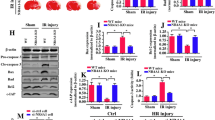
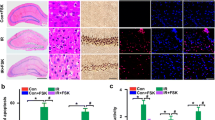
Abstract
Mitochondrial fragmentation drastically regulates mitochondrial homeostasis in brain illness. However, the role of mitochondrial fragmentation in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion (IR) injury remains unclear. Nur77, a regulator of mitochondrial homeostasis, is associated with heart and liver IR injury, but its effects on mitochondrial function in cerebral IR injury has not been studied intensively. The aim of our study is to explore whether cerebral IR injury is modulated by Nur77 via modification of mitochondrial homeostasis. Our results indicated that Nur77 was upregulated in reperfused brain tissues. Genetic ablation of Nur77 reduced infarction area and promoted neuron survival under IR burden. Biochemical analysis demonstrated that Nur77 deletion protected mitochondrial function, attenuated mitochondrial oxidative stress, preserved mitochondrial potential, and blocked mitochondria-related cell apoptosis. In addition, we illustrated that Nur77 mediated mitochondrial damage via evoking mitochondrial fragmentation that occurred through increased mitochondrial fission and decreased fusion. Besides, our results also demonstrated that Nur77 controlled mitochondrial fragmentation via upregulating INF2 in a manner dependent on the Wnt/β-catenin pathway; inhibition of the Wnt pathway abrogated the protective effect of Nur77 deletion on reperfused-mediated neurons. Altogether, our study highlights that the pathogenesis of cerebral IR injury is associated with Nur77 activation followed by augmented mitochondrial fragmentation via an abnormal Wnt/β-catenin/INF2 pathway. Accordingly, Nur77-dependent mitochondrial fragmentation and the Wnt/β-catenin/INF2 axis may represent novel therapeutic targets to reduce cerebral IR injury.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Banta KL, Wang X, Das P, Winoto A (2018) B cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) residues essential for Bcl-2’s apoptosis-inducing interaction with Nur77/Nor-1 orphan steroid receptors. J Biol Chem 293:4724–4734. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA117.001101
Bavarsad K, Barreto GE, Hadjzadeh MA, Sahebkar A (2018) Protective effects of curcumin against ischemia-reperfusion injury in the nervous system. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1169-7
Chen HZ et al (2012) The orphan receptor TR3 suppresses intestinal tumorigenesis in mice by downregulating Wnt signalling. Gut 61:714–724. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300783
Cheng Z et al (2011) Mitochondrial translocation of Nur77 mediates cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Eur Heart J 32:2179–2188. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehq496
Chenn A (2008) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cerebral cortical development. Organogenesis 4:76–80
Chun SK et al (2018) Loss of sirtuin 1 and mitofusin 2 contributes to enhanced ischemia/reperfusion injury in aged livers. Aging Cell. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12761
Fan J et al (2017) Therapeutic hypothermia attenuates global cerebral reperfusion-induced mitochondrial damage by suppressing dynamin-related protein 1 activation and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in a cardiac arrest rat model. Neurosci Lett 647:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.02.065
Gan L et al (2018) Protective effect of mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant MitoQ against iron ion (56)Fe radiation induced brain injury in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 341:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2018.01.003
Garcia-Ruiz JM et al (2017) Bloodless reperfusion with the oxygen carrier HBOC-201 in acute myocardial infarction: a novel platform for cardioprotective probes delivery. Basic Res Cardiol 112:17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0605-6
Geng C, Wei J, Wu C (2018) Yap-Hippo pathway regulates cerebral hypoxia-reoxygenation injury in neuroblastoma N2a cells via inhibiting ROCK1/F-actin/mitochondrial fission pathways. Acta Neurol Belg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-018-0944-6
Ho DH, Je AR, Lee H, Son I, Kweon HS, Kim HG, Seol W (2018) LRRK2 kinase activity induces mitochondrial fission in microglia via Drp1 and modulates neuroinflammation. Exp Neurobiol 27:171–180. https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2018.27.3.171
Hong H, Tao T, Chen S, Liang C, Qiu Y, Zhou Y, Zhang R (2017) MicroRNA-143 promotes cardiac ischemia-mediated mitochondrial impairment by the inhibition of protein kinase Cepsilon. Basic Res Cardiol 112:60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0649-7
Hu M et al (2017) Celastrol-induced Nur77 interaction with TRAF2 alleviates inflammation by promoting mitochondrial ubiquitination and autophagy. Mol Cell 66:141–153.e146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.03.008
