Abstract
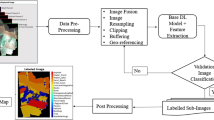
Understanding the connections between human activities and the natural environment depends heavily on information about land use and land cover (LULC) in the form of accurate LULC maps. Environmental monitoring using deep learning (DL) is rapidly growing to preserve a sustainable environment in the long term. For establishing effective policies, regulations, and implementation, DL can be a valuable tool for assessing environmental conditions and natural resources that will positively impact the ecosystem. This paper presents the assessment of land use and land cover change detection (LULCCD) and prediction using DL techniques for the southwestern coastal region, Goa, also known as the tourist destination of India. It consists of three components: (i) change detection (CD), (ii) quantification of LULC changes, and (iii) prediction. A new CD assessment framework, Spatio-Temporal Encoder-Decoder Self Attention Network (STEDSAN), is proposed for the LULCCD process. A dual branch encoder-decoder network is constructed using strided convolution with downsampling for the encoder and transpose convolution with upsampling for the decoder to assess the bitemporal images spatially. The self-attention (SA) mechanism captures the complex global spatial-temporal (ST) interactions between individual pixels over space-time to produce more distinct features. Each branch accepts the LULC map of 2 years as one of its inputs to determine binary and multiclass changes among the bitemporal images. The STEDSAN model determines the patterns, trends, and conversion from one LULC type to another for the assessment period from 2005 to 2018. The binary change maps were also compared with the existing state of the art (SOTA) CD methods, with STEDSAN having an overall accuracy of 94.93%. The prediction was made using an recurrent neural network (RNN) known as long short term memory network (LSTM) for the year 2025. Experiments were conducted to determine area-wise changes in several LULC classes, such as built-up (BU), crops (kharif crop (KC), rabi crop (RC), zaid crop (ZC), double/triple (D/T C)), current fallow (CF), plantation (PL), forests (evergreen forest (EF), deciduous forest (DF), degraded/scurb forest (D/SF) ), littoral swamp (LS), grassland (GL), wasteland (WL), waterbodies max (Wmx), and waterbodies min (Wmn). As per the analysis, over the period of 13 years, there has been a net increase in the amount of BU (1.25%), RC (1.17%), and D/TC( 2.42%) and a net decrease in DF (3.29%) and WL(1.44%) being the most dominant classes being changed. These findings will offer a thorough description of identifying trends in coastal areas that may incorporate methodological hints for future studies. This study will also promote handling the spatial and temporal complexity of remotely sensed data employed in categorizing the coastal LULC of a heterogeneous landscape.












Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the National Remote Sensing Centre, ISRO, Government of India, Hyderabad, India, but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of the National Remote Sensing Centre, ISRO, Government of India, Hyderabad, India.
Code Availability
Not applicable
Abbreviations
- AwiFs:
-
Advanced wide field sensor
- BU:
-
Built-up
- CA:
-
Cellular automata
- CD:
-
Change detection
- CF:
-
Current fallow
- CNN:
-
Convolutional neural network
- D/SF:
-
Degraded/scrub forest
- D/TC:
-
Double/triple crop
- DF:
-
Deciduous forest
- DT:
-
Decision tree
- DL:
-
Deep learning
- DNN:
-
Deep neural network
- ED-LSTM:
-
Encoder decoder LSTM
- EF:
-
Evergreen forest
- FN:
-
False negative
- FP:
-
False positive
- FCN:
-
Fully convolutional neural network
- GA:
-
Genetic algorithm
- GAN:
-
Generative adversarial networks
- GIS:
-
Geographical information systems
- GL:
-
Grassland
- ISRO:
-
Indian Space Research Organization
- KC:
-
Kharif crop
- LS:
-
Littoral swamp
- LSTM:
-
Long short term memory network
- LULC:
-
Land use and land cover
- LULCC:
-
Land use and land cover change
- LULCCD:
-
Land use and land cover change detection
- MCM:
-
Markov chain model
- MIOU:
-
Mean intersection over union
- ML:
-
Machine learning
- MLP:
-
Multilayer perceptron
- NRSC:
-
National Remote Sensing Centre
- NDBI:
-
Normalized Difference Built-up Index
- OA:
-
Overall accuracy
- PA:
-
Producer accuracy
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- PL:
-
Plantation
- RC:
-
Rabi crop
- ReLU:
-
Rectified linear unit
- RF:
-
Random forest
- RNN:
-
Recurrent neural network
- RS:
-
Remote sensing
- SA:
-
Self-attention
- SITS:
-
Satellite image time series
- SOTA:
-
State of the art
- ST:
-
Spatial-temporal
- STEDSAN:
-
Spatio-Temporal Encoder-Decoder Self Attention Network
- SVM:
-
Support vector machine
- TN:
-
True negative
- TP:
-
True positive
- UA:
-
User accuracy
- WL:
-
Wasteland
- Wmn:
-
Waterbodies min
- Wmx:
-
Waterbodies max
- Xgboost:
-
Extreme gradient boosting
- ZC:
-
Zaid crop
References
Abdi, A. M. (2020). Land cover and land use classification performance of machine learning algorithms in a boreal landscape using sentinel-2 data. GIScience & Remote Sensing, 57(1), 1–20.
