Abstract
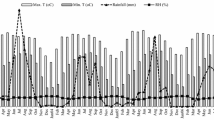
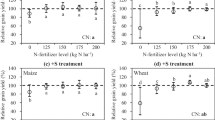
Development of a sustainable and environment friendly crop production system depends on identifying effective strategies for the management of tillage and postharvest crop residues. Three-year (2004–2007) field study was initiated on two soil types to evaluate the effect of straw management (burning, incorporation and surface mulch) and tillage (conventional tillage and zero tillage) before sowing wheat and four nitrogen rates (0, 90, 120 and 150 kg N ha−1) on crop yields, N use efficiency, and soil fertility in the northwestern India. Effect of tillage and straw management on nitrogen transformation in soils was investigated in a laboratory incubation study. In sandy loam, grain yield of wheat with straw mulch-zero-till (ZT) was 7% higher compared to when residues were burnt-ZT but it was similar to straw burnt-conventional till (CT), averaged across 3 years. In silt loam, grain yield of wheat with straw mulch-ZT was 4.4% higher compared to straw incorporated-CT, but it was similar to straw burnt-CT. Response to N application was generally observed up to 150 kg N ha−1 except in 2004–2005 on sandy loam where N response was observed up to 120 kg N ha−1, irrespective of straw and tillage treatments. In sandy loam, RE was lower (49%) for straw burnt-ZT than in other treatments (54–56%). In silt loam, RE was higher in straw mulch-ZT compared with straw incorporation-CT (65 vs. 58%). In sandy loam, AE was higher in straw burnt-CT and straw mulch-ZT compared with the other treatments (19.2 vs. 16.9 kg grain kg−1 N applied). In silt loam, AE was lower in straw incorporation-CT than in other treatments (16.0 vs. 17.6 kg grain kg−1 N applied). Rice yield and N uptake were not influenced by straw and tillage management treatments applied to the preceding wheat. Recycling of rice residue (incorporation and surface mulch) compared with straw burning increased soil organic carbon and the availability of soil P and K. There was more carbon sequestration in rice straw mulch with zero tillage (25%) than in straw incorporation with conventional tillage (17%). Soil N mineralization at 45 days after incubation was 15–25% higher in straw retention plots compared with on straw burnt plots.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajpai RK, Tripathi RP (2000) Evaluation of non-puddling under shallow water tables and alternative tillage methods on soil and crop parameters in a rice–wheat system in Uttar Pradesh. Soil Tillage Res 55:96–106. doi:10.1016/S0167-1987(00)00111-2
Beare MH, Wilson PE, Fraser PM, Butler RC (2002) Management effects of barley straw decomposition, nitrogen release, and crop production. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:848–856
Beri V, Sidhu BS, Bahl GS, Bhat AK (1995) Nitrogen and phosphorus transformations as affected by crop residue management practices and their influence on crop yield. Soil Use Manag 11:51–54. doi:10.1111/j.1475-2743.1995.tb00496.x
Bhandari AL, Ladha JK, Pathak H, Padre AT, Dawe D, Gupta RK (2002) Yield and soil nutrient changes in a long term rice–wheat rotation in India. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:162–170
Bhogal A, Young SD, Sylvester-Bradley R (1997) Straw incorporation and immobilization of spring-applied nitrogen. Soil Use Manag 13:111–116. doi:10.1111/j.1475-2743.1997.tb00568.x
Bijay-Singh, Shan YH, Johnson-Beebout SE, Yadvinder-Singh, Buresh RJ (2008) Crop residue management for lowland rice-based cropping systems in Asia. Adv Agron 98:201–270. doi:10.1016/S0065-2113(08)00204-6
Bird JA, Horwath WR, Eagle AJ, van Kessel C (2001) Immobilization of fertilizer nitrogen in rice: effects of straw management practices. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:1143–1152
Campbell CA, Selles F, Zenter RP, McConkey BG (1993) Nitrogen management for zero-till spring wheat: disposition in plant and utilization efficiency. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 24:2223–2339
Cassman KG, Peng S, Olk DC, Ladha JK, Reichardt W, Dobermann A, Singh U (1998) Opportunities for increased nitrogen use efficiency from improved resource management in irrigated rice systems. Field Crops Res 56:7–38. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(97)00140-8
Dhiman SD, Nandal DP, Om H (2000) Productivity of rice (Oryza sativa)–wheat (Triticum aestivum) cropping system as affected by its residue management and fertility levels. Indian J Agron 45:1–5
