Abstract
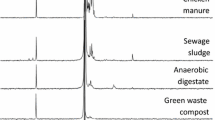
One of the bottlenecks to efficient phosphorus (P) recycling is limited understanding of the relationships between inorganic P species in waste products and their P fertilisation effects. In this study, we characterised inorganic P species in seven waste products (two biomass ashes, meat bone meal, fish sludge, catering waste and two food waste-based digestate products) and two manure products (dairy and chicken manure) by: (1) Sequential chemical fractionation, (2) X-ray powder diffraction and (3) solid-state 31P MAS-NMR spectroscopy. We then used the characterisation data to explain the results of a bioassay studying the fertilisation effects of waste and manure products after application to a nutrient-deficient model soil that was limed to two pH levels (approximately pH 5.5 and 6.9 at pH level 1 and 2), with ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum) as the experimental crop. The P in waste products was mainly present as a complex mixture of inorganic P species, predominantly Ca phosphates with differing solubility. Fertilisation effects were largely explained by sequential fractionation data, with a positive relationship between apparent P use efficiency and the H2O-soluble inorganic P fraction at pH level 1 (R2 = 0.52) and a negative relationship between apparent P use efficiency and the HCl-soluble inorganic P fraction at pH level 2 (R2 = 0.66). X-ray powder diffraction and solid-state 31P MAS-NMR spectroscopy confirmed the sequential fractionation data, but provided little additional information.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aue WP, Roufosse AH, Glimcher MJ, Griffin FG (1984) Solid-state P-31 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of synthetic phases of calcium phosphate: potential models of bone mineral. Biochemistry 23:6110–6114
Bergmann W (1993) Ernährungsstörungen bei Kulturpflanzen: Entstehung, visuelle und analytische Diagnose. Gustav Fischer, Jena
Bioforsk (2014) 2. Tabeller over virkningsgrad av husdyrgjødsel. Bioforsk Gjødslingshåndbok. http://www.bioforsk.no/ikbViewer/page/prosjekt/tema/artikkel?p_dimension_id=19190&p_menu_id=19211&p_sub_id=19191&p_document_id=97422&p_dim2=19606. Accessed 20 Mar 2015
Bleam WF, Pfeffer PE, Frye JS (1989) 31P solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of aluminium phosphate minerals. Phys Chem Miner 16:455–464
Brod E, Haraldsen TK, Krogstad T (2014) Combined waste resources as compound fertiliser to spring cereals. Acta Agric Scand Sect B Soil Plant Sci 64:329–340
Brod E, Øgaard AF, Haraldsen TK, Krogstad T (2015) Waste products as alternative phosphorus fertilisers. Part II: predicting P fertilisation effects by chemical extraction. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst. doi:10.1007/s10705-015-9731-4
Brown EH, Lehr JR, Frazier AW, Smith JP (1964) Calcium ammonium and calcium potassium pyrophosphate systems. Agric Food Chem 12:70–72
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60:309–319
Cabeza R, Steingrobe B, Römer W, Claassen N (2011) Effectiveness of recycled P products as P fertilizers, as evaluated in pot experiments. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 91:173–184
Coelho AA (2006) TOPAS V4.1, Bruker AXS. Karlsruhe, Germany
Condron LM, Turner BL, Cade-Menun BJ (2005) Chemistry and dynamics of soil organic phosphorus. In: Sims TJ, Sharpley AN (eds) Phosphorus: agriculture and the environment, Agronomy monograph, vol 46, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy, Inc., Crop Science Society of America Inc., Soil Science Society of America Inc., Madison, pp 87–121
Egnér H, Riehm H, Domingo WR (1960) Untersuchungen über die chemische Bodenanalyse als Grundlage für die Beurteilung des Nährstoffzustandes der Böden. Kungl Lantbrukshögskolans Annaler 26:199–215
EN 13654-1 (2001) Soil improvers and growing media: determination of nitrogen. Part 1: modified Kjeldahl method. CEN, Brussels
EN 13654-2 (2001) Soil improvers and growing media: determination of nitrogen. Part 2: dumas method. CEN, Brussels
EN ISO 11885 (2009) Water quality: determination of selected elements by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP–OES). CEN, Brussels
Frossard E, Tekeley P, Grimal JY (1994) Characterization of phosphate species in urban sewage sludges by high-resolution solid-state 31P NMR. Eur J Soil Sci 45:403–408
Frossard E, Bauer JP, Lothe F (1997) Evidence of vivianite in FeSO4-flocculated sludges. Water Res 31:2449–2454