Ahmed, S.A., Shankar, B., et al. (2011). Planning for conservation of heritage areas in old Goa: Issues and strategies. IDES_CPS, Civil Engineering Series-Advances in Civil Engineering ACE, Ed., pp. 11–15.
Albert, A., Kaur, J., Gonzalez, M.C. (2017). Using convolutional networks and satellite imagery to identify patterns in urban environments at a large scale. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (pp. 1357–1366).
Al-Usmani, S. M. P. (2011). Impact of mining activities on land and water areas of Goa. Journal of Coastal Environment, 2(1), 43–54.
Ansari, Z., Achuthankutty, C., & Dalal, S. (2006). Overexploitation of fishry resources, with particular reference to Goa. India: TERI Press.
Arsanjani, J.J., et al. (2011). Dynamic land use/cover change modelling: Geosimulation and multiagent-based modelling. Springer Science & Business Media.
Bai, X., Sharma, R.C., Tateishi, R., Kondoh, A., Wuliangha, B., & Tana, G. (2017). A detailed and high-resolution land use and land cover change analysis over the past 16 years in the Horqin Sandy Land, inner Mongolia. Mathematical Problems in Engineering.
Bandara, C. Wele Gedara, Patel, V., et al. (2022). A transformer-based Siamese network for change detection. arXiv:2201.01293.
Borkar, M. (2006). Sacred yet scientific; eco-theological basis of biodiversity conservation in Goa. Multiple dimensions of global environmental change, 182–194.
Bousias Alexakis, E., Armenakis, C., et al. (2021). Performance improvement of encoder/decoder-based CNN architectures for change detection from very high-resolution satellite imagery. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 47(2), 309–336.
Brauwers, G., Frasincar, F., et al. (2021). A general survey on attention mechanisms in deep learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering.
Briassoulis, H. (2009) Factors influencing land-use and land-cover change. Land cover, land use and the global change, encyclopaedia of life support systems (EOLSS), 1, 126–146.
Calderón-Loor, M., Hadjikakou, M., & Bryan, B. A. (2021). High-resolution wall-to-wall land-cover mapping and land change assessment for Australia from 1985 to 2015. Remote Sensing of Environment, 252, 112148.
Campos-Taberner, M., García-Haro, F. J., Martínez, B., Izquierdo-Verdiguier, E., Atzberger, C., Camps-Valls, G., & Gilabert, M. A. (2020). Understanding deep learning in land use classification based on sentinel-2 time series. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–12.
Chen, Z., Zhou, Y., Wang, B., Xu, X., He, N., Jin, S., & Jin, S. (2022). EGDE-NET: A building change detection method for high-resolution remote sensing imagery based on edge guidance and differential enhancement. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 191, 203–222.
Cheng, H., Wu, H., Zheng, J., Qi, K., & Liu, W. (2021). A hierarchical self-attention augmented Laplacian pyramid expanding network for change detection in high-resolution remote sensing images. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 182, 52–66.
