Abstract
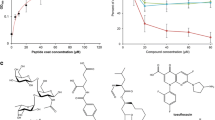
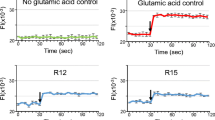
C-Mannosylation is a rare type of protein glycosylation and is reportedly critical for the proper folding and secretion of parental proteins. Still, the effects of C-mannosylation on the biological functions of these modified proteins remain to be elucidated. The Trp-x-x-Trp (WxxW) sequences, whose first tryptophan (Trp) can be C-mannosylated, constitute the consensus motifs for this glycosylation modification and are commonly found in thrombospondin type 1 repeats that regulate molecular functions of thrombospondin 1 in binding and activation of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β). TGF-β plays critical roles in the control of the central nervous system including synaptogenesis. Here, we investigated whether C-mannosylation of the synthetic Trp-Ser-Pro-Trp (WSPW) peptide may confer certain functions to this peptide in TGF-β-mediated synaptogenesis. By using primary cultured rat astrocytes and cortical neurons, we found that the C-mannosylated WSPW (C-Man-WSPW) peptide, but not non-mannosylated WSPW peptide, suppressed astrocyte-conditioned medium (ACM)-stimulated synaptogenesis. C-Man-WSPW peptide inhibited both ACM- and recombinant mature TGF-β1-induced activations of Smad 2, an important mediator in TGF-β signaling. Interactions of recombinant mature TGF-β with the C-Man-WSPW peptide were similar to those with non-C-mannosylated WSPW peptide. Taken together, our results reveal a novel function of C-mannosylation of the WxxW motif in signaling and synaptogenesis mediated by TGF-β. Molecular details of how C-mannosylation affects the biological functions of WxxW motifs deserve future study for clarification.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- ACM:
-
Astrocyte-conditioned medium
- C-Man-WSPW peptide :
-
C-Mannosylated WSPW peptide
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PSD-95:
-
Postsynaptic density protein 95
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor β
- TSP:
-
Thrombospondin
- TSR:
-
Thrombospondin type 1 repeat
References
Doucey, M.A., Hess, D., Blommers, M.J., Hofsteenge, J.: Recombinant human interleukin-12 is the second example of a C-mannosylated protein. Glycobiology 9(5), 435–441 (1999)
Krieg, J., Glasner, W., Vicentini, A., Doucey, M.A., Loffler, A., Hess, D., Hofsteenge, J.: C-Mannosylation of human RNase 2 is an intracellular process performed by a variety of cultured cells. J. Biol. Chem. 272(42), 26687–26692 (1997)
Gade, G., Kellner, R., Rinehart, K.L., Proefke, M.L.: A tryptophan-substituted member of the AKH/RPCH family isolated from a stick insect corpus cardiacum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 189(3), 1303–1309 (1992)
Hofsteenge, J., Muller, D.R., de Beer, T., Loffler, A., Richter, W.J., Vliegenthart, J.F.: New type of linkage between a carbohydrate and a protein: C-glycosylation of a specific tryptophan residue in human RNase Us. Biochemistry 33(46), 13524–13530 (1994)
Furmanek, A., Hofsteenge, J.: Protein C-mannosylation: facts and questions. Acta. Biochim. Pol. 47(3), 781–789 (2000)
Buettner, F.F., Ashikov, A., Tiemann, B., Lehle, L., Bakker, H.: C. elegans DPY-19 is a C-mannosyltransferase glycosylating thrombospondin repeats. Mol. Cell 50(2), 295–302 (2013)
Niwa, Y., Suzuki, T., Dohmae, N., Simizu, S.: Identification of DPY19L3 as the C-mannosyltransferase of R-spondin1 in human cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 27(5), 744–756 (2016)
Shcherbakova, A., Tiemann, B., Buettner, F.F., Bakker, H.: Distinct C-mannosylation of netrin receptor thrombospondin type 1 repeats by mammalian DPY19L1 and DPY19L3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 114(10), 2574–2579 (2017)
Fujiwara, M., Kato, S., Niwa, Y., Suzuki, T., Tsuchiya, M., Sasazawa, Y., Dohmae, N., Simizu, S.: C-mannosylation of R-spondin3 regulates its secretion and activity of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cells. FEBS Lett. 590(16), 2639–2649 (2016)
Frank, M., Beccati, D., Leeflang, B.R., Vliegenthart, J.F.G.: C-Mannosylation Enhances the Structural Stability of Human RNase 2. iScience 23(8), 101371 (2020)
Shcherbakova, A., Preller, M., Taft, M.H., Pujols, J., Ventura, S., Tiemann, B., Buettner, F.F., Bakker, H.: C-mannosylation supports folding and enhances stability of thrombospondin repeats. Elife 8 (2019)
Olsen, J.G., Kragelund, B.B.: Who climbs the tryptophan ladder? On the structure and function of the WSXWS motif in cytokine receptors and thrombospondin repeats. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 25(3), 337–341 (2014)