Frossard E, Skrabal P, Sinaj S, Bangerter F, Traore O (2002) Forms and exchangeability of inorganic phosphate in composted solid organic wastes. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 62:103–113
García-Albacete M, Martín A, Cartagena MC (2012) Fractionation of phosphorus biowastes: characterisation and environmental risk. Waste Manag 32:1061–1068
Güngör K, Jürgensen A, Karthikeyan KG (2007) Determination of phosphorus speciation in dairy manure using XRD and XANES spectroscopy. J Environ Qual 36:1856–1863
Hamilton H, Brod E, Hanserud H, Gracey E, Vestrum M, Steinhoff F, Mueller D, Brattebøe H (2015) Investigating cross-sectoral synergies through integrated aquaculture, fisheries and agricultural phosphorus assessments: Norway as a case. J Ind Ecol. doi:10.1111/jiec.12324
Haraldsen TK, Andersen U, Krogstad T, Sørheim R (2011) Liquid digestate from anaerobic treatment of source-separated household waste as fertilizer to barley. Waste Manag Res 29:1271–1276
He Z, Fortuna A-M, Senwo ZN, Tazisong IA, Honeycutt CW, Griffin TS (2006) Hydrochloric fractions in Hedley fractionation may contain inorganic and organic phosphates. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:893–899
Hedley M, McLaughlin M (2005) Reactions of phosphate fertilizers and by-products in soils. In: Sims TJ, Sharpley AN (eds) Phosphorus: agriculture and the environment, Agronomy monograph, vol 46, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy Inc., Crop Science Society of America Inc., Soil Science Society of America Inc., Madison, pp 181–252
Hedley MJ, Stewart JWB, Chauhan BS (1982) Changes in inorganic and organic soil phosphorus fractions induced by cultivation practices and by laboratory incubations. Soil Sci Soc Am J 46:970–976
Henriksen A, Selmer-Olsen AR (1970) Automatic methods for determining nitrate and nitrite in water and soil extracts. Analyst 95:514–518
Hinedi ZR, Chang AC, Yesinowski JP (1989) Phosphorus-31 magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance of wastewater sludges and sludge-amended soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 53:1053–1056
Hinsinger P (2001) Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes: a review. Plant Soil 237:173–195
Hunger S, Cho H, Sims JT, Sparks DL (2004) Direct speciation of phosphorus in alum-amended poultry litter: solid-state 31P NMR investigation. Environ Sci Technol 38:674–681
Hunger S, Sims JT, Sparks DL (2008) Evidence for struvite in poultry litter: effect of storage and drying. J Environ Qual 37:1617–1625
ICDD (2013) The international centre for diffraction data. http://www.icdd.com/index.htm. Accessed 21 May–23 June 2014
Jeng A, Haraldsen TK, Vagstad N, Grønlund A (2004) Meat and bone meal as nitrogen fertilizer to cereals in Norway. Agric Food Sci 13:268–275
Keeling AA, Paton I, Mullett JAJ (1994) Germination and growth of plants in media containing unstable refuse-derived compost. Soil Biol Biochem 26:767–772
Kim B, Gautier M, Michel P, Gourdon R (2013) Physical–chemical characterization of sludge and granular materials from a vertical flow constructed wetland for municipal wastewater treatment. Water Sci Technol 68:2257–2263
Kratz S, Haneklaus S, Schnug E (2010) Chemical solubility and agricultural performance of P containing recycling fertilizers. Landbauforschung vTI Agric For Res 60:227–240
Krogstad T, Sogn TA, Asdal Å, Sæbø A (2005) Influence of chemically and biologically stabilized sewage sludge on plant-available phosphorous in soil. Ecol Eng 25:51–60
Krupa-Żuczek K, Kowalski Z, Wzorek Z (2008) Manufacturing of phosphoric acid from hydroxyapatite, contained in the ashes of the incinerated meat-bone wastes. Pol J Chem Technol 10:13–20
Kuo S (1994) Phosphorus. In: Sparks DL, Page AL, Helmke PA, Loeppert RH, Soltanpour PN, Tabatabai MA, Johnston CT, Sumner ME (eds) Methods of soil analysis Part 3, chemical methods. American Society of Agronomy, Inc., Madison, pp 869–919
Liebisch F, Bünemann EK, Huguenin-Elie O, Jeangros B, Frossard E, Oberson A (2013) Plant phosphorus nutrition indicators evaluated in agricultural grasslands managed at different intensities. Eur J Agron 44:67–77
Lindsay WL (1979) Chemical equilibria in soils. Wiley, New York
Meteorologisk Institutt (2013) Været i Norge. Meteorologisk Institutt. http://www.met.no/Klima/Varet_i_Norge/. Accessed 20 Mar 2015