Choudri, B., Chachadi, A., et al. (2006). Status of groundwater availability and recharge in the mining watersheds of North Goa. Multiple dimensions of global environmental change: TERI Press.
Commission of India, P. (2011). Goa Development Report. https://niti.gov.in/planningcommission.gov.in/docs/plans/stateplan/sdr/sdr_goa1909.pdf. Accessed 17 Oct 2022.
De Sousa, S. (1999). Effect of mining rejects on the nutrient chemistry of Mandovi estuary, Goa.
Du, B., Ru, L., Wu, C., & Zhang, L. (2019). Unsupervised deep slow feature analysis for change detection in multi-temporal remote sensing images. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 57(12), 9976–9992.
Ekim, B., Sertel, E., et al. (2021). Deep neural network ensembles for remote sensing land cover and land use classification. International Journal of Digital Earth, 1–14.
gee-assessment-tools (2020). Area estimation and accuracy assessment. https://area2.readthedocs.io/en/latest/background.html/. Accessed 24 Nov 2022.
Gharbia, R., Khalifa, N.E.M., & Hassanien, A.E. (2020). Land cover classification using deep convolutional neural networks. In: International conference on intelligent systems design and applications (pp. 911–920).
Girap, M. (2006). Remote sensing and application of GIS in natural resources management with reference to land-use/land-cover in the state of Goa. Multiple dimensions of global environmental change, 83.
Giri, C., Long, J., Abbas, S., Murali, R. M., Qamer, F. M., Pengra, B., & Thau, D. (2015). Distribution and dynamics of mangrove forests of South Asia. Journal of Environmental Management, 148, 101–111.
Glorot, X., Bengio, Y., et al. (2010). Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In: Proceedings of the thirteenth international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics (pp. 249–256).
Han, H., Yang, C., & Song, J. (2015). Scenario simulation and the prediction of land use and land cover change in Beijing China. Sustainability, 7(4), 4260–4279.
He, T., Wang, S., et al. (2021). Multi-spectral remote sensing land-cover classification based on deep learning methods. The Journal of Supercomputing, 77(3), 2829–2843.
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J., et al. (1997). Long short-term memory. Neural Computation, 9(8), 1735–1780.
Hu, Y., Zhen, L., & Zhuang, D. (2019). Assessment of land-use and land-cover change in Guangxi China. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1–13.
ISFR (2019). India state of forest report. Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change Dehradun.
Jakati, D. M. (2021). Development of mining in Goa and its environmental impacts-a geographical perspective. PalArch’s Journal of Archaeology of Egypt/Egyptology, 18(7), 2979–2988.
Jamali, A. (2021). Improving land use land cover mapping of a neural network with three optimizers of multi-verse optimizer, genetic algorithm, and derivative-free function. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 24(3), 373–390.
Kalinicheva, E., Sublime, J., & Trocan, M. (2020). Unsupervised satellite image time series clustering using object-based approaches and 3D convolutional autoencoder. Remote Sensing, 12(11), 1816.
Kerins, P., Guzder-Williams, B., Mackres, E., Rashid, T., & Pietraszkiewicz, E. (2021). Mapping urban land use in India and Mexico using remote sensing and machine learning.
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J., et al. (2014) Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv:1412.6980.
Kotha, M., Kunte, P., et al. (2013). Land-cover change in Goa–An integrated RS–GIS approach.
Kulkarni, K., Vijaya, P., et al. (2021). NDBI based prediction of land use land cover change. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 49(10), 2523–2537.
Kunte, P. D., Jauhari, N., Mehrotra, U., Kotha, M., Hursthouse, A. S., & Gagnon, A. S. (2014). Multi-hazards coastal vulnerability assessment of Goa, India, using geospatial techniques. Ocean & Coastal Management, 95, 264–281.
Lambin, E. F., Turner, B. L., Geist, H. J., Agbola, S. B., Angelsen, A., Bruce, J. W., Coomes, O. T., Dirzo, R., Fischer, G., & Folke, C. (2001). The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Global Environmental Change, 11(4), 261–269.