Eagle AJ, Bird JA, Hill JE, Horwath WR, van Kessel C (2001) Nitrogen dynamics and fertilizer use efficiency in rice following straw incorporation and winter flooding. Agron J 93:1346–1354
Erenstein O, Farooq U, Malik RK, Sharif M (2007) Adoption and impacts of zero tillage as a resource conserving technology in the irrigated plains of South Asia. Comprehensive assessment of water management in agriculture research report 19. International Water Management Institute, Colombo
Gajri PR, Arora VK, Prihar SS (1992) Tillage management for efficient water and nitrogen use in wheat following rice. Soil Tillage Res 24:167–182. doi:10.1016/0167-1987(92)90099-W
Ghidey F, Alberts EE (1993) Residue type and placement effects on decomposition: field study and model evaluation. Trans ASAE 36:1611–1617
Gomez K, Gomez A (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research. Wiley, New York
Gupta RK, Yadvinder-Singh, Ladha JK, Jagmohan-Singh, Bijay-Singh, Gurpreet-Singh, Pathak H (2007) Yield and phosphorus transformations in a rice–wheat system with crop residue and phosphorus management. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:1500–1507. doi:10.2136/sssaj2006.0325
Helmke PA, Sparks DL (1996) Lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium and cesium. In: Sparks DL et al (eds) Methods of soil analysis part 3. Chemical methods. American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 551–574
Hobbs PR, Gupta RK (2004) Problems and challenges of no-till farming for the rice–wheat systems of the Indo-Gangetic plains in South Asia. In: Lal R, Hobbs PR, Uphoff N, Hansen DO (eds) Sustainable agriculture and the rice–wheat system. Ohio State University and Marcel Dekker, Ohio, pp 101–119
IRRI (1992) IRRISTAT version 92. Department of Statistics, International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos
IRRI (2008) Site-specific nutrient management. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños. Available at www.irrri.org/irrc/ssnm. Accessed 09 July 2008
Linquist BA, Brouder SM, Hill JE (2006) Winter straw and water management effects on soil nitrogen dynamics in California rice systems. Agron J 98:1050–1059. doi:10.2134/agronj2005.0350
Majid A, Astam M, Hashmi NJ (1987) Potential use of minimum tillage in wheat after rice. In: AR Klatt (ed) Wheat production constraints in tropical environment. Proceedings of the international conference, Chiang Mai, pp 71–77, 19–23 January 1987
Mary B, Recous S, Darwis D, Robin D (1996) Interactions between decomposition of plant residues and nitrogen cycling in soil. Plant Soil 181:71–82. doi:10.1007/BF00011294
Mulvaney RL (1996) Nitrogen—inorganic forms. In: Sparks DL, Page AL, Helmke PA, Loeppert RH, Soltanpour PN, Tabtabai MA, Johnston CT, Sumner ME (eds) Methods of soil analysis part 3. Chemical methods. Soil Science Society of America Inc., American Society of Agronomy Inc, Madison, pp 1123–1184
Narang RS, Brar SS, Kumar S (1999) Effect of crop-residue incorporation load on nitrogen requirement of succeeding crops and soil productivity in rice (Oryza sativa)–wheat (Triticum aestivum) system. Indian J Agron 44:8–11
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1996) Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In: D Sparks DL, Page AL, Helmke PA, Loeppert RH, Soltanpour PN, Tabtabai MA, Johnston CT, Sumner ME (eds) Methods of soil analysis part 3. SSSA book ser. no. 5. ASA and SSSA, Madison, pp 961–1010
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. USDA circ. 939. U.S. Gov. Print Office, Washington, DC
Pathak H, Sarkar MC (1997) Nitrogen supplementation with rice straw in an Ustochrept. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 45:103–107
Pathak H, Singh R, Bhatia A, Jain N (2006) Recycling of rice straw to improve wheat yield and soil fertility and reduce atmospheric pollution. Paddy Water Environ 4:111–117. doi:10.1007/s10333-006-0038-6
Patra AK, Chhonkar PK, Khan MA (2004) Nitrogen loss and wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) yields in response to zero-tillage and sowing time in a semi-arid tropical environment. J Agron Crop Sci 190:324–331. doi:10.1111/j.1439-037X.2004.00112.x
Phillips RE, Blevins RE, Thomas GW, Frye WW, Phillips SH (1980) No-tillage agriculture. Science 208:1108–1113. doi:10.1126/science.208.4448.1108
Rahman MA, Chikushi J, Saifizzaman M, Lauren JG (2005) Rice straw mulching and nitrogen response of no-till wheat following rice in Bangladesh. Field Crops Res 91:71–81. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2004.06.010