Christopherson, K.S., Ullian, E.M., Stokes, C.C., Mullowney, C.E., Hell, J.W., Agah, A., Lawler, J., Mosher, D.F., Bornstein, P., Barres, B.A.: Thrombospondins are astrocyte-secreted proteins that promote CNS synaptogenesis. Cell 120(3), 421–433 (2005)
Tan, K., Duquette, M., Liu, J.H., Dong, Y., Zhang, R., Joachimiak, A., Lawler, J., Wang, J.H.: Crystal structure of the TSP-1 type 1 repeats: a novel layered fold and its biological implication. J. Cell Biol. 159(2), 373–382 (2002)
Hofsteenge, J., Blommers, M., Hess, D., Furmanek, A., Miroshnichenko, O.: The four terminal components of the complement system are C-mannosylated on multiple tryptophan residues. J. Biol. Chem. 274(46), 32786–32794 (1999)
Gouyer, V., Demouveaux, B., Lacroix, G., Valque, H., Gottrand, F., Desseyn, J.L.: Non-C-mannosylable mucin CYS domains hindered proper folding and secretion of mucin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 506(4), 812–818 (2018)
Hilton, D.J., Watowich, S.S., Katz, L., Lodish, H.F.: Saturation mutagenesis of the WSXWS motif of the erythropoietin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 271(9), 4699–4708 (1996)
Taylor, K.M., Trimby, A.R., Campbell, A.K.: Mutation of recombinant complement component C9 reveals the significance of the N-terminal region for polymerization. Immunology 91(1), 20–27 (1997)
Sweetwyne, M.T., Murphy-Ullrich, J.E.: Thrombospondin1 in tissue repair and fibrosis: TGF-beta-dependent and independent mechanisms. Matrix. Biol. 31(3), 178–186 (2012)
Ihara, Y., Manabe, S., Ikezaki, M., Inai, Y., Matsui, I.S., Ohta, Y., Muroi, E., Ito, Y.: C-Mannosylated peptides derived from the thrombospondin type 1 repeat interact with Hsc70 to modulate its signaling in RAW264.7 cells. Glycobiology 20(10), 1298–1310 (2010)
Eroglu, C., Barres, B.A.: Regulation of synaptic connectivity by glia. Nature 468(7321), 223–231 (2010)
Chung, W.S., Barres, B.A.: The role of glial cells in synapse elimination. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 22(3), 438–445 (2012)
Allen, N.J., Eroglu, C.: Cell Biology of Astrocyte-Synapse Interactions. Neuron 96(3), 697–708 (2017)
Ullian, E.M., Sapperstein, S.K., Christopherson, K.S., Barres, B.A.: Control of synapse number by glia. Science 291(5504), 657–661 (2001)
Diniz, L.P., Almeida, J.C., Tortelli, V., Vargas Lopes, C., Setti-Perdigao, P., Stipursky, J., Kahn, S.A., Romao, L.F., de Miranda, J., Alves-Leon, S.V., de Souza, J.M., Castro, N.G., Panizzutti, R., Gomes, F.C.: Astrocyte-induced synaptogenesis is mediated by transforming growth factor beta signaling through modulation of D-serine levels in cerebral cortex neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 287(49), 41432–41445 (2012)
Diniz, L.P., Tortelli, V., Garcia, M.N., Araujo, A.P., Melo, H.M., Silva, G.S., Felice, F.G., Alves-Leon, S.V., Souza, J.M., Romao, L.F., Castro, N.G., Gomes, F.C.: Astrocyte transforming growth factor beta 1 promotes inhibitory synapse formation via CaM kinase II signaling. Glia 62(12), 1917–1931 (2014)
Romao, L.F., Sousa Vde, O., Neto, V.M., Gomes, F.C.: Glutamate activates GFAP gene promoter from cultured astrocytes through TGF-beta1 pathways. J. Neurochem. 106(2), 746–756 (2008)
Derynck, R., Zhang, Y., Feng, X.H.: Smads: transcriptional activators of TGF-beta responses. Cell 95(6), 737–740 (1998)
Manabe, S., Marui, Y., Ito, Y.: Total synthesis of mannosyl tryptophan and its derivatives. Chem. Eur. J. 9(6), 1435–1447 (2003)
Muroi, E., Manabe, S., Ikezaki, M., Urata, Y., Sato, S., Kondo, T., Ito, Y., Ihara, Y.: C-Mannosylated peptides derived from the thrombospondin type 1 repeat enhance lipopolysaccharide-induced signaling in macrophage-like RAW264.7 cells. Glycobiology 17(9), 1015–1028 (2007)
Michikawa, M., Gong, J.S., Fan, Q.W., Sawamura, N., Yanagisawa, K.: A novel action of alzheimer’s amyloid beta-protein (Abeta): oligomeric Abeta promotes lipid release. J. Neurosci. 21(18), 7226–7235 (2001)
Lawler, J., Hynes, R.O.: The structure of human thrombospondin, an adhesive glycoprotein with multiple calcium-binding sites and homologies with several different proteins. J. Cell Biol. 103(5), 1635–1648 (1986)
Derynck, R., Budi, E.H.: Specificity, versatility, and control of TGF-beta family signaling. Sci. Signal 12(570) (2019)
Cho, K.O., Hunt, C.A., Kennedy, M.B.: The rat brain postsynaptic density fraction contains a homolog of the Drosophila discs-large tumor suppressor protein. Neuron 9(5), 929–942 (1992)