Liang, J., Xu, J., Shen, H., & Fang, L. (2020). Land-use classification via constrained extreme learning classifier based on cascaded deep convolutional neural networks. European Journal of Remote Sensing, 53(1), 219–232.
Liu, R., Cheng, Z., Zhang, L., & Li, J. (2019). Remote sensing image change detection based on information transmission and attention mechanism. IEEE Access, 7, 156349–156359.
Lv, Z., Liu, T., Benediktsson, J. A., & Falco, N. (2021). Land cover change detection techniques: Very-high-resolution optical images: A review. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 10(1), 44–63.
Lyu, H., Lu, H., & Mou, L. (2016). Learning a transferable change rule from a recurrent neural network for land cover change detection. Remote Sensing, 8(6), 506.
Mahender, K., Kunte, P., et al. (2013). Land cover change in Goa: An integrated RS-GIS approach.
Mascarenhas, A. (1999). The coastal regulation zone of Goa: Oceanographic, environmental and societal perspectives. Current Science, 77(12), 1598–1605.
Mascarenhas, A. (2009). Some implications of coastal regulation zone (CRZ) legislation for the coast of Goa. Geological Society of Goa, Dhempe College, Miramar, Goa (India).
Misra, A., Vethamony, P., et al. (2015). Assessment of the land use/land cover (LU/LC) and mangrove changes along the Mandovi-Zuari estuarine complex of Goa, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8(1), 267–279.
Mnih, V., Heess, N., Graves, A., et al. (2014). Recurrent models of visual attention. Advances in neural information processing systems.
Mou, L., Bruzzone, L., & Zhu, X. X. (2018). Learning spectral-spatial-temporal features via a recurrent convolutional neural network for change detection in multispectral imagery. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 57(2), 924–935.
Murali, R.M., Vethamony, P., Saran, A., & Jayakumar, S. (2006). Change detection studies in coastal zone features of Goa, India by remote sensing. Current Science, 816–820.
Nagi, H.M., Rodrigues, R.S., ManiMurali, R., & Jagtap, T. (2014). Using remote sensing and GIS techniques for detecting land cover changes of mangrove habitats in Goa, India.
Nandargi, S., Mulye, S., et al. (2014). Spatio-temporal rainfall variability and rainstorm analysis over the Goa state, India. Studies in Atmospheric Science, 1, 8–23.
Ngoy, K. I., Qi, F., & Shebitz, D. J. (2021). Analyzing and predicting land use and land cover changes in New Jersey using multi-layer perceptron-Markov chain model. Earth, 2(4), 845–870.
Noronha, L., Siqueira, A., Sreekesh, S., Qureshy, L., & Kazi, S. (2002). Goa: Tourism, migrations, and ecosystem transformations. AMBIO: A Journal of the Human Environment, 31(4), 295–302.
NRSC, H. (2010). National land use and land cover mapping using multi-temporal AWiFS data. https://bhuvan-app1.nrsc.gov.in/2dresources/thematic/LULC250/0809.pdf. Accessed 14 Dec 2022.
Olofsson, P., Foody, G. M., Herold, M., Stehman, S. V., Woodcock, C. E., & Wulder, M. A. (2014). Good practices for estimating area and assessing accuracy of land change. Remote Sensing of Environment, 148, 42–57.
Panandiker, A.P., de Mello, L., Kotha, M., & Chachadi, A. (2021). Examining the temporal change in land cover/land use in five watersheds in Goa, India using a geospatial approach. In: Re-envisioning remote sensing applications (pp. 193–208). CRC Press.
Pandey, P. C., Koutsias, N., Petropoulos, G. P., Srivastava, P. K., & Ben Dor, E. (2021). Land use/land cover in view of earth observation: Data sources, input dimensions, and classifiers-a review of the state of the art. Geocarto International, 36(9), 957–988.
Panuju, D. R., Paull, D. J., & Griffin, A. L. (2020). Change detection techniques based on multispectral images for investigating land cover dynamics. Remote Sensing, 12(11), 1781.