Rao SC, Dao TH (1996) Nitrogen placement and tillage effects on dry matter and nitrogen accumulation and redistribution in winter wheat. Agron J 88:165–171
Rice CW, Smith MS (1982) Denitrification in no-till and plowed soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 46:1168–1171
Samra JS, Bijay-Singh, Kumar K (2003) Managing crop residues in the rice–wheat system of the Indo-Gangetic plain. In: Ladha JK et al (eds) Improving the productivity and sustainability of rice–wheat systems: Issues and impacts. ASA spec. publ. 65. ASA, CSSA, and SSSA, Madison, pp 173–195
Sharma AR, Mitra BN (1992) Integrated nitrogen management in rice (Oryza sativa)–wheat (Triticum aestivum) cropping system. Indian J Agric Sci 62:70–72
Sidhu HS, Manpreet-Singh, Humphreys E, Yadvinder-Singh, Balwinder-Singh, Dhillon SS, Blackwell J, Bector V, Malkeet-Singh, Sarbjeet-Singh (2007) The happy seeder enables direct drilling of wheat into rice stubble. Aust J Exp Agric 47:844–854. doi:10.1071/EA06225
Singh M, Sharma SN (2000) Effect of wheat residue management practices and nitrogen rates on productivity and nutrient uptake of rice (Oryza sativa)–wheat (Triticum aestivum) cropping system. Indian J Agric Sci 70:835–839
Singh P, Aipe KC, Prasad R, Sharma SN, Singh S, Singh P (1998) Relative effect of zero and conventional tillage on growth and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and soil fertility under rice (Oryza sativa)–wheat cropping system. Indian J Agron 43:204–207
Singh Y, Bhardwaj AK, Singh SP, Singh RK, Chaudhary DC, Saxena A, Singh V, Kumar A (2002) Effect of rice (Oryza sativa) establishment methods, tillage practices in wheat (Triticum aestivum) and fertilization on soil physical properties and rice–wheat productivity on a clay loam Mollisol of Uttaranchal. Indian J Agric Sci 72:200–205
Srivastava AP, Panwar JS, Garg RN (2000) Influence of tillage on soil properties and wheat productivity in rice (Oryza sativa)–wheat (Triticum aestivum) cropping system. Indian J Agric Sci 70:207–210
Surekha K, Padma Kumar AP, Narayana Reddy M, Satyanarayana K, Sta Cruz PC (2003) Crop residue management to sustain soil fertility and irrigated rice yields. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 67:145–154. doi:10.1023/A:1025543810663
Terman GL (1979) Volatilization of nitrogen as ammonia from surface applied fertilizers: Organic amendments and crop residues. Adv Agron 31:169–223
Thakur KS, Singh MN (1987) Effect of organic wastes and N levels on transplanted rice. Indian J Agron 32:161–164
Thuy NH, Yuhua S, Bijay-Singh, Wang K, Cai Z, Yadvinder-Singh, Buresh RJ (2008) Nitrogen supply in rice-based cropping systems as affected by crop residue management. Soil Sci Soc Am J 72:514–523. doi:10.2136/sssaj2006.0403
Timsina J, Connor DJ (2001) Productivity and management of rice–wheat systems: issues and challenges. Field Crops Res 69:93–132. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(00)00143-X
Verma TS, Bhagat RM (1992) Impact of rice straw management practices on yield, nitrogen uptake and soil properties in a wheat–rice rotation in northern India. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 33:97–106
Yadvinder-Singh, Bijay-Singh, Ladha JK, Khind CS, Gupta RK, Meelu O, Pasuquin E (2004a) Long-term effects of organic inputs on yield and soil fertility in the rice–wheat rotation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:845–853
Yadvinder-Singh, Bijay-Singh, Ladha JK, Khind CS, Khera TS, Bueno CS (2004b) Effects of residue decomposition on productivity and soil fertility in rice–wheat rotation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:854–864
Yadvinder-Singh, Bijay-Singh, Timsina J (2005) Crop residue management for nutrient cycling and improving soil productivity in rice-based cropping systems in the tropics. Adv Agron 85:269–407. doi:10.1016/S0065-2113(04)85006-5
Acknowledgments
The research was funded by the Indian Council of Agriculture Research, New Delhi, through the project “Managing Rice Straw in following wheat for enhanced soil and crop productivity in rice–wheat cropping system”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadvinder-Singh, Gupta, R.K., Gurpreet-Singh et al. Nitrogen and residue management effects on agronomic productivity and nitrogen use efficiency in rice–wheat system in Indian Punjab. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 84, 141–154 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-008-9233-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-008-9233-8