Ji WK, Hatch AL, Merrill RA, Strack S, Higgs HN (2015) Actin filaments target the oligomeric maturation of the dynamin GTPase Drp1 to mitochondrial fission sites. Elife 4:e11553. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11553
Jin X et al (2017) Dysregulation of INF2-mediated mitochondrial fission in SPOP-mutated prostate cancer. PLoS Genet 13:e1006748. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006748
Jin Q et al (2018) DUSP1 alleviates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing the Mff-required mitochondrial fission and Bnip3-related mitophagy via the JNK pathways. Redox Biol 14:576–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.004
Jokinen R, Pirnes-Karhu S, Pietilainen KH, Pirinen E (2017) Adipose tissue NAD(+)-homeostasis, sirtuins and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases -important players in mitochondrial metabolism and metabolic health. Redox Biol 12:246–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.02.011
Jovancevic N et al (2017) Medium-chain fatty acids modulate myocardial function via a cardiac odorant receptor. Basic Res Cardiol 112:13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0600-y
Kang Z, Zhu H, Luan H, Han F, Jiang W (2014) Curculigoside A induces angiogenesis through VCAM-1/Egr-3/CREB/VEGF signaling pathway. Neuroscience 267:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.02.050
Lan R et al (2018) Xiao-Xu-Ming decoction reduced mitophagy activation and improved mitochondrial function in cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury. Behav Neurol 2018:4147502. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4147502
Lee HY, Back K (2017a) Melatonin is required for H2 O2- and NO-mediated defense signaling through MAPKKK3 and OXI1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Pineal Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12379
Lee K, Back K (2017b) Overexpression of rice serotonin N-acetyltransferase 1 in transgenic rice plants confers resistance to cadmium and senescence and increases grain yield. J Pineal Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12392
Li R, Xin T, Li D, Wang C, Zhu H, Zhou H (2018) Therapeutic effect of Sirtuin 3 on ameliorating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the role of the ERK-CREB pathway and Bnip3-mediated mitophagy. Redox Biol 18:229–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.07.011
Martin JL, Gruszczyk AV, Beach TE, Murphy MP, Saeb-Parsy K (2018) Mitochondrial mechanisms and therapeutics in ischaemia reperfusion injury. Pediatr Nephrol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-3984-5
Nauta TD, van den Broek M, Gibbs S, van der Pouw-Kraan TC, Oudejans CB, van Hinsbergh VW, Koolwijk P (2017) Identification of HIF-2alpha-regulated genes that play a role in human microvascular endothelial sprouting during prolonged hypoxia in vitro. Angiogenesis 20:39–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-016-9527-4
Park H et al (2018) Extracellular vesicles derived from hypoxic human mesenchymal stem cells attenuate GSK3beta expression via miRNA-26a in an ischemia-reperfusion injury model. Yonsei Med J 59:736–745. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2018.59.6.736
Perez MJ, Jara C, Quintanilla RA (2018) Contribution of Tau pathology to mitochondrial impairment in neurodegeneration. Front Neurosci 12:441. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00441
Reynolds MS et al (2016) Beta-cell deletion of Nr4a1 and Nr4a3 nuclear receptors impedes mitochondrial respiration and insulin secretion. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 311:E186–E201. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00022.2016
Russell AL, Richardson MR, Bauman BM, Hernandez IM, Saperstein S, Handa RJ, Wu TJ (2018) Differential responses of the HPA axis to mild blast traumatic brain injury in male and female mice. Endocrinology 159:2363–2375. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2018-00203
Shen YQ et al (2018) Combination of melatonin and rapamycin for head and neck cancer therapy: suppression of AKT/mTOR pathway activation, and activation of mitophagy and apoptosis via mitochondrial function regulation. J Pineal Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12461
Shi ZY et al (2017) Protective effect of autophagy in neural ischemia and hypoxia: negative regulation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Int J Mol Med 40:1699–1708. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2017.3158
Singh V, Krishan P, Shri R (2018) Antioxidant-mediated neuroprotection by Allium schoenoprasum L. leaf extract against ischemia reperfusion-induced cerebral injury in mice. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 29:403–410. https://doi.org/10.1515/jbcpp-2017-0070