Pati, C., Panda, A. K., Tripathy, A. K., Pradhan, S. K., & Patnaik, S. (2020). A novel hybrid machine learning approach for change detection in remote sensing images. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal, 23(5), 973–981.
Pednekar, S.M., Prabhu Matondkar, S., & Kerkar, V. (2012). Spatiotemporal distribution of harmful algal flora in the tropical estuarine complex of Goa, India. The Scientific World Journal, 2012.
Peng, D., Bruzzone, L., Zhang, Y., Guan, H., Ding, H., & Huang, X. (2020). SemiCDNet: A semisupervised convolutional neural network for change detection in high resolution remote-sensing images. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing.
Peng, D., Bruzzone, L., Zhang, Y., Guan, H., & He, P. (2021). SCDNET: A novel convolutional network for semantic change detection in high resolution optical remote sensing imagery. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 103, 102465.
Rajesh, S., Nisia, T. G., Arivazhagan, S., & Abisekaraj, R. (2020). Land cover/land use mapping of LISS IV imagery using object-based convolutional neural network with deep features. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 48(1), 145–154.
Ramachandran, P., Parmar, N., Vaswani, A., Bello, I., Levskaya, A., & Shlens, J. (2019). Stand-alone self-attention in vision models. arXiv:1906.05909.
Ranjan, R. (2018). The role of political-industry nexus in promoting illegal extraction of mineral resources and deforestation: A case of iron ore mining in Goa. Resources Policy, 57, 122–136.
Riebsame, W., Meyer, W., & Turner, B. (1994). Modeling land use and cover as part of global environmental change. Climatic Change, 28(1–2), 45–64.
Rousset, G., Despinoy, M., Schindler, K., & Mangeas, M. (2021). Assessment of deep learning techniques for land use land cover classification in southern new Caledonia. Remote Sensing, 13(12), 2257.
Roy, A., Srivastava, V., et al. (2012). Geospatial approach to identification of potential hotspots of land-use and land-cover change for biodiversity conservation. Current Science, 1174–1180.
Roy, P., Giriraj, A., et al. (2008). Land use and land cover analysis in Indian context. Journal of Applied Sciences, 8(8), 1346–1353.
Rußwurm, M., Körner, M., et al. (2017). Multi-temporal land cover classification with long short-term memory neural networks. International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing & Spatial Information Sciences, 42.
Samanta, S., Kunte, P.D., & Mahender, K. (2012). Coastal geomorphology and land use changes along coastal parts of Goa: An RS-GIS approach.
Sampath Kumar, P., Mahtab, A., Roy, A., Srivastava, V., Roy, P., & Isro, D. (2014). Impact of drivers on the land use/land cover change in Goa, India. In: Proceedings of the international symposium, India geospatial forum, hyderabad, India (pp. 5–7).
Santos, L. A., Ferreira, K., Picoli, M., Camara, G., Zurita-Milla, R., & Augustijn, E.-W. (2021). Identifying spatiotemporal patterns in land use and cover samples from satellite image time series. Remote Sensing, 13(5), 974.
Sarupria, M., Manjare, S. D., & Girap, M. (2019). Environmental impact assessment studies for mining area in Goa, India, using the new approach. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(1), 1–17.
Sefrin, O., Riese, F. M., & Keller, S. (2021). Deep learning for land cover change detection. Remote Sensing, 13(1), 78.
Series, I.R.S.S. (2013). National natural resources management system.
Shi, W., Zhang, M., Zhang, R., Chen, S., & Zhan, Z. (2020). Change detection based on artificial intelligence: State-of-the-art and challenges. Remote Sensing, 12(10), 1688.
Shirin, C., Yogita, M., & Anuradha, J. (2006). Depletion of fresh water in the mining regions of Goa, India: Gendered impacts and responses. Multiple dimensions of global environmental change, 44.
Sibanda, S., Ahmed, F., et al. (2021). Modelling historic and future land use/land cover changes and their impact on wetland area in Shashe sub-catchment, Zimbabwe. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 7(1), 57–70.
Silva, S. D., Nielsen, K. B., & Bedi, H. P. (2020). Land use planning, dispossession and contestation in Goa, India. The Journal of Peasant Studies, 47(6), 1301–1326.
