Abstract
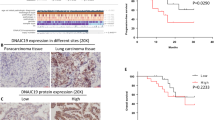
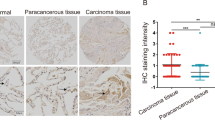
Rhomboid domain containing 1 (RHBDD1) gene, which was reported to be upregulated in human several cancer, was associated with carcinogenesis. However, the potential biological function of RHBDD1 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) carcinogenesis remains still not known. In this study, we aimed to investigate the role of RHBDD1 and its underlying molecular mechanism in NSCLC. The gene RHBDD1 expression was detected in NSCLC tissues and matched nontumor adjacent tissues. In vitro experiments, NSCLC cell lines (A549, H1650, H358 and H1299) were performed to investigate the biological function of RHBDD1 and its molecular mechanism. Our findings showed that the mRNA and protein expression levels of RHBDD1 were notably increased in human NSCLC tissues and cell lines, especially in A549 and H1650 cells. Moreover, silencing of RHBDD1 by RNAi notably inhibited NSCLC cell proliferation and increased cell apoptosis. Caspase-3/7 activity was remarkably increased in cells treated with RHBDD1 siRNA. RHBDD1 silencing notably reduced the number of invading cells. Furthermore, our findings showed that silencing of RHBDD1 notably inhibited the mRNA and protein expression levels of ZEB1 in A549 and H1650 cells. The phosphorylation of PI3K and AKT was also remarkably decreased by RHBDD1 silencing. ZEB1/AKT overexpression reversed the effect of RHBDD1 silencing on NSCLC cell growth and invasion. Taken together, our findings indicated that RHBDD1 silencing inhibited cell growth and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by mediating ZEB1/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, implying that RHBDD1 was possibly a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target for NSCLC treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caramel J, Ligier M, Puisieux A (2018) Pleiotropic rules for ZEB1 in cancer. Cancer Res 78:30–35. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2476
Duma N, Santana-Davila R, Molina JR (2019) Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc 94:1623–1640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.01.013
Fumarola C, Bonelli MA, Petronini PG, Alfieri RR (2014) Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in non small cell lung cancer. Biochem Pharmacol 90:197–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2014.05.011
Hai L et al (2018) Jagged1 is clinically prognostic and promotes invasion of glioma-initiating cells by activating NF-kappaB(p65) signaling. Cell Physiol Biochem 51:2925–2937. https://doi.org/10.1159/000496044
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C (2018) The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 553:446–454. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25183
Huang C et al (2018) Silencing of rhomboid domain containing 1 to inhibit the metastasis of human breast cancer cells in vitro. Iran J Basic Med Sci 21:1161–1166. https://doi.org/10.22038/IJBMS.2018.29788.7191
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE, Adjei AA (2008) Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc 83:584–594. https://doi.org/10.4065/83.5.584
Monticelli M et al (2018) The post-surgical era of GBM: how molecular biology has impacted on our clinical management. A review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 170:120–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2018.05.015
Petrosyan F, Daw H, Haddad A, Spiro T, Sood R (2015) Gene expression profiling for early-stage NSCLC. Am J Clin Oncol 38:103–107. https://doi.org/10.1097/COC.0b013e31828d95d8
Rotow J, Bivona TG (2017) Understanding and targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat Rev Cancer 17:637–658. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2017.84
Shirai YT et al (2019) CNOT3 targets negative cell cycle regulators in non-small cell lung cancer development. Oncogene 38:2580–2594. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0603-7
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2018) Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin 68:7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21442
Song W et al (2015) Rhomboid domain containing 1 promotes colorectal cancer growth through activation of the EGFR signalling pathway. Nat Commun 6:8022. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9022
Sun S et al (2019) miRNA-708 functions as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer by targeting ZEB1 through Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res 11:5338–5356
Urban S (2006) Rhomboid proteins: conserved membrane proteases with divergent biological functions. Genes Dev 20:3054–3068. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1488606
Wakelee H, Kelly K, Edelman MJ (2014) Years of progress in the systemic therapy of non-small cell lung cancer. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. https://doi.org/10.14694/EdBook_AM.2014.34.177
Wang J et al (2017) Analysis of gene expression profiles of non-small cell lung cancer at different stages reveals significantly altered biological functions and candidate genes. Oncol Rep 37:1736–1746. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5380
Wang Y et al (2008) A novel member of the Rhomboid family, RHBDD1, regulates BIK-mediated apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:3822–3829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-8452-0
Wu J, He Z, Yang XM, Li KL, Wang DL, Sun FL (2017) RCCD1 depletion attenuates TGF-beta-induced EMT and cell migration by stabilizing cytoskeletal microtubules in NSCLC cells. Cancer Lett 400:18–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.04.021
Yuan G, Quan J, Dong D, Wang Q (2018) Long nnoncoding RNA CAT104 promotes cell viability, migration, and invasion in gastric carcinoma cells through activation of microRNA-381-inhibiting zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) expression. Oncol Res 26:1037–1046. https://doi.org/10.3727/096504017x15144748428127
Zhang M et al (2018a) RHBDD1 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis through the Wnt signaling pathway and its downstream target ZEB1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37:22. 10.1186/s13046-018-0687-5
Zhang X et al (2018b) Rhomboid domain-containing protein 1 promotes breast cancer progression by regulating the p-Akt and CDK2 levels. Cell Commun Signal 16:65. 10.1186/s12964-018-0267-5
Zhao C, Ling X, Li X, Hou X, Zhao D (2019) MicroRNA-138-5p inhibits cell migration, invasion and EMT in breast cancer by directly targeting RHBDD1. Breast Cancer 26:817–825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-019-00989-w
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Joint Foundation of Science & Technology Department of Yunnan Province and Kunming Medical University (2019FE001(-115)), and grants from the Foundation from Health Commission of Yunnan Province (2018NS0271).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Wang, R., Li, X. et al. RHBDD1 silencing inhibited cell growth and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by mediating ZEB1/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J Mol Histol 52, 503–510 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09943-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09943-z