Steffen J, Koehler CM (2018) ER-mitochondria contacts: actin dynamics at the ER control mitochondrial fission via calcium release. J Cell Biol 217:15–17. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201711075
Stepanova A, Kahl A, Konrad C, Ten V, Starkov AS, Galkin A (2017) Reverse electron transfer results in a loss of flavin from mitochondrial complex I: potential mechanism for brain ischemia reperfusion injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 37:3649–3658. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X17730242
Tang Y et al (2016) Hypothermia-induced ischemic tolerance is associated with Drp1 inhibition in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury of mice. Brain Res 1646:73–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.05.042
Wei Z, Li HH (2015) IGFBP-3 may trigger osteoarthritis by inducing apoptosis of chondrocytes through Nur77 translocation. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:15599–15610
Xing XS, Liu F, He ZY (2015) Akt regulates beta-catenin in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep 11:3122–3128. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.3000
Yu W, Gao D, Jin W, Liu S, Qi S (2018) Propofol prevents oxidative stress by decreasing the ischemic accumulation of succinate in focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neurochem Res 43:420–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2437-z
Zhao H, Luo Y, Chen L, Zhang Z, Shen C, Li Y, Xu R (2018) Sirt3 inhibits cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through normalizing Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and blocking mitochondrial fission. Cell Stress Chaperones. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-018-0917-y
Zhou H et al (2017) Mff-dependent mitochondrial fission contributes to the pathogenesis of cardiac microvasculature ischemia/reperfusion injury via induction of mROS-mediated cardiolipin oxidation and HK2/VDAC1 disassociation-involved mPTP opening. J Am Heart Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.116.005328
Zhou H et al (2018a) Effects of melatonin on fatty liver disease: the role of NR4A1/DNA-PKcs/p53 pathway, mitochondrial fission, and mitophagy. J Pineal Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12450
Zhou H, Ma Q, Zhu P, Ren J, Reiter RJ, Chen Y (2018b) Protective role of melatonin in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury: from pathogenesis to targeted therapy. J Pineal Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12471
Zhou H, Shi C, Hu S, Zhu H, Ren J, Chen Y (2018c) BI1 is associated with microvascular protection in cardiac ischemia reperfusion injury via repressing Syk-Nox2-Drp1-mitochondrial fission pathways. Angiogenesis 21:599–615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-018-9611-z
Zhou H et al (2018d) NR4A1 aggravates the cardiac microvascular ischemia reperfusion injury through suppressing FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy and promoting Mff-required mitochondrial fission by CK2alpha. Basic Res Cardiol 113:23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0682-1
Zhou H, Wang S, Hu S, Chen Y, Ren J (2018e) ER-mitochondria microdomains in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury: a fresh perspective. Front Physiol 9:755. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00755
Zhou J et al (2018f) Mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant MitoQ provides neuroprotection and reduces neuronal apoptosis in experimental traumatic brain injury possibly via the Nrf2-ARE pathway. Am J Transl Res 10:1887–1899
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Dr. Zhenhai Zhang, Dr. Chunsen Shen and Dr. Yunjun Li. Due to the personal reason, these authors have left from PLA army general hospital and are working in Xiangya hospital. According to their request and their new hospital policy, they ask to remove their name from the original submission. All the authors have approved this decision. Thanks for their contributions to this work.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81100917) and Beijing Nova program (Z171100001117096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HZ, YCL, and LHC conceived the research; WLP, HZ and RXX performed the experiments; all authors participated in discussing and revising the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The animal study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All experimental protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee of Department of neurosurgery, PLA army general hospital, Beijing, China, Beijing, China. The ethics reference number: SCSSJN20112.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, H., Pan, W., Chen, L. et al. Nur77 promotes cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury via activating INF2-mediated mitochondrial fragmentation. J Mol Hist 49, 599–613 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-018-9798-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-018-9798-8