Singh, G., Kamal, R. K., et al. (2015). Assessment of groundwater quality in the mining areas of Goa, India. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 8(6), 588.
Singh, I., Singh, S., Kushwaha, S., Ashutosh, S., & Singh, R. (2004). Assessment and monitoring of estuarine mangrove forests of Goa using satellite remote sensing. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 32(2), 167–174.
Sonak, S., Kazi, S., Sonak, M., & Abraham, M. (2006). Factors affecting land-use and land-cover changes in the coastal wetlands of Goa. Citeseer.
State biodiversity board, G. (2019). State action plan on climate change for the state of Goa. https://gsbb.goa.gov.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Draft-Goa%20SAPCC-for-public-inputs.pdf. Accessed 09 Jan 2023.
Town, Country Planning, G.o.G. (2011). Regional plan Goa 2021. https://tcp.goa.gov.in/land-use-plan-regional-plan-for-goa-2021/. Accessed 27 Dec 2022.
Turner, B.L., Clark, W.C., Kates, R.W., Richards, J.F., Mathews, J.T., & Meyer, W.B. (1993). The earth as transformed by human action: Global and regional changes in the biosphere over the past 300 years. Cambridge University Press.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, Ł., & Polosukhin, I. (2017). Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems, 30.
Vaz, E., Taubenböck, H., Kotha, M., & Arsanjani, J. J. (2017). Urban change in Goa, India. Habitat International, 68, 24–29.
Verma, D., Jana, A., et al. (2019). LULC classification methodology based on simple convolutional neural network to map complex urban forms at finer scale: Evidence from Mumbai. arXiv:1909.09774.
Wang, D., Chen, X., Jiang, M., Du, S., Xu, B., & Wang, J. (2021). ADS-NET: An attention-based deeply supervised network for remote sensing image change detection. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 101, 102348.
Wang, X., Girshick, R., Gupta, A., & He, K. (2018). Non-local neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 7794–7803).
Wilson, D. (1997). Paradoxes of tourism in Goa. Annals of Tourism Research, 24(1), 52–75.
Yang, X. (2020). An overview of the attention mechanisms in computer vision. In: Journal of physics: Conference series (vol. 1693, pp 012173).
Yedage, A., Harmalkar, S., et al. (2017). S. analysis and simulation of land use/land cover change in the Quepem Tehsil Goa, India. Journal of Advances in Remote Sensing and GIS, 5(1), 67–76.
Yedage, A., Sawant, N., & Malave, V. (2015). Change detection analysis using geo-spatial technique: A case study of south Goa. Studies, 10, 11.
You, Y., Cao, J., & Zhou, W. (2020). A survey of change detection methods based on remote sensing images for multi-source and multi-objective scenarios. Remote Sensing, 12(15), 2460.
Zhang, C., Yue, P., Tapete, D., Jiang, L., Shangguan, B., Huang, L., & Liu, G. (2020). A deeply supervised image fusion network for change detection in high resolution bi-temporal remote sensing images. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 166, 183–200.
Zheng, Z., Zhong, Y., Tian, S., Ma, A., & Zhang, L. (2022). ChangeMask: Deep multi-task encoder-transformer-decoder architecture for semantic change detection. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 183, 228–239.
Zhu, Q., Guo, X., Deng, W., Guan, Q., Zhong, Y., Zhang, L., & Li, D. (2022). Land-use/land-cover change detection based on a Siamese global learning framework for high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 184, 63–78.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Remote Sensing Centre, Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), Government of India, Hyderabad, India, for providing time series data in form of LULC maps from 2005–06 to 2017–18 for the Goa Region.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Nitesh Naik, Kandasamy Chandrasekaran, Meenakshi Venkatesan Sundaram, and Prabhavathy Panneer. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Nitesh Naik, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Naik, N., Chandrasekaran, K., Meenakshi Sundaram, V. et al. Assessment of land use and land cover change detection and prediction using deep learning techniques for the southwestern coastal region, Goa, India. Environ Monit Assess 196, 527 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12598-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12598-y