Masliah, E., Terry, R.D., Alford, M., DeTeresa, R.: Quantitative immunohistochemistry of synaptophysin in human neocortex: an alternative method to estimate density of presynaptic terminals in paraffin sections. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 38(6), 837–844 (1990)
Massague, J.: TGF-beta signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 753–791 (1998)
Derynck, R., Zhang, Y.E.: Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature 425(6958), 577–584 (2003)
Stegmuller, J., Huynh, M.A., Yuan, Z., Konishi, Y., Bonni, A.: TGFbeta-Smad2 signaling regulates the Cdh1-APC/SnoN pathway of axonal morphogenesis. J. Neurosci. 28(8), 1961–1969 (2008)
Nakashima, H., Tsujimura, K., Irie, K., Ishizu, M., Pan, M., Kameda, T., Nakashima, K.: Canonical TGF-beta Signaling Negatively Regulates Neuronal Morphogenesis through TGIF/Smad Complex-Mediated CRMP2 Suppression. J. Neurosci. 38(20), 4791–4810 (2018)
Patel, M.R., Weaver, A.M.: Astrocyte-derived small extracellular vesicles promote synapse formation via fibulin-2-mediated TGF-beta signaling. Cell Rep. 34(10), 108829 (2021)
Munger, J.S., Harpel, J.G., Gleizes, P.E., Mazzieri, R., Nunes, I., Rifkin, D.B.: Latent transforming growth factor-beta: structural features and mechanisms of activation. Kidney Int. 51(5), 1376–1382 (1997)
Schultz-Cherry, S., Chen, H., Mosher, D.F., Misenheimer, T.M., Krutzsch, H.C., Roberts, D.D., Murphy-Ullrich, J.E.: Regulation of transforming growth factor-beta activation by discrete sequences of thrombospondin 1. J. Biol. Chem. 270(13), 7304–7310 (1995)
Mizuta, H., Kuga, K., Suzuki, T., Niwa, Y., Dohmae, N., Simizu, S.: Cmannosylation of Rspondin2 activates Wnt/betacatenin signaling and migration activity in human tumor cells. Int. J. Oncol. 54(6), 2127–2138 (2019)
Okamoto, S., Murano, T., Suzuki, T., Uematsu, S., Niwa, Y., Sasazawa, Y., Dohmae, N., Bujo, H., Simizu, S.: Regulation of secretion and enzymatic activity of lipoprotein lipase by C-mannosylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 486(2), 558–563 (2017)
Yoshimoto, S., Katayama, K., Suzuki, T., Dohmae, N., Simizu, S.: Regulation of N-glycosylation and secretion of Isthmin-1 by its C-mannosylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Gen. Subj. 1865(3), 129840 (2021)
Miura, K., Suzuki, T., Sun, H., Takada, H., Ishizawa, Y., Mizuta, H., Dohmae, N., Simizu, S.: Requirement for C-mannosylation to be secreted and activated a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 4 (ADAMTS4). Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Gen. Subj. 1865(3), 129833 (2021)
Murphy-Ullrich, J.E., Suto, M.J.: Thrombospondin-1 regulation of latent TGF-beta activation: A therapeutic target for fibrotic disease. Matrix. Biol. 68–69, 28–43 (2018)
Schultz-Cherry, S., Lawler, J., Murphy-Ullrich, J.E.: The type 1 repeats of thrombospondin 1 activate latent transforming growth factor-beta. J. Biol. Chem. 269(43), 26783–26788 (1994)
Raulo, E., Tumova, S., Pavlov, I., Pekkanen, M., Hienola, A., Klankki, E., Kalkkinen, N., Taira, T., Kilpelainen, I., Rauvala, H.: The two thrombospondin type I repeat domains of the heparin-binding growth-associated molecule bind to heparin/heparan sulfate and regulate neurite extension and plasticity in hippocampal neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 280(50), 41576–41583 (2005)
Funding
This work was supported in part by a grant from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan JP16H06290 (to Y.Ito); a Wakayama Medical Award for Young Researchers 2013 and 2015 (to M.I.); and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science Grant-in-Aid 19K09784 to M.I. and 20K09605 to K.N.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.I. performed the experiments. S.M. and Y. Ito prepared the peptides and biotinylated peptides. Y. Ihara contributed experimental materials and tools. K.U. interpreted the data, wrote the paper, and supervised the entire project. K.N. designed the research, performed the experiments, interpreted the data, and wrote the paper. K.N. and Y. Ihara take full responsibility for the entire manuscript. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishitsuji, K., Ikezaki, M., Manabe, S. et al. Thrombospondin type 1 repeat-derived C-mannosylated peptide attenuates synaptogenesis of cortical neurons induced by primary astrocytes via TGF-β. Glycoconj J 39, 701–710 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-021-10030-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-021-10030-y