS2. Cell Death Dis 8(12):3220. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-017-0077-5
Wei S, Liu K, He Q, Gao Y, Shen L (2019) PES1 is regulated by CD44 in liver cancer stem cells via miR-105-5p. FEBS Lett 593(14):1777–1786. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13459
Wu W, Guo L, Liang Z, Liu Y, Yao Z (2020) Lnc-SNHG16/miR-128 axis modulates malignant phenotype through WNT/β-catenin pathway in cervical cancer cells. J Cancer 11(8):2201–2212
Xiao H, Zhang F, Zou Y, Li J, Liu Y, Huang W (2018) The function and mechanism of long non-coding RNA-ATB in cancers. Front Physiol 9:321
Xu S, Yi XM, Tang CP, Ge JP, Zhang ZY, Zhou WQ (2016) Long non-coding RNA ATB promotes growth and epithelial–mesenchymal transition and predicts poor prognosis in human prostate carcinoma. Oncol Rep 36(1):10–22. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2016.4791
Yang Z, Hu T (2020) Long noncoding RNA HOXC-AS3 facilitates the progression of invasive mucinous adenocarcinomas of the lung via modulating FUS/FOXM1. Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 56(1):15–23
Yang X, Wang CC, Lee WYW, Trovik J, Chung TKH, Kwong J (2018) Long non-coding RNA HAND2-AS1 inhibits invasion and metastasis in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma through inactivating neuromedin U. Cancer Lett 413:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.10.028
Yang Z, Sun Q, Guo J, Wang S, Song G, Liu W, Liu M, Tang H (2019) GRSF1-mediated MIR-G-1 promotes malignant behavior and nuclear autophagy by directly upregulating TMED5 and LMNB1 in cervical cancer cells. Autophagy 15(4):668–685. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2018.1539590
Yu X, Liang C, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Chen H (2019) Inhibitory short peptides targeting EPS8/ABI1/SOS1 tri-complex suppress invasion and metastasis of ovarian cancer cells. BMC Cancer 19(1):878
Zhang E, He X, Zhang C, Su J, Lu X, Si X, Chen J, Yin D, Han L, De W (2018) A novel long noncoding RNA HOXC-AS3 mediates tumorigenesis of gastric cancer by binding to YBX1. Genome Biol 19(1):154. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1523-0
Zhu Z, Xu L, Wan Y, Zhou J, Fu D, Chao H, Bao K, Zeng T (2018) Inhibition of E-cadherin expression by lnc-RNA H19 to facilitate bladder cancer metastasis. Cancer Biomark 22(2):275–281. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-170998
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: YJ, YL; Performed the experiments: RZ, JS; Statistical analysis: RZ, JS; Wrote the paper: RZ, JS. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Our study was approved by the Medical ethics committee of Xiangyang Central Hospital.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, R., Song, J., Jin, Y. et al. Long noncoding RNA HOXC-AS3 enhances the progression of cervical cancer via activating ErbB signaling pathway. J Mol Histol 52, 991–1006 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10007-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10007-z