Møberg JP, Petersen L (1982) Øvelsesvejledning til geologi og jordbundslære II. Den Kongelige Veterinær- og Landbohøyskole, København
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Nanzer S, Oberson A, Huthwelker T, Eggenberger U, Frossard E (2014) The molecular environment of phosphorus in sewage sludge ash: implications for bioavailability. J Environ Qual 43:1050–1060
Norwegian Ministry of Agriculture and Food (2003) Forskrift om gjødselvarer mv. av organisk opphav. http://www.lovdata.no/for/sf/ld/xd-20030704-0951.html#27. Accessed 27 Jan 2014
Øgaard AF (1996) Effect of fresh and composted cattle manure on phosphate retention in soil. Acta Agric Scand Sect B Soil Plant Sci 46:98–105
Oladeji OO, O’Connor GA, Sartain JB (2008) Relative phosphorus phytoavailability of different phosphorus sources. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 39:2398–2410
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. US Gov Print Office, Washington, pp 1–19
Ott C, Rechberger H (2012) The European phosphorus balance. Resour Conserv Recycl 60:159–172
Pierzynski GM, McDowell RW, Sims JT (2005) Chemistry, cycling and potential movement of inorganic phosphorus in soils. In: Sims TJ, Sharpley AN (eds) Phosphorus: agriculture and the environment, Agronomy monograph, vol 46, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy Inc., Crop Science Society of America Inc., Soil Science Society of America Inc., Madison, pp 53–86
Rietveld H (1969) A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J Appl Cryst 2:65–71
Rothwell WP, Waugh JS, Yesinowski JP (1980) High-resolution variable-temperature P-31 NMR of solid calcium phosphates. J Am Chem Soc 102:2637–2643
Roufosse AH, Aue WP, Roberts JE, Glimcher MJ, Griffin RG (1984) Investigation of the mineral phase of bone by solid-state phosphorus-31 magic angle sample spinning nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry 23:6115–6120
Scarlett NV, Madsen I (2008) Quantitative Phase Analysis. In: Dinnebier RE, Billinge S (eds) Powder diffraction: theory and practice, 1st edn. RSC Publishing, Cambridge, pp 298–329
Scarlett NVY, Madsen IC, Cranswick LMD, Lwin T, Groleau E, Stephenson G, Aylmore M, Agron-Olshina N (2002) Outcomes of the international union of crystallography commission on powder diffraction round robin on quantitative phase analysis: samples 2, 3, 4, synthetic bauxite, natural granodiorite and pharmaceuticals. J Appl Crystallogr 35:383–400
Selmer-Olsen AR (1971) Determination of ammonium in soil extracts by an automated indophenol method. Analyst 96:565–568
Sharpley A, Moyer B (2000) Phosphorus forms in manure and compost and their release during simulated rainfall. J Environ Qual 29:1462–1469
Smith KA, van Dijk TA (1987) Utilisation of phosphorus and potassium from animal manures on grassland and forage crops. In: van der Meer HG, Unwin RJ, van Dijk TA, Ennik GC (eds) Animal manure on grassland and fodders crops. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 87–102
Taylor AW, Frazier AW, Gurney EL (1963) Solubility products of magnesium ammonium and magnesium potassium phosphates. J Chem Soc 59:1580–1584
Toor GS, Hunger S, Peak JD, Sims JT, Sparks DL (2006) Advances in the characterization of phosphorus in organic wastes: environmental and agronomic applications. Adv Agron 89:1–72
Ylivainio K, Uusitalo R, Turtola E (2008) Meat bone meal and fox manure as P sources for ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum) grown on a limed soil. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 81:267–278
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the research projects CenBio (Bioenergy Innovation Centre, Grant No. 193817) and Innovative utilization of wood ash (Grant No. 215935). Both are co-funded by the Research Council of Norway and research and industry partners. We thank Sissel Jørgensen for the acquisition of solid-state 31P MAS-NMR spectra, Kurt Johansen for help with the bioassay and Jonas Sottmann for help with analyses of the XRD data. We also acknowledge the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments on our script. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brod, E., Øgaard, A.F., Hansen, E. et al. Waste products as alternative phosphorus fertilisers part I: inorganic P species affect fertilisation effects depending on soil pH. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 103, 167–185 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-015-9734-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-015-9734-1